Military
5 Diesel Firing Orders
Diesel Engine Firing Orders: Understanding the Basics

When it comes to diesel engines, the firing order is a critical aspect of their operation. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines rely on the heat generated by compression to ignite the fuel, rather than a spark plug. In this article, we will delve into the world of diesel firing orders, exploring what they are, how they work, and the common firing orders used in various diesel engines.
What is a Firing Order?

The firing order of a diesel engine refers to the sequence in which the fuel is injected into the cylinders. This sequence is crucial in ensuring that the engine runs smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal vibration. The firing order is typically defined by the manufacturer and is specific to each engine model.
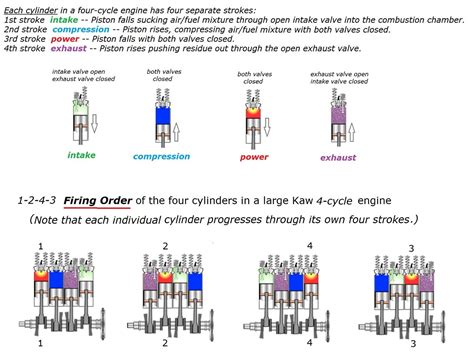
How Does a Diesel Firing Order Work?

In a diesel engine, the firing order is determined by the rotation of the crankshaft and the position of the fuel injectors. As the crankshaft rotates, it creates a series of compression strokes, which generate heat and pressure in the cylinders. The fuel injectors are timed to inject fuel into the cylinders at the precise moment when the compression stroke is at its peak, causing the fuel to ignite and produce power.
Common Diesel Firing Orders

There are several common firing orders used in diesel engines, including: * 1-3-4-2: This is a common firing order used in many inline-four cylinder diesel engines. * 1-5-3-6-2-4: This firing order is often used in inline-six cylinder diesel engines. * 1-3-5-2-4-6: This firing order is commonly used in V6 diesel engines. * 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2: This firing order is often used in V8 diesel engines. * 1-14-9-4-3-12-10-5-8-7-2-13-6-11: This firing order is commonly used in large, multi-cylinder diesel engines.
💡 Note: The firing order may vary depending on the specific engine model and manufacturer, so it's essential to consult the engine's manual or manufacturer's specifications for the correct firing order.
Importance of Correct Firing Order

Using the correct firing order is crucial for the proper operation of a diesel engine. An incorrect firing order can lead to: * Reduced engine performance and efficiency * Increased fuel consumption and emissions * Premature wear and tear on engine components * Potential engine damage or failure
Factors Affecting Firing Order

Several factors can affect the firing order of a diesel engine, including: * Engine design and configuration * Fuel type and quality * Injection timing and pressure * Engine speed and load
Adjusting the Firing Order

In some cases, the firing order may need to be adjusted to optimize engine performance or to compensate for changes in engine operating conditions. This can be done by: * Adjusting the injection timing and pressure * Modifying the engine’s fuel system * Using specialized software or tools to reprogram the engine’s computer
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, the firing order is a critical aspect of diesel engine operation, and understanding the basics of firing orders is essential for anyone working with diesel engines. By recognizing the importance of correct firing order and being aware of the factors that can affect it, individuals can optimize engine performance, reduce emissions, and prolong engine life.
What is the most common firing order for a 4-cylinder diesel engine?

+
The most common firing order for a 4-cylinder diesel engine is 1-3-4-2.
Can the firing order be adjusted to improve engine performance?

+
Yes, the firing order can be adjusted to optimize engine performance, but this should only be done by a qualified technician or mechanic.
What are the consequences of using an incorrect firing order?

+
Using an incorrect firing order can lead to reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption and emissions, premature wear and tear on engine components, and potential engine damage or failure.