Energy Pyramid Practice Answers: Unlock Your Study Success
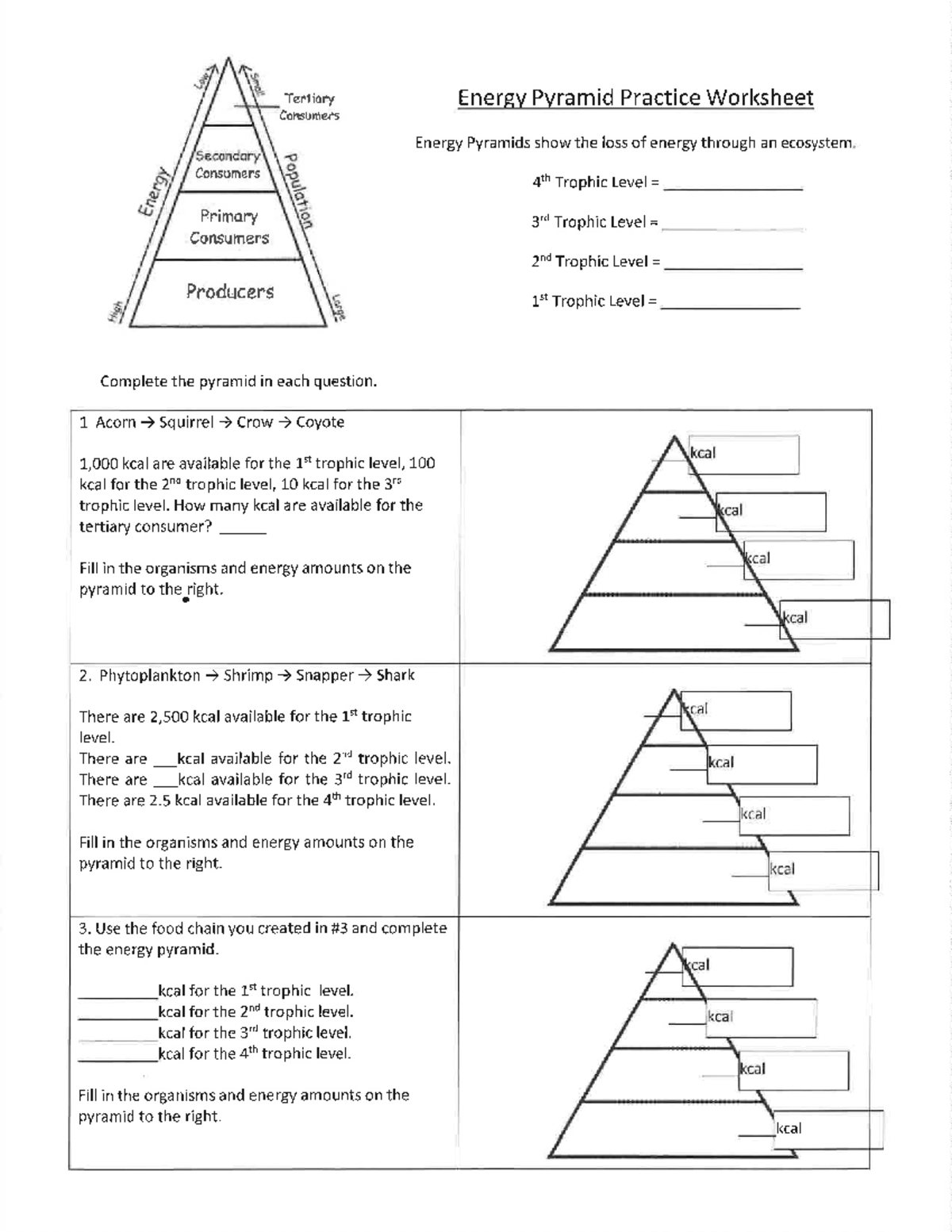
In the world of environmental science and ecosystem studies, understanding the energy pyramid is key to unlocking many fundamental principles that govern life on Earth. This intricate model doesn't just showcase the amount of energy available at different trophic levels but also helps us comprehend the efficiency of energy transfer, the interaction between species, and the sustainability of ecosystems. Let's dive into how you can master this concept for your studies.
Understanding the Energy Pyramid

The energy pyramid, often referred to as the ecological pyramid, is a graphical representation of the energy flow within an ecosystem. Here’s what you need to know:
- Each level of the pyramid represents a trophic level.
- The base represents primary producers, like plants, algae, and phytoplankton.
- Subsequent levels represent primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on.
- The width of each level indicates the amount of energy available, which typically decreases as you move up the pyramid.

Key Features of the Energy Pyramid

The following are some crucial aspects of the energy pyramid you need to remember:
- Energy Transfer Efficiency: Only about 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, often known as the “10% rule”.
- Biomass Distribution: Generally, biomass decreases at higher trophic levels.
- Impact on Ecosystem Health: The pyramid shape shows how fewer organisms can be supported at higher levels due to energy constraints.
Practicing Energy Pyramid Problems

To truly master the energy pyramid, you need to practice solving problems related to it. Here are some exercises:
Sample Problem 1: Calculating Energy Transfer

Given that a primary producer has 1000 units of energy:
- Calculate how much energy is available for primary consumers.
- How much energy can be transferred to secondary consumers?
Sample Problem 2: Population Estimation

If a given ecosystem supports 100,000 individuals at the primary producer level, estimate:
- The number of primary consumers supported.
- The population of secondary consumers.
| Trophic Level | Energy (Units) | Estimated Population |
|---|---|---|
| Producers | 1000 | 100,000 |
| Primary Consumers | 100 | [Your Answer Here] |
| Secondary Consumers | 10 | [Your Answer Here] |

🔎 Note: Remember that the figures provided here are for educational purposes. Real ecosystems can vary greatly in their energy transfer rates.
Sample Problem 3: Ecological Impact

Consider how human activities might affect energy pyramid dynamics:
- What would happen if we reduced the primary producer population by 50%?
- How would this impact subsequent levels of the energy pyramid?
Practicing these problems will not only solidify your understanding of the energy pyramid but also provide insights into how ecosystems function and respond to changes.
Importance of the Energy Pyramid in Studies

Here’s why mastering the energy pyramid is crucial for your academic success:
- Ecosystem Modeling: It’s foundational for modeling and predicting ecosystem behavior under various conditions.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Understanding energy transfer helps in assessing the impact of development projects on ecosystems.
- Conservation Biology: Knowledge of the pyramid can guide conservation efforts by highlighting vulnerable species and habitats.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Optimizing energy transfer within managed ecosystems can enhance productivity and sustainability.
- Food Web Analysis: The pyramid aids in analyzing the complexities of food webs, trophic cascades, and species interactions.
Learning Tips for the Energy Pyramid

Here are some strategies to help you excel in your studies related to energy pyramids:
- Visual Learning: Draw or use software to visualize energy pyramids with real or hypothetical data.
- Interactive Exercises: Engage with online tools or apps that simulate energy transfer in ecosystems.
- Group Study: Discuss energy pyramid problems in groups to tackle complex scenarios from different angles.
- Practical Examples: Relate concepts to everyday examples like agriculture, fishing, or wildlife conservation.
- Regular Reviews: Consistently revisit the material, ensuring you understand how different factors influence the pyramid.
By employing these strategies, you not only learn about the energy pyramid but also build a more comprehensive understanding of how ecosystems work, providing you with a competitive edge in your academic pursuits.
As we conclude this exploration of the energy pyramid, remember that mastering this concept is like unlocking a door to understanding ecosystem dynamics. Whether you're studying for a biology exam, working on environmental projects, or simply looking to deepen your knowledge, the principles learned here are fundamental. They highlight the interconnectedness of life, the delicate balance of energy flow, and the importance of each species within an ecosystem. So, keep practicing, keep visualizing, and let the energy pyramid guide you through the complexities of our natural world.
Why is there a decrease in energy at higher trophic levels?

+
At each trophic level, some energy is lost as heat during metabolic processes, not all organisms are consumed, and not all consumed energy is assimilated into the biomass of the consumer. This results in a significant decrease in available energy as you move up the food chain.
Can an ecosystem have an inverted pyramid?

+
While traditional energy pyramids are depicted as upright, there are exceptions, especially in aquatic ecosystems where phytoplankton, the primary producers, can have a lower biomass than their consumers due to rapid turnover rates.
How does human impact affect the energy pyramid?

+
Human activities like habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing can alter the structure of the energy pyramid by reducing the base (producers) or disrupting the transfer of energy, leading to imbalances and potential ecosystem collapse.