6 Essential Facts About DNA Structure Worksheet

Unlocking the Secrets of DNA: 6 Essential Facts About DNA Structure
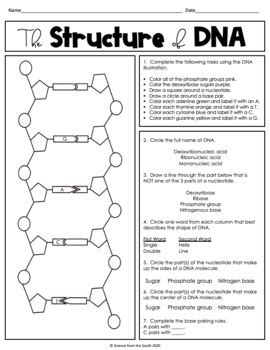
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecular blueprint for life, containing the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms. The discovery of the DNA structure by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 revolutionized the field of genetics and paved the way for major advances in fields such as genetic engineering, forensic science, and molecular biology.
Fact #1: DNA is a Double Helix

The DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder, with two complementary strands of nucleotides that are coiled together in a double helix structure. This structure was first proposed by Watson and Crick and has since been confirmed by numerous experiments and observations.
💡 Note: The double helix structure of DNA is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases, which are arranged in a specific pattern of adenine-thymine (A-T) and guanine-cytosine (G-C) pairs.
Fact #2: DNA is Composed of Nucleotides
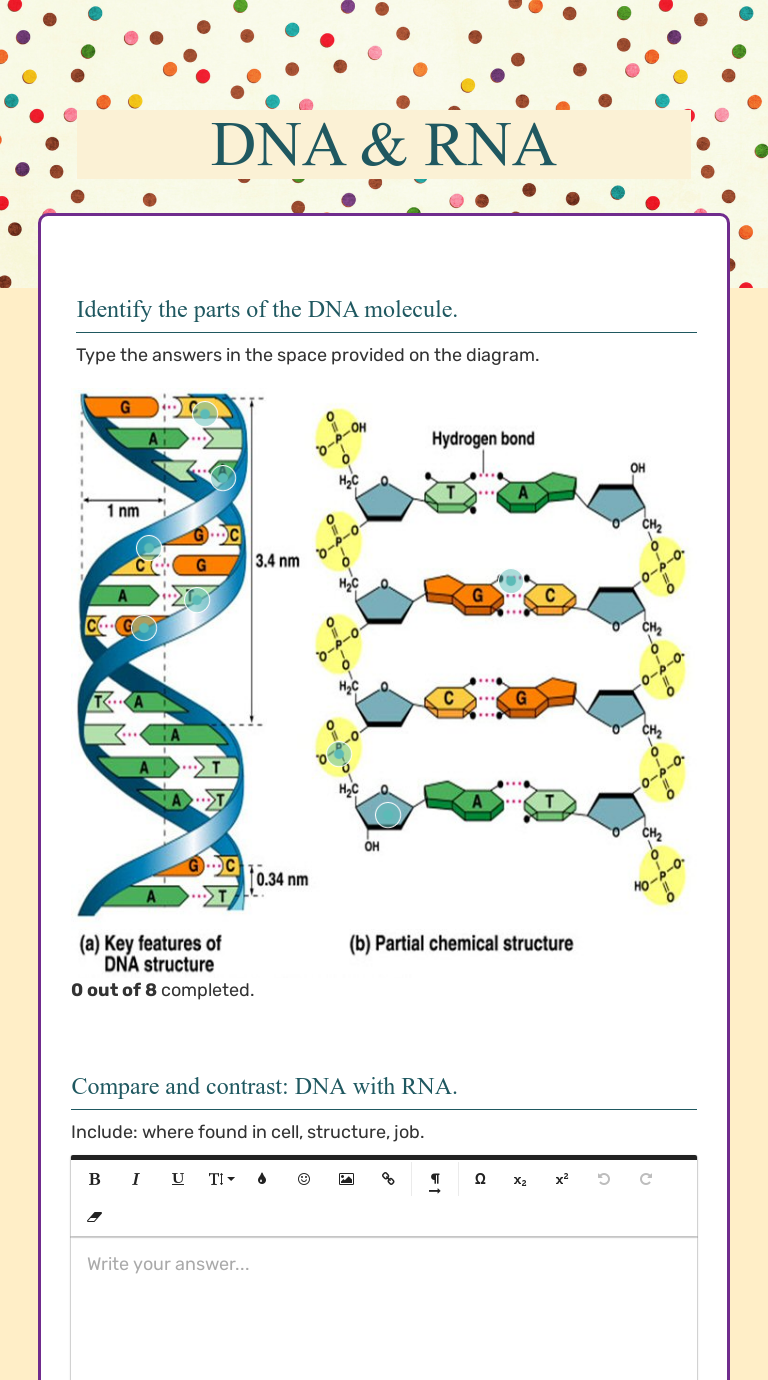
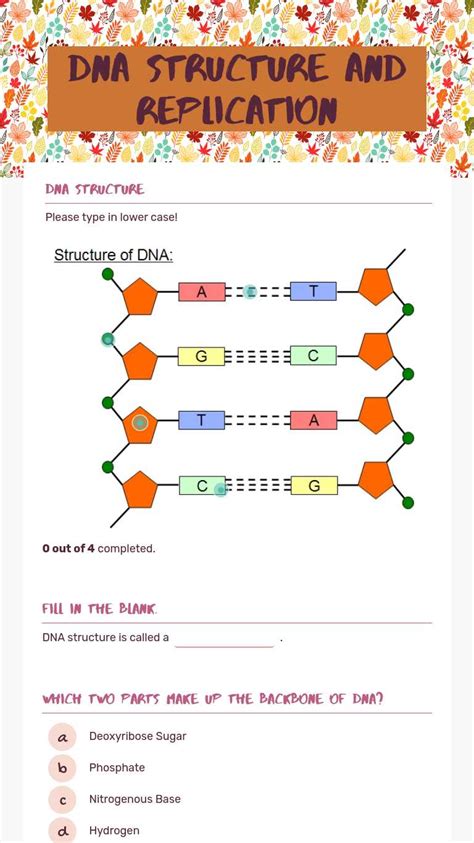
DNA is composed of four types of nucleotides, each consisting of a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T). These nucleotides are linked together in a chain, with the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the backbone of the DNA molecule.
Fact #3: DNA Replication is Semi-Conservative

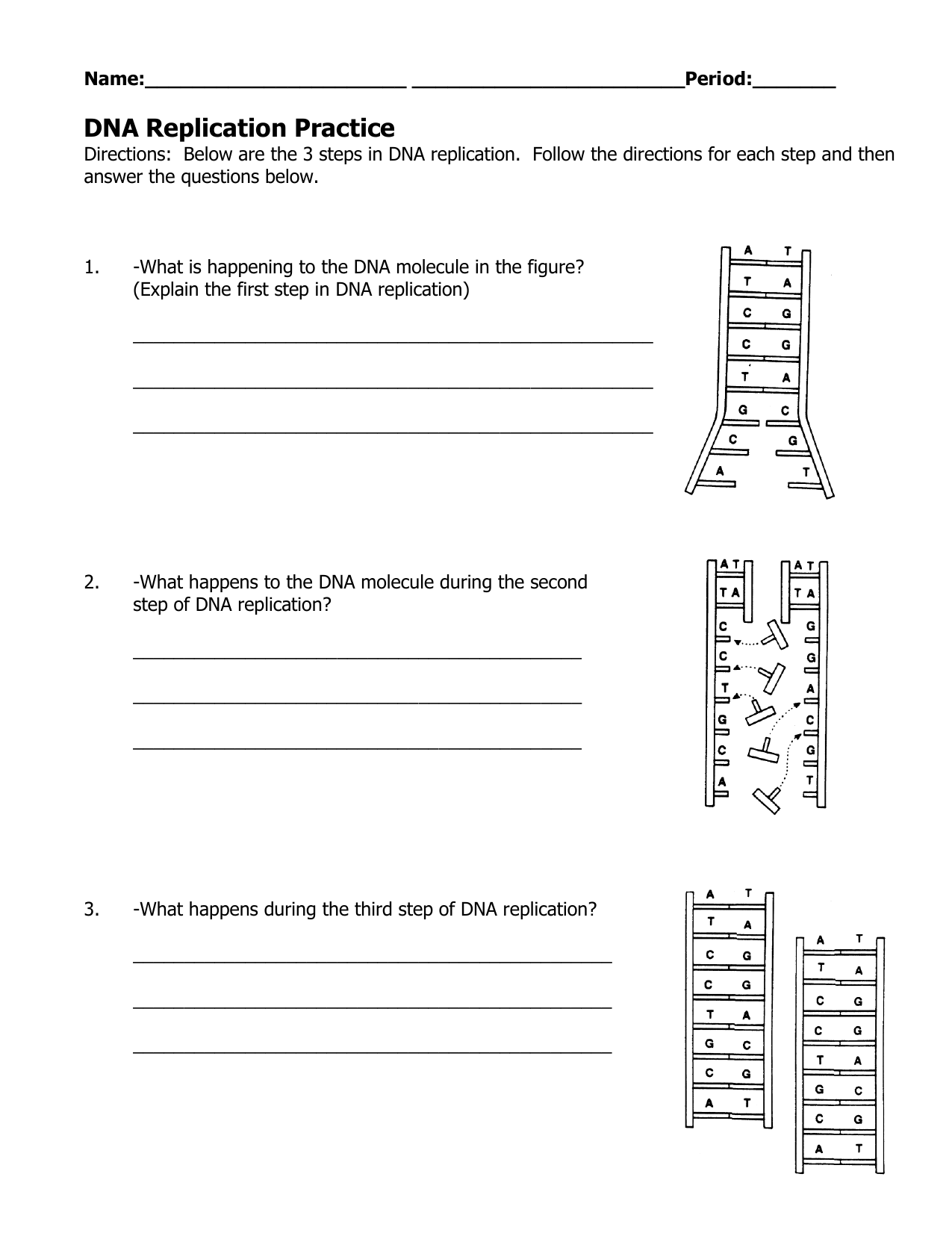
When a cell divides, its DNA must be replicated so that each daughter cell receives a complete copy of the genetic material. DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning that the new DNA molecule is composed of one old strand (the template strand) and one newly synthesized strand.
🔄 Note: The semi-conservative nature of DNA replication was demonstrated by the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which showed that the newly synthesized DNA molecule contains one old strand and one new strand.
Fact #4: DNA Mutation Can Occur Through Various Mechanisms

DNA mutation occurs when there is a change in the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. This can happen through various mechanisms, including:
- Point mutations: a single nucleotide change, such as a substitution or deletion
- Frameshift mutations: a change in the reading frame of the genetic code, caused by insertions or deletions of nucleotides
- Chromosomal mutations: changes in the structure or number of chromosomes
Fact #5: DNA Repair Mechanisms Exist to Correct Errors
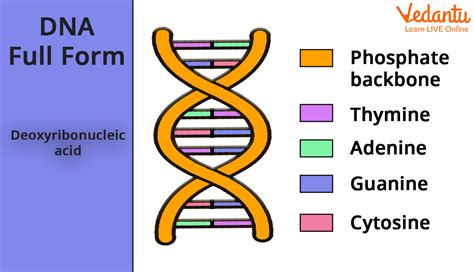
Cells have developed various mechanisms to repair errors in the DNA molecule, including:
- Proofreading: the correction of errors during DNA replication
- Mismatch repair: the correction of errors in the base pairing of nucleotides
- Nucleotide excision repair: the removal of damaged nucleotides and their replacement with new ones
🛠️ Note: DNA repair mechanisms are essential for maintaining the integrity of the genetic material and preventing mutations that can lead to genetic disorders or cancer.
Fact #6: DNA Structure Can be Influenced by Environmental Factors

The structure of DNA can be influenced by environmental factors, such as:
- Temperature: high temperatures can cause the DNA molecule to denature, or unwind
- pH: changes in pH can affect the stability of the DNA molecule
- Radiation: exposure to ionizing radiation can cause damage to the DNA molecule
| Environmental Factor | Effect on DNA Structure |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Denaturation of DNA molecule |
| pH | Affects stability of DNA molecule |
| Radiation | Causes damage to DNA molecule |

In conclusion, the structure of DNA is a complex and fascinating molecule that plays a critical role in the function of all living organisms. Understanding the essential facts about DNA structure is crucial for advances in fields such as genetic engineering, forensic science, and molecular biology.
What is the double helix structure of DNA?
+
The double helix structure of DNA is a twisted ladder-like structure, with two complementary strands of nucleotides that are coiled together.
What are the four types of nucleotides that make up DNA?

+
The four types of nucleotides that make up DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T).
What is the purpose of DNA repair mechanisms?
+
DNA repair mechanisms exist to correct errors in the DNA molecule, maintaining the integrity of the genetic material and preventing mutations that can lead to genetic disorders or cancer.
Related Terms:
- DNA Structure Worksheet PDF
- Dna structure worksheet answers quizlet
- DNA Worksheet with Answers
- DNA structure worksheet coloring



