5 Easy Steps to Convert Radians to Degrees

Converting radians to degrees is a fundamental skill in mathematics and various fields like engineering, physics, and astronomy. Understanding how to make this conversion not only helps you in practical applications but also deepens your comprehension of mathematical relationships. This article will guide you through five easy steps to convert radians to degrees, ensuring you have a smooth, straightforward process to follow.
Understanding the Basics

Before jumping into the steps, let’s briefly understand why we might need to convert between radians and degrees:
- Radians are the standard unit of angular measure used in higher mathematics and for theoretical analysis.
- Degrees are more familiar to most people and are commonly used in navigation and everyday applications.
Step 1: Know the Conversion Factor

The first step is to understand the relationship between radians and degrees. Here’s how they are related:
- 1 radian = 180° / π
The ratio of a full circle in degrees (360°) to its measure in radians (2π) gives us this conversion factor.
Step 2: Prepare Your Angle in Radians

If you already have an angle in radians, ensure it’s expressed in a manner that’s easy to work with:
- Check if the angle is in terms of π. If not, convert it to this form for simplicity.
For example, if you have an angle of 3 radians, it would be 3π / π or 3π * (180° / π).
Step 3: Apply the Conversion Factor

Now, multiply your angle in radians by the conversion factor:
- Angle in radians * (180° / π) = Angle in degrees
So, for 3 radians:
[ 3\pi \times \frac{180^\circ}{\pi} = 540^\circ ]Step 4: Simplify the Expression

If your angle includes π, you can cancel out π:
- The π’s cancel out, leaving you with a simple multiplication.
Using our example:
[ 3 \times 180^\circ = 540^\circ ]Step 5: Verify Your Answer
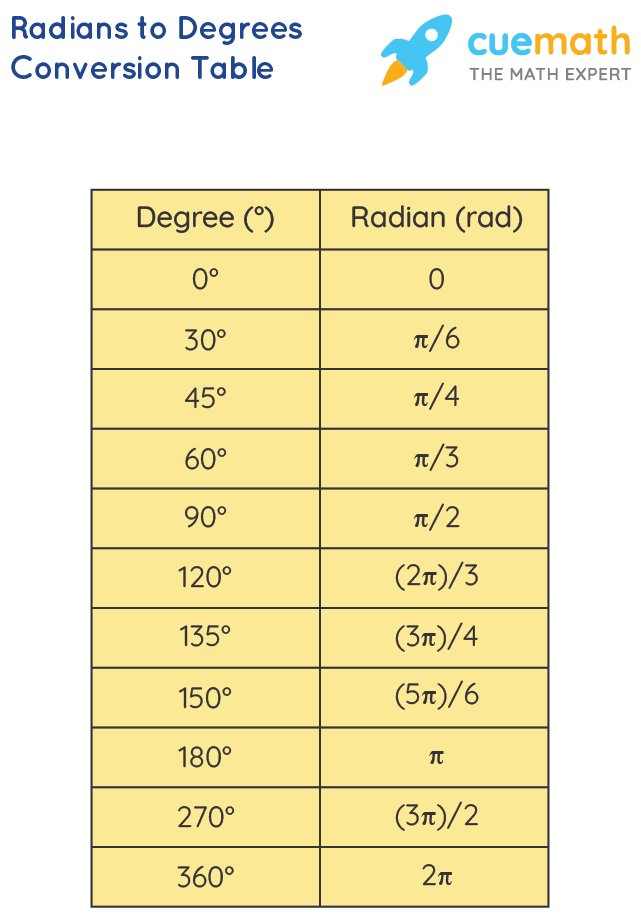
It’s always a good practice to check your work:
- Ensure your answer is reasonable. For instance, an angle in degrees should be within the range of 0° to 360° (for a single revolution).
- If your angle is larger, you might consider simplifying it to the equivalent positive angle less than 360°.
💡 Note: When dealing with negative angles or angles greater than 2π radians, consider the direction of rotation. Positive angles rotate counterclockwise, and negative angles rotate clockwise.
In summary, converting radians to degrees is an essential skill for anyone involved in mathematical or technical fields. By following these five straightforward steps, you can ensure accurate and effortless conversions. From understanding the basic relationship between radians and degrees, through applying the conversion factor, to verifying your final answer, this process is designed to be user-friendly and logically constructed.
Why do we use radians in mathematics?

+
Radians are used because they provide a more natural unit of measure for circular functions. They simplify many mathematical formulas, especially those involving calculus, trigonometry, and periodicity.
Can you convert degrees to radians using a similar method?

+
Yes, you can convert degrees to radians by multiplying by the factor π / 180°. This process is just the reverse of converting radians to degrees.
What if my angle in radians contains π?

+
Angles in radians often include π to simplify calculations, especially in calculus. When converting, π cancels out in the conversion process, leaving you with a degree value.
Are there tools or calculators that can do this conversion?

+
Yes, there are numerous online tools, apps, and calculators that can convert radians to degrees and vice versa. However, understanding the process helps in troubleshooting and verifying calculations.
Can converting radians to degrees ever give a negative result?

+
The conversion itself will yield a positive result because degrees measure angles and not direction. However, if the original angle was negative, it indicates a clockwise rotation, and you would interpret the positive degree value accordingly.
Related Terms:
- Radians to degrees calculator
- Degrees and radians worksheet answers