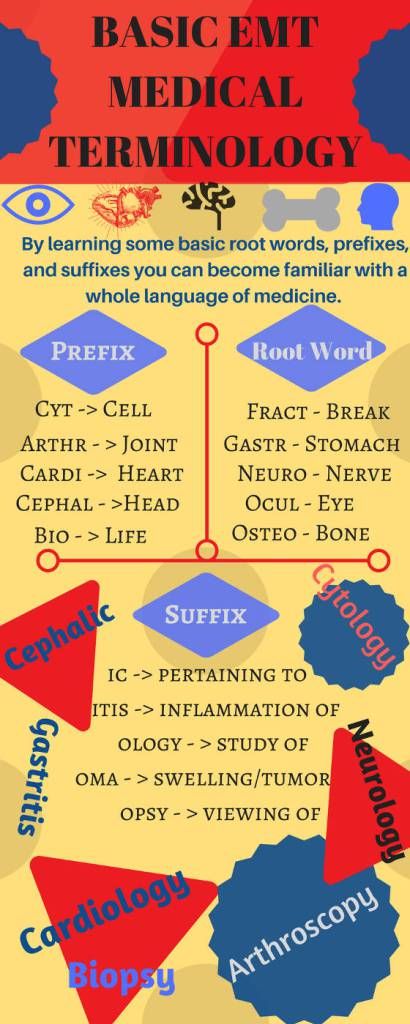
10 Essential EMT Medical Terms You Need to Know

Understanding emergency medical technician (EMT) terminology is crucial for anyone involved in or interested in the emergency medical services (EMS) field. Whether you're aspiring to become an EMT, you work in healthcare, or you simply want to understand more about the services provided in emergency situations, knowing these terms will enhance your knowledge and communication skills. Here are ten essential EMT medical terms that are commonly used in the field:
1. Scene Safety

Scene safety is a paramount concept in EMT operations. Before any medical intervention or care can be provided, the EMTs must ensure that the scene is safe for themselves, the patient, and any bystanders. This involves:
- Assessing for hazards like traffic, unstable structures, or hazardous materials.
- Using personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriately.
- Calling for additional support if the situation requires specialized teams.
⚠️ Note: EMTs must always prioritize their safety to ensure they can assist the patient effectively.
2. Primary Assessment

The primary assessment is the initial evaluation of a patient to identify life-threatening conditions. This includes:
- Assessing airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs).
- Checking for any signs of severe bleeding or shock.
- Determining the patient’s level of consciousness using tools like the AVPU scale (Alert, Verbal, Pain, Unresponsive).
3. Vital Signs

Vital signs provide critical information about the body’s basic functions. EMTs routinely check:
- Blood pressure (BP).
- Pulse rate.
- Respiratory rate.
- Temperature.
- Glucose level, if necessary.
4. Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
The Glasgow Coma Scale is a tool used to assess a patient’s level of consciousness. It scores based on:
- Eye-opening (E).
- Verbal response (V).
- Motor response (M).
The total score can give a quick indication of neurological function:
| Score | Description |
|---|---|
| 13-15 | Mild dysfunction |
| 9-12 | Moderate dysfunction |
| 3-8 | Severe dysfunction |

5. AVPU Scale

The AVPU scale is another tool for assessing the level of consciousness, where:
- A - Alert.
- V - Responds to Verbal stimuli.
- P - Responds to Painful stimuli.
- U - Unresponsive.
6. Advanced Life Support (ALS)

ALS refers to a higher level of prehospital care by specially trained paramedics, involving:
- Advanced airway management.
- Administration of medications.
- Cardiac monitoring and interventions like defibrillation.
7. Basic Life Support (BLS)

BLS covers fundamental care techniques for life-threatening emergencies like cardiac arrest, including:
- CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation).
- Use of automated external defibrillators (AED).
- Choking management.
8. Medical Control

Medical control refers to the oversight provided by a physician or medical director to ensure that EMTs provide care according to medical protocols. This can be:
- Direct Medical Control: Immediate guidance via radio or phone.
- Indirect Medical Control: Following pre-approved medical protocols and guidelines.
9. Patient Refusal

Patient refusal is a significant term where a competent patient declines the offered medical treatment or transport. EMTs must ensure:
- The patient is informed of the risks.
- The refusal is documented according to EMS guidelines.
10. Triage

In mass casualty incidents, triage is used to prioritize treatment:
- Immediate (Red): Critical injuries requiring immediate attention.
- Delayed (Yellow): Injuries that can wait for a short time.
- Minimal (Green): Minor injuries or conditions.
- Expectant (Black): Fatal or non-survivable injuries in a limited resource situation.
💡 Note: Triage systems can vary, but the principle of prioritizing care remains consistent.
Learning these ten EMT medical terms is just the beginning of understanding the extensive knowledge base required for emergency medical services. Whether you're on the path to becoming an EMT or just interested in this vital field, these terms will help you appreciate the nuances of emergency care and enhance your communication with those in the profession. Remember, continuous learning and adaptation to new protocols and terminologies are key in EMS, ensuring that the care provided is both timely and effective.
What is the difference between ALS and BLS?

+
Advanced Life Support (ALS) involves more complex interventions like drug administration and advanced airway management, typically performed by paramedics. Basic Life Support (BLS) focuses on foundational emergency procedures such as CPR and basic airway management, which EMTs are trained to perform.
How is the AVPU scale used?

+
The AVPU scale is used to quickly assess a patient’s level of consciousness in emergency situations. It helps EMTs determine if a patient is alert, responds to verbal stimuli, responds only to pain, or is unresponsive, guiding initial treatment priorities.
Why is scene safety so critical for EMTs?

+
Scene safety is crucial because an unsafe scene can endanger the EMTs, the patient, and bystanders. Ensuring safety allows EMTs to provide care without additional risks or interruptions, which is vital for effective emergency response.