Master Motion: Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 5

In the realm of physics education, worksheets play a pivotal role in reinforcing classroom teachings, and the Constant Velocity Particle Model (CVPM) worksheet 5 is a prime example of how foundational concepts can be tested and understood through practical application. CVPM, which focuses on understanding motion where an object moves at a constant velocity, is essential for building a solid foundation in kinematics. This post will delve into the worksheet in detail, exploring its structure, objectives, and the principles of constant velocity motion.
What is the Constant Velocity Particle Model?

The Constant Velocity Particle Model (CVPM) represents one of the earliest models students learn when studying physics, particularly in mechanics. Here, we model an object moving along a straight line with a consistent speed and direction, meaning the velocity does not change over time. This model is important because:
- It introduces students to the concept of velocity as a vector.
- It illustrates the relationship between position, time, and velocity through simple mathematical functions.
- It lays the groundwork for more complex motions with varying acceleration.
The Basics of Constant Velocity

At the heart of CVPM is the equation of motion for constant velocity:
x = x0 + vt
where:
- x is the final position,
- x0 is the initial position,
- v is the velocity (which is constant in this model), and
- t is time.
🚨 Note: Velocity is a vector; even though its magnitude (speed) remains constant, its direction must also be considered in the context of motion.
Structure and Objectives of CVPM Worksheet 5
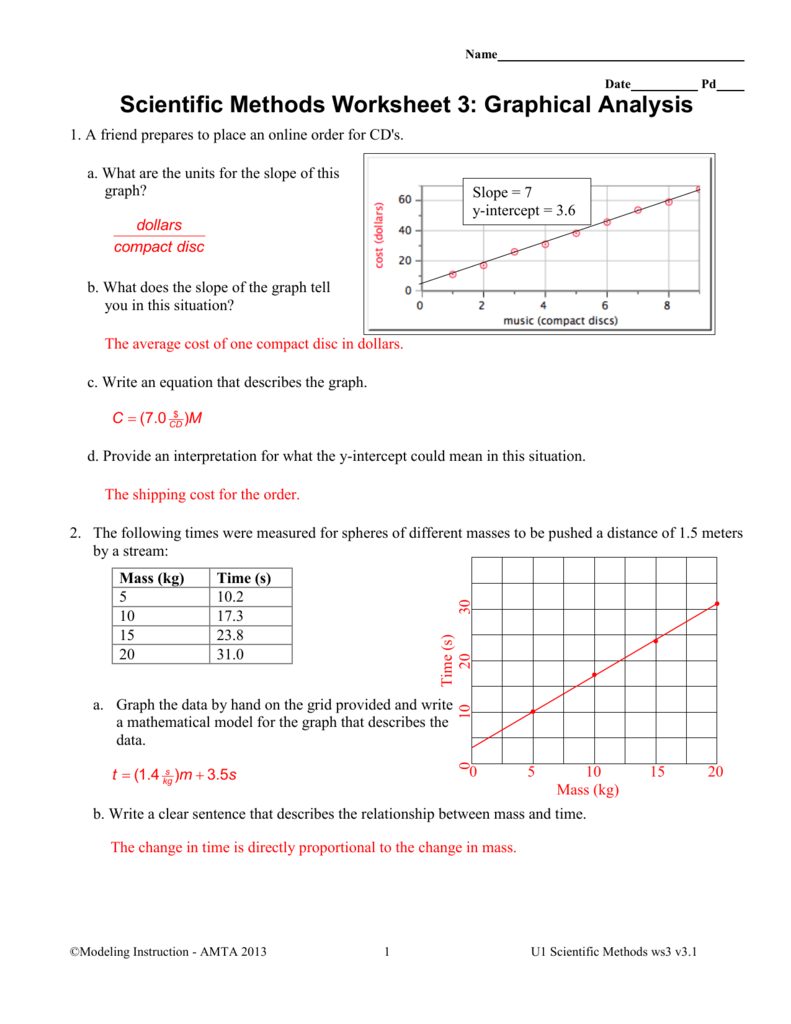
Worksheet 5 in the CVPM series typically focuses on:
- Graph interpretation: Understanding position-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time graphs for constant velocity motion.
- Data analysis: Using gathered data to calculate velocity from position measurements over time.
- Problem-solving: Applying the constant velocity equation to real-life scenarios or hypothetical problems.
Graph Interpretation

Graphs are crucial tools for visualizing motion:
- Position-Time Graphs: The slope represents the velocity, which will be constant for a CVPM. A straight line implies constant velocity.
- Velocity-Time Graphs: A straight horizontal line indicates constant velocity. The area under this graph gives displacement.
- Acceleration-Time Graphs: Since acceleration is zero in CVPM, this graph will be a horizontal line at the y-axis, meaning no change in velocity over time.
Data Analysis

Students are often provided with data sets or instructed to collect data through experiments. Here’s how they might work with this:
- Calculate velocity from change in position divided by time, ensuring the units are consistent.
- Plotting these data points on a graph to visually confirm constant velocity.
📌 Note: Ensuring that the initial position (x0) is correctly accounted for in calculations is crucial when analyzing data from experiments or solving problems.
Problem Solving

The worksheet includes problems where students need to:
- Determine unknown velocities or times given other parameters.
- Convert between units to ensure proper application of the equation.
- Understand relative motion where multiple objects move at constant velocities.
Application in Real Life

The principles of constant velocity are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they apply to many real-life scenarios:
- Traffic Flow: Analyzing the steady flow of cars on highways can use CVPM to understand the relationship between speed, distance, and time.
- Conveyor Belts: Items moving at constant speeds along a conveyor belt can be modeled using CVPM.
- Spacecraft Travel: Spacecraft cruising in space for long distances before reaching their targets.
Here's a table showing examples of constant velocity applications:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Traffic Flow | Understanding speed limits and average speeds over long distances. |
| Conveyor Belts | Ensuring constant movement in manufacturing processes for efficiency. |
| Spacecraft Travel | Planning missions where spacecraft travel at a constant speed after escaping Earth's gravity. |

How to Solve CVPM Problems

Solving problems in constant velocity requires the following steps:
- Identify the known variables: initial and final positions, time, or velocity.
- Set up the equation: x = x0 + vt.
- Solve for the unknown by rearranging the equation. For instance, if velocity is unknown, v = (x - x0) / t.
- Double-check units for consistency.
- Verify your answer by considering if it fits within the physical constraints of the problem.
🔔 Note: Always consider the direction of motion when solving constant velocity problems; velocity is a vector, so negative values indicate opposite directions.
To sum up, CVPM worksheet 5 serves as an excellent tool for mastering the concept of constant velocity. By engaging with graphs, data analysis, and practical problem-solving, students not only solidify their understanding of basic kinematic principles but also see how these concepts play out in real-world applications. This practice fosters a deeper comprehension of motion, setting the stage for exploring more complex motion with acceleration and change in direction.
What is the significance of constant velocity in physics?

+
Constant velocity signifies that an object’s speed and direction do not change, which simplifies the analysis of motion. It’s fundamental for understanding kinematic relationships and lays the foundation for studying more complex motions.
Why is graph interpretation important in CVPM?

+
Graphs provide visual representations of motion, allowing for the intuitive understanding of how position, velocity, and time relate in constant velocity situations. They help in identifying the slope of position-time graphs to calculate velocity and understanding velocity-time graphs to confirm constant velocity.
How can I use CVPM to solve real-world problems?

+
CVPM can be applied in scenarios like traffic management to understand vehicle speeds, conveyor belt systems for consistency in manufacturing processes, or calculating the time for spacecraft to travel to specific destinations in space.



