Earth Systems Worksheet Answers: Master the Basics Now

Unlocking the mysteries of Earth's dynamic systems isn't just a subject for scientists; it's an essential part of our curriculum that helps us understand the world we live in. From the shifting tectonic plates to the ever-changing atmosphere, each component of Earth's systems offers a wealth of knowledge. This comprehensive guide is designed to help students and enthusiasts alike to master the basics of Earth systems through a detailed Earth Systems Worksheet.
Understanding Earth’s Systems

The Earth can be viewed as an integrated system made up of several interacting spheres:
- Atmosphere: The layer of gases surrounding the planet.
- Hydrosphere: All water bodies and ice on the planet.
- Lithosphere: The solid outer section of Earth, including the crust and part of the upper mantle.
- Biosphere: Encompassing all life and biological activity on Earth.
Each sphere has its own characteristics and they interact in complex ways to create our planet’s unique climate, landforms, and life-supporting environments.
Essential Concepts in Earth Systems

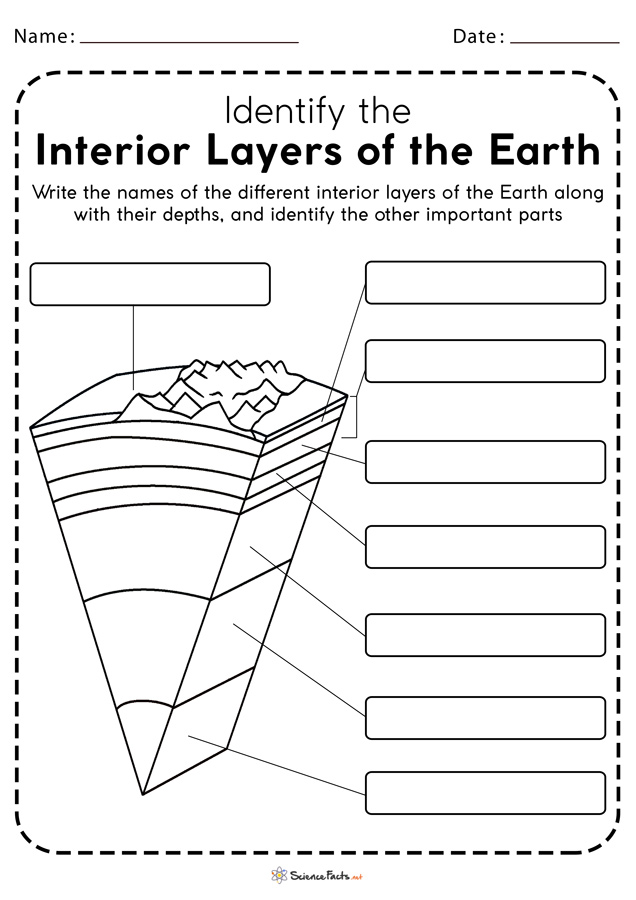
Earth’s Interior Layers

Understanding the structure of Earth is fundamental:
- Crust: The outermost layer, on which we live, varies in thickness.
- Mantle: Comprises the majority of Earth’s volume, semi-fluid in nature.
- Core: Made up of an outer core (liquid) and an inner core (solid), both primarily composed of iron.
Tectonic Plates

The lithosphere is broken into massive tectonic plates. Their movements result in:
- Volcanic activity
- Earthquakes
- Plate boundary interactions like convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries
Weather and Climate

The atmosphere influences Earth’s climate through:
- The greenhouse effect
- Ocean currents
- Jet streams
The Water Cycle

The continuous movement of water through the hydrosphere:
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Precipitation
- Collection
Interconnected Systems

The interactions among Earth’s systems are what make our planet habitable:
- Geochemical Cycles: Like the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorus cycle which regulate essential elements for life.
- Natural Hazards: Events like tsunamis, hurricanes, and landslides are products of Earth systems interacting under certain conditions.
Worksheet Answer Guide

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the Earth’s atmosphere composed of? | Nitrogen (78.09%), Oxygen (20.95%), Argon (0.93%), Carbon Dioxide (0.04%), with traces of other gases. |
| Describe the basic structure of Earth. | From the outside in: Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core. |
| How do tectonic plates cause earthquakes? | When plates move, friction at their edges can cause them to lock. Stress builds until the plates suddenly release, sending shockwaves through the crust. |

🔍 Note: These answers provide a simplified understanding of complex Earth systems. Students are encouraged to explore further for a more detailed comprehension.
Understanding Earth's systems not only aids in academic excellence but also helps in appreciating our environment. Each of the Earth's spheres has its unique functions and interactions. Here are a few ways these systems impact daily life:
- Weather Forecasts: Thanks to understanding atmospheric circulation, we can predict and prepare for weather changes.
- Water Supply: The water cycle ensures the availability of fresh water, crucial for all life.
- Geological Hazards: Knowing about plate tectonics helps in predicting potential risks and preparing for natural disasters.
- Climate: Changes in one part of the system can influence the global climate, affecting agriculture, habitat, and health.
In wrapping up this insightful journey into Earth's systems, we've ventured through the delicate balance of our planet's components. By mastering these basics, students and enthusiasts are better equipped to understand the processes shaping our world, from the deep magma flows beneath the Earth to the visible rain clouds in the sky. This knowledge not only fosters academic curiosity but also instills a sense of responsibility towards our planet, encouraging sustainable living and environmental conservation.
What are the key processes in the rock cycle?
+
The key processes include weathering, erosion, transportation, deposition, compaction, cementation, melting, and cooling.
How does human activity impact Earth’s systems?

+
Human activities like deforestation, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions significantly alter Earth’s systems, leading to climate change and habitat destruction.
What is the role of the biosphere in Earth systems?

+
The biosphere plays a critical role by interacting with the other spheres to recycle nutrients, regulate the climate, and maintain the planet’s habitability.