Engineering an Empire: Maya Civilization Worksheet Solutions

When we delve into the tapestry of ancient civilizations, the Maya Civilization stands as a remarkable thread with its unique blend of architecture, astronomy, mathematics, and cultural innovations. This blog post aims to explore and provide detailed solutions to common queries and worksheets that students and enthusiasts might have when studying the Maya civilization.
History of the Maya

The Maya civilization flourished in the Yucatán Peninsula, Guatemala, Belize, and parts of Honduras and El Salvador from around 2000 BC to the 16th century AD. Known for their sophisticated calendar systems, monumental architecture, and hieroglyphic script, understanding their history can be a complex endeavor. Here are key points:
- Pre-Classic Period (2000 BC - 250 AD): Development of agriculture, architecture, and societal structures.
- Classic Period (250 - 900 AD): Known for large cities, complex political systems, and artistic developments.
- Post-Classic Period (900 - 1542 AD): Rise of new cities, decline of classic Mayan civilization, and eventual arrival of the Spanish.
🌱 Note: The transitions between periods are not abrupt but rather gradual shifts in cultural focus and power dynamics.
Here is a timeline for quick reference:
| Period | Years | Key Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Classic | 2000 BC - 250 AD | Agriculture, Early Settlements, Proto-Writing |
| Classic | 250 - 900 AD | Monumental Architecture, Long Count Calendar, Artistic Flourishing |
| Post-Classic | 900 - 1542 AD | Collapse of Classic Cities, New Political Centers, European Contact |

Architecture and Engineering

The engineering feats of the Maya civilization are impressive, showcasing their understanding of astronomy, geometry, and environmental adaptation:
- Pyramids: Unlike the smooth-sided pyramids of Egypt, Mayan pyramids were stepped, allowing for ceremonial practices on each level.
- City Planning: Cities like Tikal and Palenque were meticulously planned to align with celestial events.
- Water Management: They developed systems like the chultuns (underground cisterns) and aqueducts.
- Causeways (Sakbes): Raised roads or causeways connected cities and ceremonial centers.
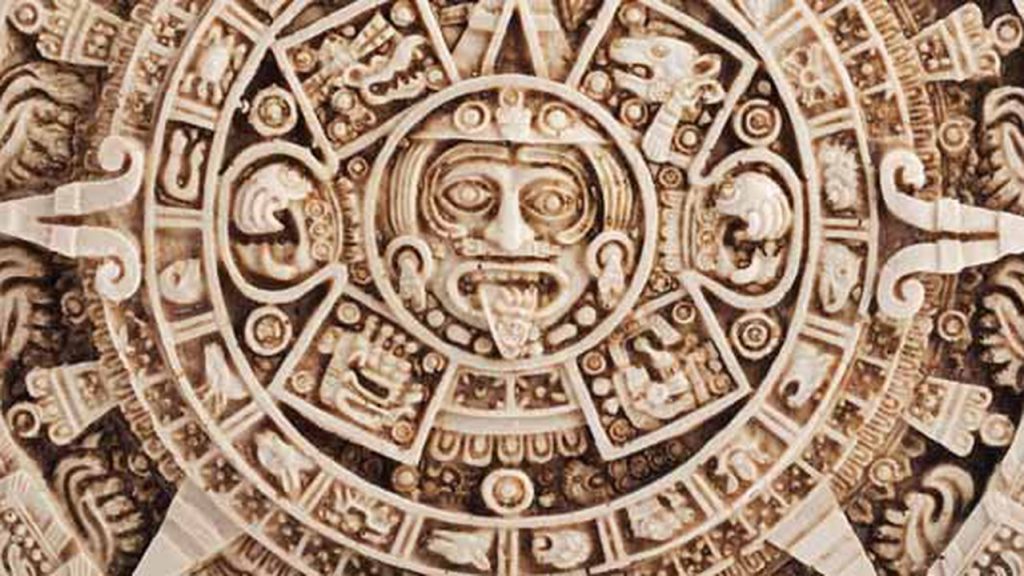
Astronomy, Mathematics, and the Calendar

Mayans had a profound interest in the cosmos, which influenced their calendar, writing system, and religious practices:
- The Long Count Calendar: A system of dating which tracks days from a mythic starting point with incredible precision.
- Mathematical Innovations: Use of a vigesimal (base-20) numerical system with zero as a placeholder, far ahead of their time.
- Venus Calendar: Known for tracking the movements of Venus with the 260-day Tzolkin cycle.
Social and Cultural Aspects

The Maya civilization’s social structure was hierarchical, with kings at the top, followed by nobility, priests, merchants, farmers, and slaves. Their cultural practices included:
- Religious Rituals: Bloodletting ceremonies, human sacrifices, and elaborate rites to maintain cosmic order.
- Writing System: Their script included about 800 glyphs, allowing for the recording of history, legends, and astronomical data.
- Ballgames: More than sports, the games had religious significance and could determine political outcomes.
FAQ Section

What caused the decline of the Maya civilization?

+
The decline of the Maya civilization remains partially a mystery, but contributing factors include environmental degradation, drought, internal warfare, and the possible introduction of diseases by earlier contacts with outsiders.
How did the Maya use astronomy in their daily lives?

+
Astronomy influenced agriculture, calendar creation, architecture, and religious ceremonies. They observed celestial bodies to predict eclipses, solstices, and equinoxes which played a significant role in timing events and building orientations.
What is unique about Mayan mathematics?

+
One unique feature is their use of the concept of zero, which was crucial in their calculations. Their numerical system was vigesimal (base-20), contrasting with the decimal system used widely today.
Were there any significant environmental impacts on Mayan civilization?

+
Yes, environmental changes like extended droughts, deforestation, and soil depletion had a profound impact on Maya agriculture and societal stability, contributing to their decline.
In summary, the Maya civilization provides a fascinating study in ancient culture, science, and engineering. Their contributions to calendar systems, astronomy, mathematics, and architectural engineering were extraordinary. Their legacy, rich with symbols and layers of understanding, continues to enlighten us about human ingenuity and the relationship between societies and the environment. Studying the Maya civilization not only enriches our knowledge of the past but also offers insights into the complexities of human civilization across time.