Circular Flow Economics Answer Key: Free Worksheet

Understanding circular flow economics is crucial for comprehending how our economy functions. This concept illustrates the reciprocal relationship between businesses and households, showcasing how goods, services, money, and resources flow through an economy. Here's a comprehensive look into the circular flow model, its components, and how it applies to everyday economic activities.
Economics of the Circular Flow
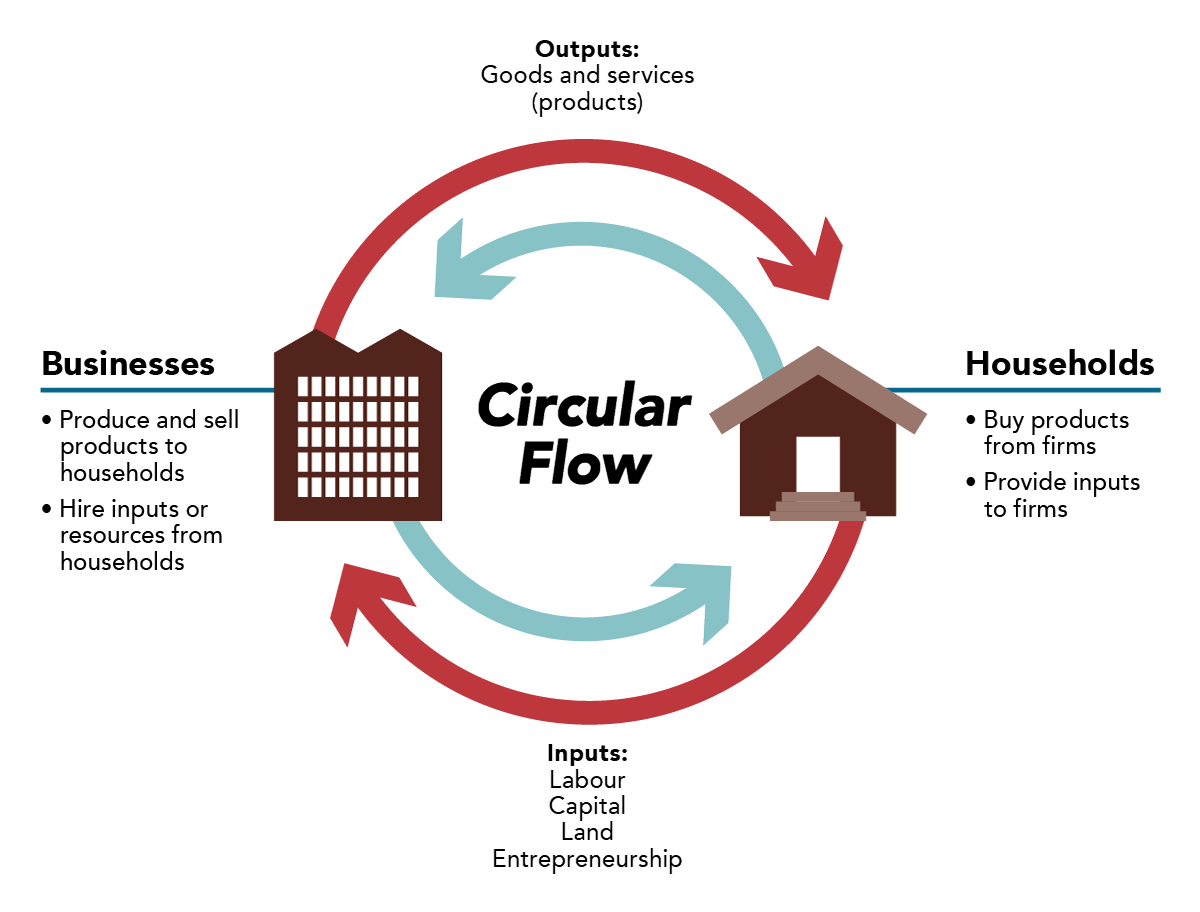
The circular flow model is a visual representation of how money moves through an economy. At its core, it shows the interactions between households (consumers) and firms (businesses), but there are several layers to this:
- Goods and Services Market: This is where households buy goods and services from firms, using their income.
- Factor Market: Conversely, this market deals with households selling their labor, land, capital, and entrepreneurial ability to firms.
💡 Note: It’s important to understand that the flow of money isn’t one-way; it circulates back into the economy through these interactions.
Key Components
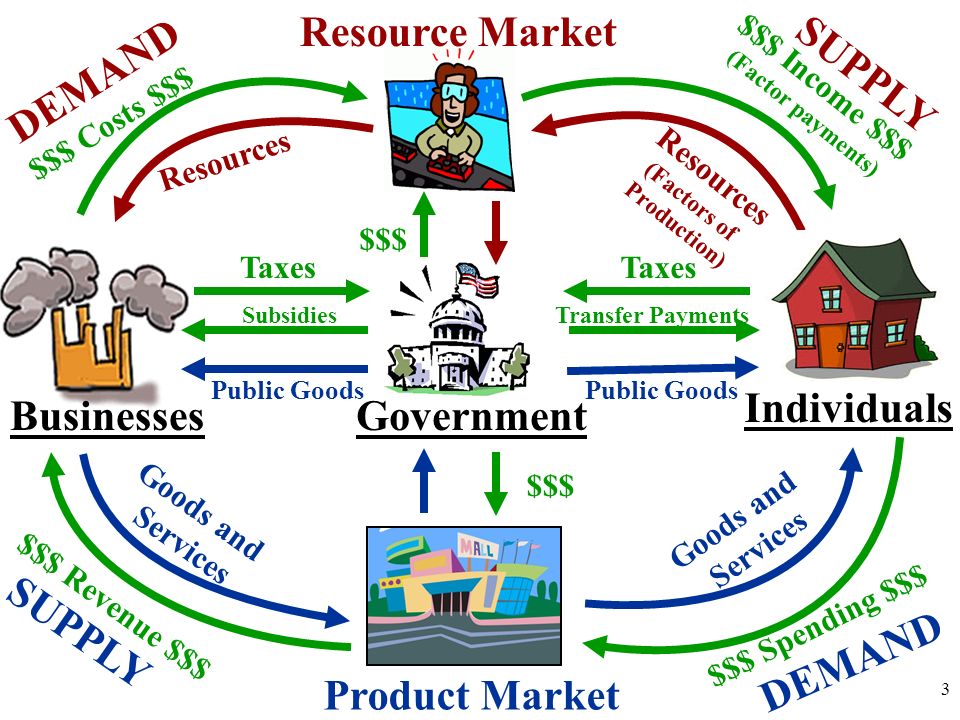
The model typically includes:
- Households: The units that consume goods and services and provide resources in the factor market.
- Firms: The producers of goods and services that require resources from households.
- Markets: Two types exist – goods and services market and the factor market.
- Financial Markets: Where saving, lending, and borrowing take place, affecting both firms and households.
| Market | Flow From Households to Firms | Flow From Firms to Households |
|---|---|---|
| Goods & Services | Income (Money) | Goods and Services |
| Factor Market | Resources (Labor, Capital, etc.) | Income (Wages, Rent, etc.) |

Application in Real Life

The circular flow model isn’t just a theoretical construct; it applies directly to how economies operate in real life:
- Purchasing Power: When households earn income, they increase their purchasing power, which leads to more consumption, fueling production by firms.
- Investment: Firms invest in capital, which requires money from savings, which in turn come from household income.
- Government: Government taxes households and firms, then uses this money to provide public services, further influencing the flow.
The Role of Government
Government plays a significant role in the circular flow through:
- Taxation: Collecting taxes from both households and firms.
- Subsidies: Providing financial assistance to firms to encourage production or consumption.
- Public Services: Using tax revenue to provide services like education, healthcare, infrastructure, etc.
🌟 Note: While taxes might reduce the income flow back to households, the services provided by the government enhance household and firm productivity, creating a balanced flow.
The Importance of Circular Flow

The circular flow of income provides several insights into economic systems:
- Equilibrium: It helps illustrate how economies achieve a balance between production and consumption.
- Inflation: When money flow increases disproportionately to goods flow, it can lead to inflation.
- Leakages and Injections: Savings, taxes, and imports are leakages, while investments, government spending, and exports are injections, altering the circular flow.
Through understanding the circular flow, individuals, businesses, and policymakers can:
- Predict economic trends and make informed decisions.
- Identify areas where economic policy interventions might be necessary.
- Appreciate the interconnectedness of economic activities.
Summing up, the circular flow model is a fundamental tool for economic analysis. It captures the essence of how an economy operates through the flow of money, resources, and goods between different sectors. Whether you're a student, an economist, or someone interested in how economies work, grasping this concept provides a clearer picture of economic interactions, helping in understanding complex economic phenomena.
What is the main benefit of the circular flow model?
+
The main benefit of the circular flow model is to understand how money circulates through an economy, showing the relationships and interdependencies between households, firms, and markets. It provides a simplified way to visualize economic activities, helping in predicting economic outcomes and crafting policy interventions.
How does government participation affect the circular flow?

+
The government participates by taxing, which removes money from the circular flow (leakage), but it also injects money back into the economy through spending on public services, subsidies, and transfer payments, influencing both production and consumption patterns.
Can the circular flow model explain economic growth?

+
Yes, economic growth can be analyzed through the lens of the circular flow model. Growth occurs when there are increases in production, employment, income, and consumption. This is often facilitated by investments (injections into the economy) which stimulate more economic activity, leading to growth.
What are ‘leakages’ in the circular flow?
+
Leakages are withdrawals from the circular flow, reducing the money supply available for spending. These include savings, taxes, and imports, which take money out of the immediate consumption loop.
Related Terms:
- Circular flow Worksheet pdf
- Circular flow model