5 Essential Tips for Understanding Codominance and Incomplete Dominance

When delving into the intricate world of genetics, understanding how traits are inherited becomes paramount. Two pivotal concepts in this realm are codominance and incomplete dominance, both of which can significantly impact the appearance and characteristics of offspring. Let’s explore these fascinating genetic phenomena through essential tips that will enhance your grasp of them.
Understanding Genetic Concepts

At its core, genetics involves the study of genes, how they function, and how they interact to produce traits. Here are the key points:
- Gene: A segment of DNA that codes for a specific trait.
- Alleles: Different versions of the same gene, which might produce different expressions of the trait.
- Dominance: Refers to the relationship between alleles where one allele masks the effect of another.
Codominance Explained

In codominance, two different alleles inherited from the parents are both fully expressed, contributing equally to the phenotype of the offspring. Here's how you can understand and identify codominance:
1. Recognizing Codominance

- Look for traits where both parental phenotypes are visibly present in the offspring.
- Classic Example: The ABO blood group system in humans where type AB individuals have both A and B antigens.
2. Visual Examples


Codominance often results in striking visual patterns or textures, making it easier to recognize in plant and animal species.
Incomplete Dominance Explained

Unlike codominance, incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele is completely dominant over the other, leading to a blending of the traits. Here's how to understand this:
1. Identifying Incomplete Dominance
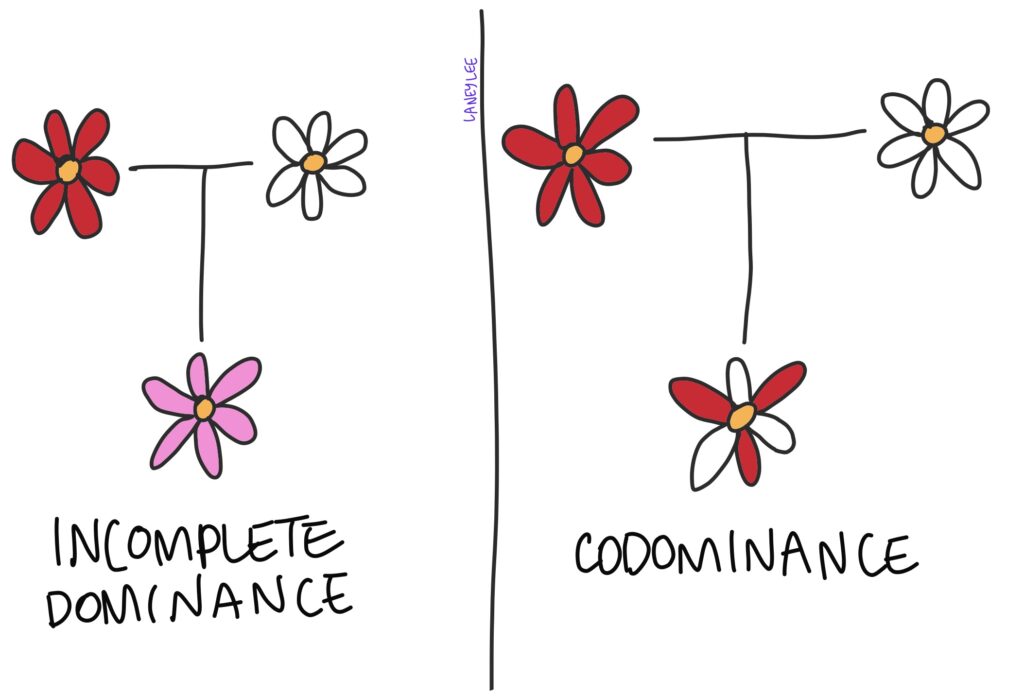
- Observe offspring traits that are intermediate between those of the parents.
- Classic Example: In snapdragons, a red ® and white (W) flower cross results in pink (RW) flowers.
2. Example Cases


This phenomenon is not as visually stark as codominance but still produces intriguing results in the offspring’s appearance.
Comparing Codominance and Incomplete Dominance

To distinguish between the two:
| Codominance | Incomplete Dominance | |
|---|---|---|
| Phenotypic Result | Both alleles express fully | A blended expression of alleles |
| Example | AB blood type | Pink snapdragons |
| Visual Outcome | Distinct, separate traits | Intermediate trait |

🧬 Note: In both cases, the F1 generation will exhibit phenotypes that differ from both parental homozygous phenotypes.
Now let's delve into how these genetic principles can be seen in real-world examples:
Real-World Applications

- Plant Breeding: Farmers and horticulturists use codominance to develop unique flower patterns or to predict the colors of fruits and vegetables.
- Medical Genetics: Understanding blood types through codominance is crucial for blood transfusions and organ transplants.
- Animal Husbandry: Breeders can use incomplete dominance to enhance desirable traits in livestock or pets.
3. Common Misconceptions

- Misunderstanding Codominance as “Double Dominance”: Codominance does not mean one allele is dominant over another; rather, they both express themselves.
- Assuming Complete Dominance in Blended Traits: Not all mixed results indicate incomplete dominance; sometimes other genetic factors are at play.
The Genetic Nitty-Gritty
To grasp these concepts at a deeper level:
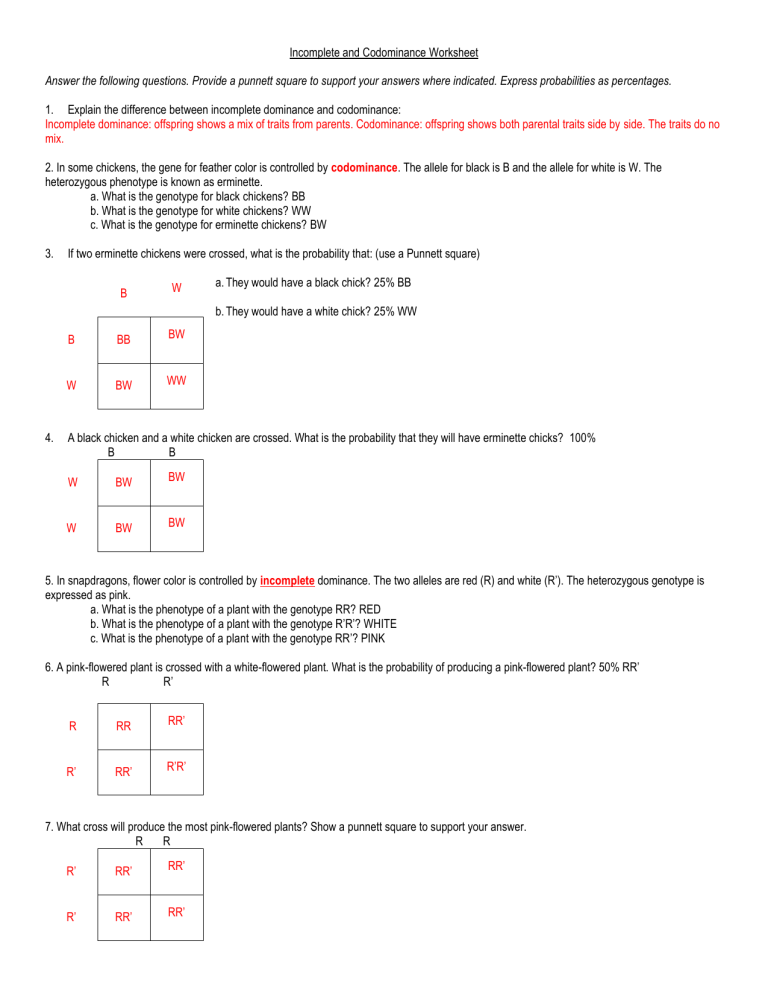
- Understand Punnett Squares: These diagrams help predict the probabilities of offspring phenotypes.
- Explore Molecular Biology: Knowledge of how DNA sequences translate into physical traits can demystify these genetic interactions.
🧬 Note: Punnett squares work on the principle of independent assortment but are especially useful in cases of codominance and incomplete dominance.
As we've explored the nuances of codominance and incomplete dominance, it's clear that genetics is a complex tapestry of interactions between genes. Here's a brief recap to solidify your understanding:
- Key Differences: Codominance results in both alleles expressing their traits fully, while incomplete dominance produces a middle-ground phenotype.
- Real-World Impact: From agriculture to medicine, these genetic principles have practical applications.
- Genetic Exploration: Delving into the molecular level of genetics provides insight into why these patterns occur.
Let's summarize the essential tips for understanding these genetic principles:
- Recognize Codominance and Incomplete Dominance: Look for clear visual indicators in the offspring.
- Understand the Mechanisms: Codominance means both alleles are expressed, while incomplete dominance results in a blend of traits.
- Appreciate Applications: These genetic concepts are not just theoretical but have real-world implications in various fields.
- Stay Curious: Continuous learning about molecular biology and genetics enhances understanding.
As we wrap up, here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify any lingering doubts:
Can codominance occur in multiple genes?

+
Yes, codominance can happen with multiple gene pairs, although it’s rarer. An example would be speckled feathers in chickens where multiple genes for different colors are expressed simultaneously.
What’s the difference between codominance and incomplete dominance?

+
Codominance occurs when both alleles are expressed, whereas incomplete dominance results in an intermediate phenotype, where one allele does not completely dominate the other.
Are there any examples of incomplete dominance in humans?

+
Yes, one example is familial hypercholesterolemia, where individuals with one dominant and one recessive allele show moderate levels of cholesterol, an intermediate between the extreme levels of affected and unaffected individuals.



