Box and Whisker Plots: Interactive Worksheets for Mastery

Box and whisker plots, often simply referred to as box plots, are powerful visual tools used in statistics to graphically depict groups of numerical data through their quartiles. These plots excel in conveying information about the distribution, central tendency, and variability of the data in an easy-to-digest format. This article delves into how you can master the use of box and whisker plots through interactive worksheets, making statistics not only understandable but also engaging.
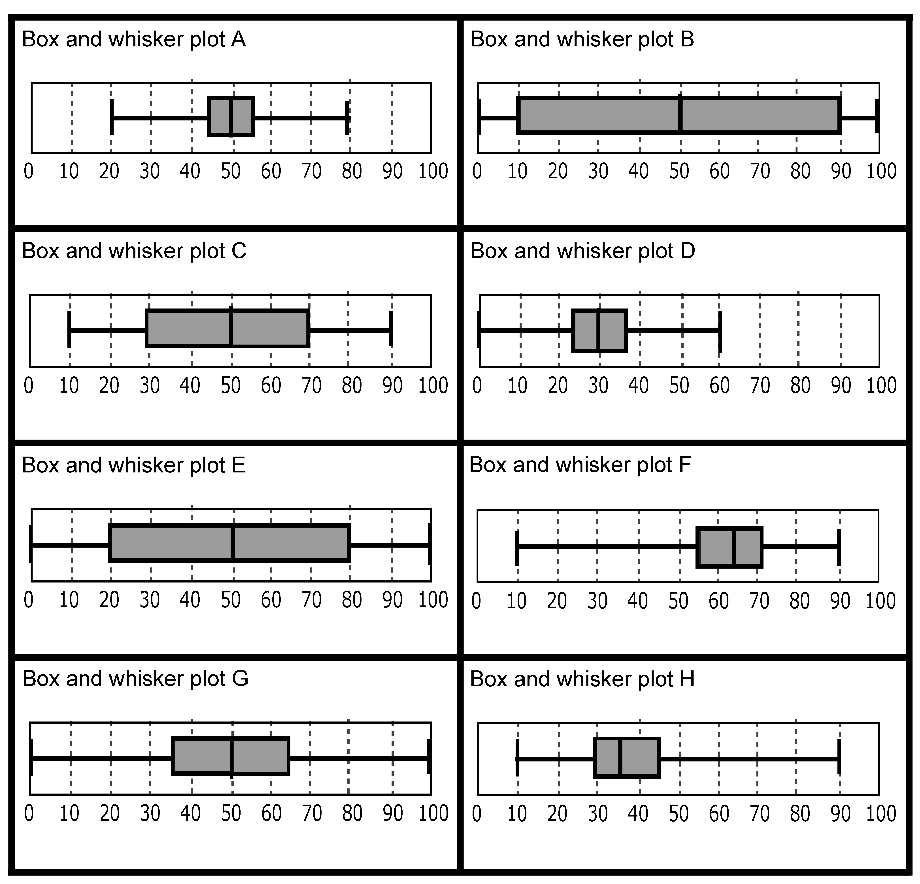
What is a Box and Whisker Plot?

A box plot or box and whisker plot consists of:
- A box which spans from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3).
- A line inside the box marking the median (Q2).
- Two lines extending from the box known as whiskers. One whisker reaches the smallest value, the other to the largest value within a specified range.
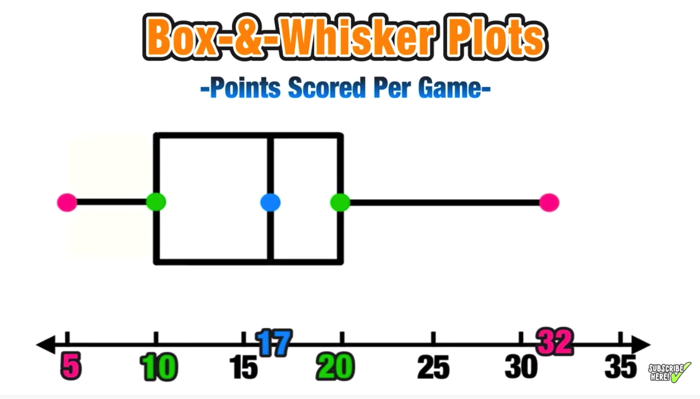
Understanding Quartiles

To understand a box plot, you need to be familiar with the concept of quartiles:
- Q1 - The 25th percentile, also known as the first quartile. 25% of the data points fall below this value.
- Q2 (Median) - The 50th percentile; half the data lies above and below this point.
- Q3 - The 75th percentile, the third quartile. 75% of the data points fall below this value.
The Importance of Interactive Worksheets

Interactive worksheets on box plots serve several critical functions:
- They facilitate active learning through participation and engagement.
- They allow for real-time feedback which helps in understanding concepts better.
- They provide an environment where mistakes are learning opportunities, not setbacks.
Types of Interactive Worksheets

Here are some types of interactive worksheets designed to master box plots:
- Data Input Worksheets: These allow students to input data and see the box plot change dynamically.
- Interpretation Exercises: Worksheets where students must analyze provided box plots to answer questions about quartiles, range, and outliers.
- Construction Worksheets: Students can build their own box plots from given data sets.
- Comparison Sheets: These encourage comparison between different sets of data represented by multiple box plots.
How to Create an Interactive Worksheet
Creating an effective interactive worksheet involves the following steps:
- Define Learning Objectives: Determine what statistical concepts you want to teach.
- Select Software or Platform: Tools like Excel, Python, or online platforms can be used.
- Prepare Data Sets: Ensure the data is relevant and at the right difficulty level for your students.
- Design Interaction: Decide how students will interact with the worksheet, whether by clicking, dragging, or typing data.
- Integration of Visuals: Include charts and plots that update based on student input.
- Feedback Mechanism: Incorporate real-time feedback to guide learning.
- Testing and Iteration: Test the worksheet to ensure it works as intended and refine based on feedback.
🚨 Note: Interactive worksheets should be user-friendly, visually appealing, and accessible on various devices.
Teaching Strategies Using Interactive Worksheets
Here are effective strategies for teaching with interactive box plot worksheets:
- Guided Discovery: Start with basic concepts, let students explore, and then guide them through more complex interpretations.
- Collaborative Learning: Encourage group work where students explain their plots to peers.
- Scaffolded Learning: Begin with simpler exercises, gradually increasing the complexity.
- Real-World Application: Show real data sets from relevant fields to keep interest piqued.
Mastering Box Plots Through Practice

Practice is key when mastering box and whisker plots:
- Repetition: Regularly revisit concepts through worksheets to reinforce learning.
- Variety: Use different types of data sets to show the versatility of box plots.
- Critical Thinking: Encourage students to analyze and critique the plots they create or see.
🚨 Note: Consistent practice helps in internalizing the mechanics of box plots, making their interpretation second nature.
Interactive worksheets for box plots transform a potentially dry statistical tool into an engaging learning experience. By allowing students to interact, manipulate, and interpret data in real-time, these worksheets deepen their understanding of statistical distributions, variability, and central tendencies. The dynamic feedback loop provided by these tools encourages active learning, making the process of mastering box plots not just about understanding but about applying knowledge effectively.
What is the significance of outliers in box plots?

+
Outliers in box plots indicate data points that fall outside the typical range (IQR). They can reveal unusual data, errors in data collection, or genuine variability in the dataset. Understanding outliers helps in making informed decisions about data cleaning or further investigation.
How do you handle large data sets in box plots?
+
For large data sets, software can automatically generate box plots, but it’s important to understand the underlying principles. Summarize data using quartiles and ensure the scale accommodates the range of your data without becoming too compressed.
Can box plots be used for categorical data?

+
Box plots are primarily used for numerical data to show distribution. For categorical data, you would first convert it into numerical data if possible, or consider alternative visual tools like bar charts or pie charts.