Codominance Worksheet: Master Genetics With Answer Key

Delving into the realm of genetics, particularly in understanding codominance, is an enlightening journey. Imagine plants, animals, and even human populations exhibiting fascinating traits that blend in a most spectacular manner, rather than one allele overpowering the other in complete dominance. This is the world of codominance, where both alleles of a gene pair express themselves independently and equally in the phenotype of the heterozygous individual. Let's embark on a quest to unravel the intricacies of codominance through a comprehensive worksheet, complete with an answer key to guide you through.
Understanding Codominance

Before diving into the worksheet, let's establish a clear understanding of codominance:
- Codominance: A situation where neither allele is dominant over the other, and both alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote.
- Heterozygous: An individual having two different alleles for a particular gene.
- Phenotype: The physical expression of the genotype.
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an individual with respect to a specific characteristic or set of characteristics.
Examples of Codominance

Here are a few examples to visualize codominance:
- Blood Types in Humans: A prime example of codominance is the ABO blood group system. Both the A and B alleles are expressed equally in the AB blood type.
- Feather Color in Chickens: Chickens exhibiting both black and white feathers in a pattern called flecking showcase codominance.
- Horse Coat Color: The roan coat color in horses where red (chestnut) and white hairs are present equally.
Codominance Worksheet

Now, let's dive into our codominance worksheet. Use the following scenarios to test your understanding of codominance:
Worksheet Problems

- If a person with blood type AB (genotype IAIB) mates with a person who has blood type O (genotype ii), what are the possible blood types of their offspring?
- In a flock of chickens where both black and white feathers occur, a black feathered (BB) chicken mates with a white feathered (WW) chicken. What would the offspring look like?
- Explain how codominance differs from incomplete dominance using examples.
Worksheet Answer Key
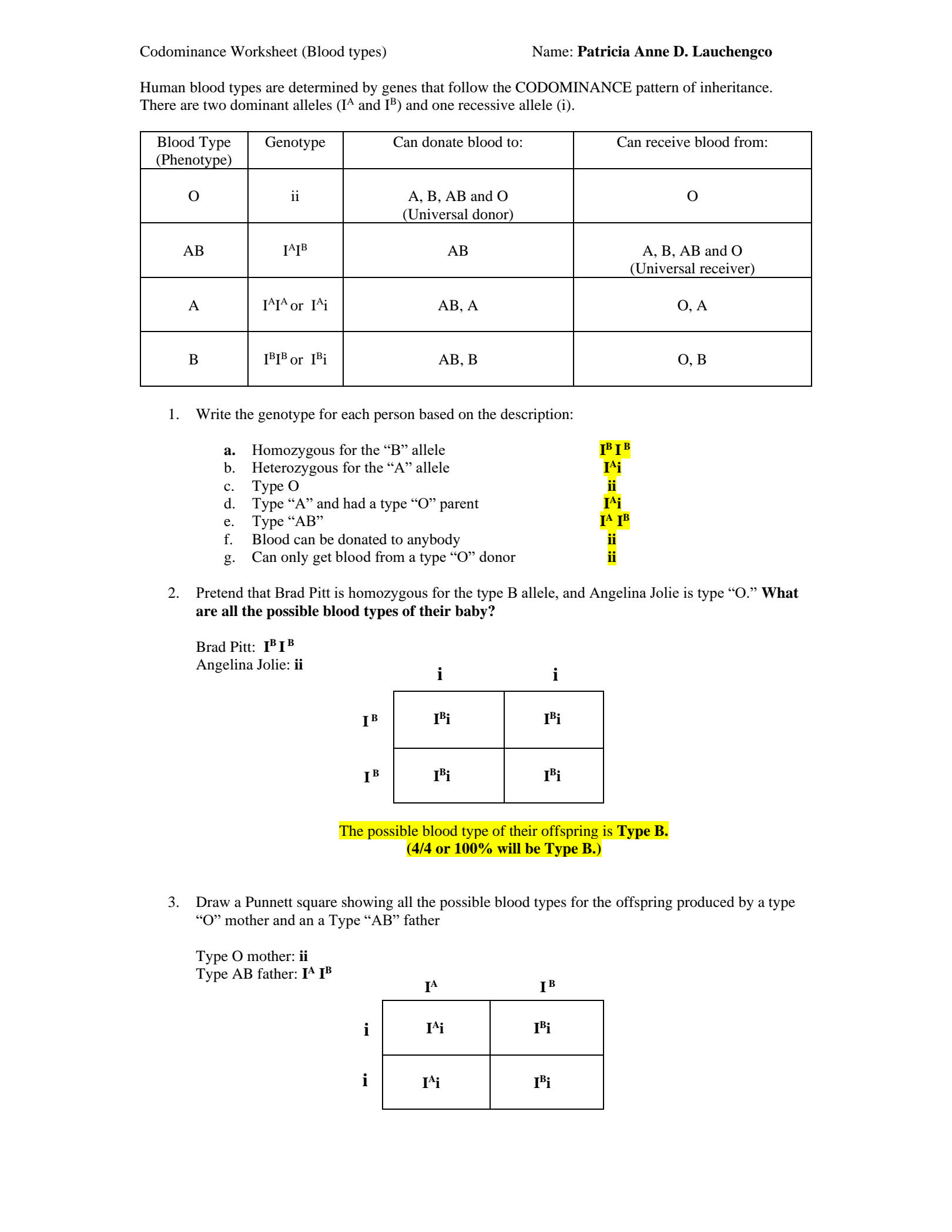
- The possible blood types of the offspring are A (genotype IAi) and B (genotype IBi). Here, each offspring will inherit one allele from each parent. Since blood type O does not produce antigens, A and B will be expressed independently.
- The offspring will exhibit codominance with a flecking pattern of black and white feathers because the alleles for black and white feathers are expressed equally.
- In Codominance: Both alleles are expressed independently, for example, in the ABO blood group, both A and B are fully expressed.
In Incomplete Dominance: The heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes. For instance, in snapdragons, red flowers crossed with white can produce pink flowers.
💡 Note: For the purpose of this worksheet, we are assuming a simple genetic model where there are only two alleles for each gene. Real-world genetics can be more complex with multiple alleles and polygenic traits.
How Codominance Plays a Role in Agriculture

Understanding codominance is not just an academic exercise; it has practical applications, especially in agriculture:
- Selective Breeding: Farmers can use codominance to select and breed for specific traits in livestock and crops.
- Genetic Diversity: Codominance promotes genetic diversity, which can be crucial for survival against pests and diseases.
- Health and Nutrition: Certain traits expressed through codominance might be linked to nutritional quality or resistance to environmental stressors.
In the final stretch of our journey through codominance, we've explored the mechanics of this genetic phenomenon, provided a worksheet with an answer key to solidify understanding, and delved into its real-world applications in agriculture. Codominance not only adds color and variety to the biological world but also holds practical significance for industries like farming. The key takeaway is that genetics, through mechanisms like codominance, equips life forms with diverse traits that can be harnessed for sustainability and better understanding of our biological world. Now, here's a brief FAQ section for some common questions that might arise as you continue your exploration of codominance:
What is the difference between codominance and incomplete dominance?

+
In codominance, both alleles in a heterozygote are equally expressed, creating a phenotype where both traits are visibly represented. In incomplete dominance, the phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes, where one allele does not completely mask the other’s effects.
Can codominance occur in humans?

+
Yes, codominance is exemplified in humans with the ABO blood group system where both A and B alleles are fully expressed in individuals with the AB blood type.
Why is codominance important in livestock breeding?

+
Codominance allows breeders to introduce multiple beneficial traits into livestock, enhancing disease resistance, increasing yield, or improving product quality without losing the original traits, thus maintaining or increasing genetic diversity.