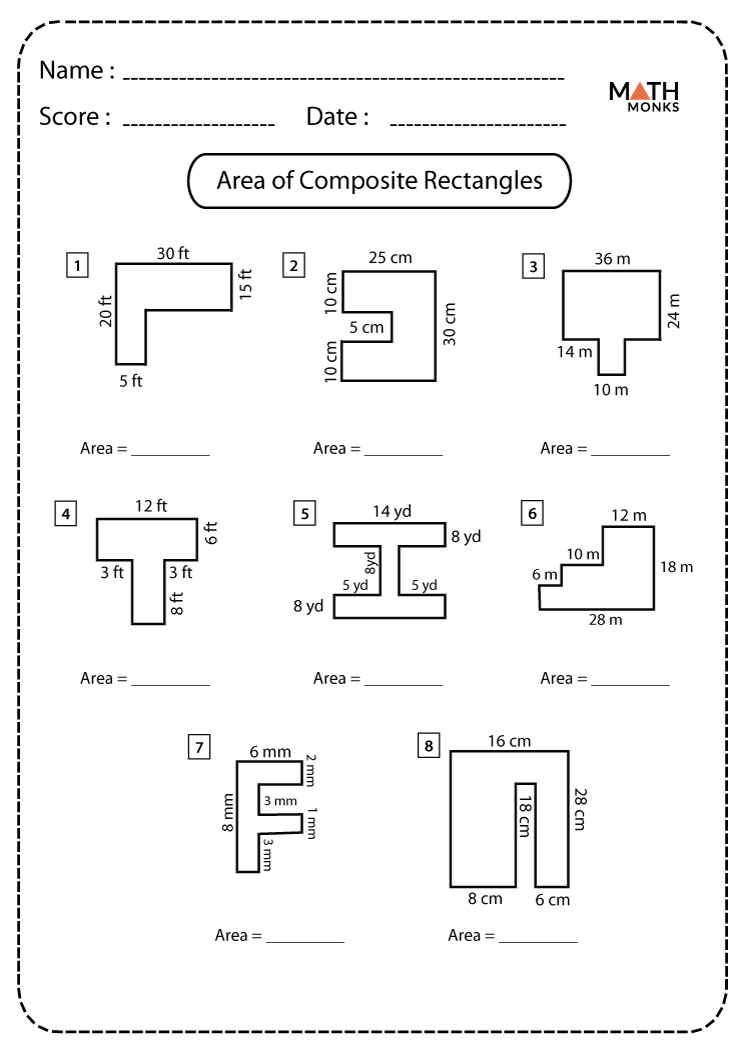
Composite Figures Worksheet: Boost Geometry Skills Easily

Mastering Composite Figures in Geometry

Geometry isn't just about recognizing basic shapes; it often involves understanding and calculating the area, perimeter, and properties of composite figures. Composite figures are created by combining two or more simple geometric shapes like rectangles, squares, circles, and triangles. This concept, though initially challenging, can significantly improve your problem-solving skills and spatial visualization. Let's dive into how we can master these complex forms.
Understanding Composite Figures

At the core, a composite figure or composite shape is any two-dimensional figure that can be deconstructed into simpler figures. Here’s what you need to know:
- Types of Shapes: Most commonly, composite figures include rectangles, squares, triangles, trapezoids, and sectors of circles.
- Visual Deconstruction: Learning to "see" the simpler shapes within the complex one is the first step towards understanding composite figures.
- Real-life Applications: These shapes are everywhere in architecture, art, and design, making their study highly practical.
Step-by-Step Approach to Solving Composite Figure Problems

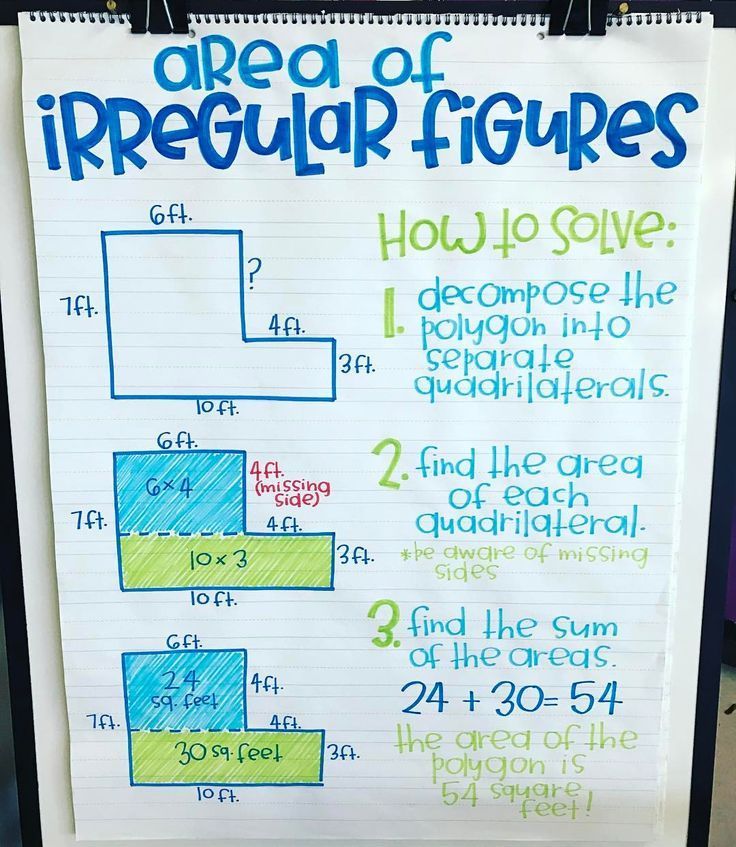
1. Break Down the Composite Figure

Begin by sketching or visualizing how you can break the composite figure into simpler, more familiar shapes:
- Identify which basic shapes are combined to form the composite figure.
- Draw lines to partition the figure mentally or on paper into these shapes.
- Label the dimensions of each shape carefully.
2. Calculate the Area of Each Basic Shape
Using the formulas for each basic shape:
- Rectangle: Area = Length × Width
- Square: Area = Side × Side
- Triangle: Area = (Base × Height) / 2
- Circle: Area = πr²
- Trapezoid: Area = (a + b) × h / 2, where a and b are the parallel sides and h is the height.
⚠️ Note: Ensure the units are consistent when calculating areas.
3. Sum Up the Areas

Once you have calculated the areas of all the component shapes, add them together to find the total area of the composite figure:
- Remember to include or exclude overlaps if present.
- If the figure has cutouts, subtract these areas from the total.
4. Calculate Perimeter
If you are tasked with finding the perimeter:
- Trace the outer edges of the figure.
- Add up all the exterior line segments. Be aware of shared edges with interior shapes.
Strategies for Composite Figure Problems

Here are some strategies to tackle composite figure problems efficiently:
- Practice Visualization: Regularly practicing to visualize or draw composite figures helps in quick deconstruction.
- Use Grid Paper: Initially, working on grid paper can make it easier to partition figures accurately.
- Check for Symmetry: Symmetrical composite figures often have properties that can be used to simplify calculations.
- Work Backwards: Sometimes, if you know the total area, you can work backwards to find missing dimensions or areas of component shapes.
Enhancing Geometry Skills with Composite Figures

Beyond solving problems, mastering composite figures can:
- Improve your ability to estimate area and volume in real-life situations.
- Help in understanding architectural and engineering drawings.
- Boost your performance in standardized tests where geometry problems often include composite figures.
Engaging with composite figures isn't just about calculating areas and perimeters. It's a training ground for logical reasoning, where you learn to:
- Deconstruct complex problems into simpler parts.
- Understand spatial relationships between shapes.
- Develop a methodical approach to geometry problem-solving.
From calculating the area of a backyard with irregular boundaries to designing intricate patterns, composite figures serve as the foundation for many practical applications.
Why are composite figures important in geometry?

+
Composite figures teach us to analyze and solve complex geometric problems by breaking them down into simpler shapes, enhancing our problem-solving abilities and spatial visualization.
What are common challenges when working with composite figures?

+
Common challenges include accurately deconstructing the figure into basic shapes, dealing with overlapping regions, and ensuring consistent units for measurement.
How can I practice with composite figures?

+
You can practice by sketching on grid paper, using geometry software, or solving real-life problems where shapes are not perfectly regular, like designing a garden layout or estimating material for irregularly shaped rooms.
What if I get stuck while solving a composite figure problem?

+
If stuck, try different angles of visualization, use online resources for step-by-step examples, or ask for guidance from a teacher or study group.



