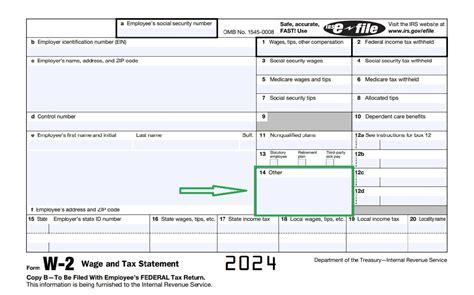
12 W2 Box Codes

Understanding the 12 W2 Box Codes
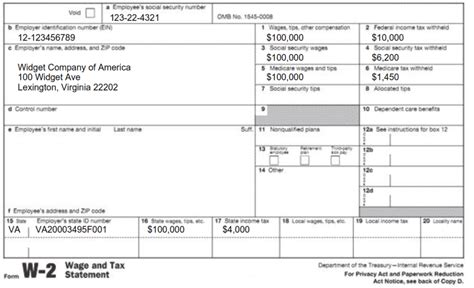
The W2 form is a crucial document for employees and employers alike, as it reports an employee’s annual wages and taxes withheld. The form is divided into several boxes, each containing specific information. This article will delve into the 12 W2 box codes, explaining what each box represents and why it’s essential for tax purposes.
Box 1: Wages, Tips, Other Compensation
Box 1 reports the total amount of wages, tips, and other compensation paid to the employee during the tax year. This figure includes salaries, wages, tips, and other forms of compensation, but excludes non-taxable benefits like health insurance premiums. It’s crucial to verify the accuracy of this box, as it directly affects the employee’s taxable income.
Box 2: Federal Income Tax Withheld
Box 2 displays the total amount of federal income tax withheld from the employee’s wages during the tax year. This amount is calculated based on the employee’s W4 form, which determines their tax filing status, number of allowances, and other factors. Federal income tax withheld is a critical component of an employee’s tax return, as it reduces their tax liability.
Box 3: Social Security Wages

Box 3 reports the total amount of wages subject to Social Security tax. This figure is typically lower than the amount in Box 1, as some forms of compensation are exempt from Social Security tax. Social Security wages are vital for determining an employee’s Social Security benefits, as well as their Medicare eligibility.
Box 4: Social Security Tax Withheld

Box 4 displays the total amount of Social Security tax withheld from the employee’s wages during the tax year. This amount is calculated as a percentage of the employee’s Social Security wages (Box 3). Social Security tax withheld is used to fund Social Security benefits and Medicare, so it’s essential to ensure accurate reporting.
Box 5: Medicare Wages and Tips

Box 5 reports the total amount of wages and tips subject to Medicare tax. This figure is typically the same as Box 1, as most forms of compensation are subject to Medicare tax. Medicare wages and tips are used to determine an employee’s Medicare eligibility and benefits, so accurate reporting is crucial.
Box 6: Medicare Tax Withheld
Box 6 displays the total amount of Medicare tax withheld from the employee’s wages during the tax year. This amount is calculated as a percentage of the employee’s Medicare wages and tips (Box 5). Medicare tax withheld is used to fund Medicare benefits, so it’s essential to ensure accurate reporting.
Box 7: Social Security Tips

Box 7 reports the total amount of tips received by the employee that are subject to Social Security tax. This figure is typically reported by employees who receive tips, such as food servers or bartenders. Social Security tips are vital for determining an employee’s Social Security benefits, as well as their Medicare eligibility.
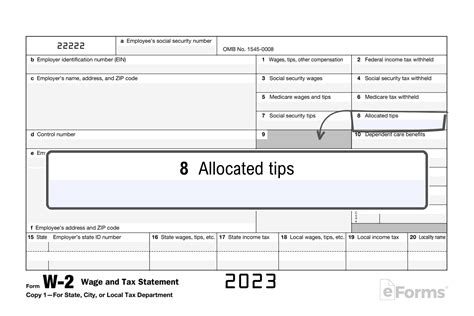
Box 8: Allocated Tips
Box 8 displays the total amount of allocated tips reported by the employer. Allocated tips are amounts reported by the employer as tips received by the employee, but not actually received by the employee. Allocated tips are used to ensure accurate reporting of tips income, but they can be subject to dispute between employers and employees.
Box 9: Advance EIC Payment
Box 9 reports the total amount of Advance Earned Income Credit (EIC) payments made to the employee during the tax year. The Advance EIC is a program that allows eligible employees to receive a portion of their EIC in their paychecks, rather than waiting until tax filing season. Advance EIC payments can help low-income employees receive essential financial support, but they must meet specific eligibility requirements.
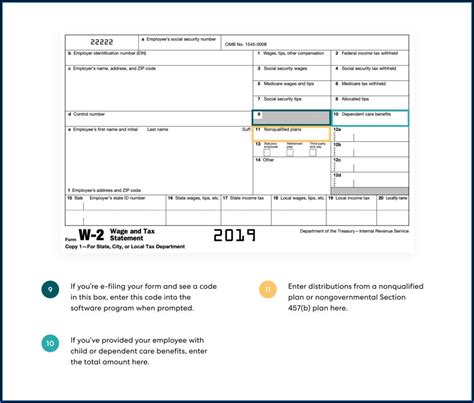
Box 10: Dependent Care Benefits
Box 10 reports the total amount of dependent care benefits provided to the employee during the tax year. Dependent care benefits include amounts paid for childcare or adult care, and may be subject to income tax. Dependent care benefits can help employees balance work and family responsibilities, but they must meet specific eligibility requirements.Box 11: Nonqualified Plans
Box 11 reports the total amount of distributions from nonqualified plans, such as deferred compensation plans or stock option plans. Nonqualified plans can provide employees with additional retirement savings opportunities, but they may be subject to income tax and other restrictions.Box 12: Codes
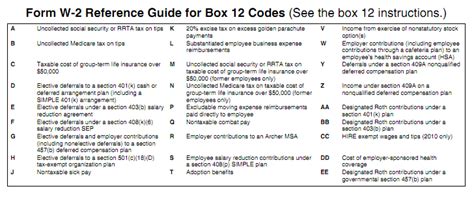
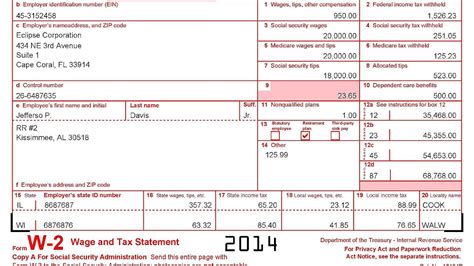
Box 12 is a catch-all box that reports various codes and amounts related to the employee’s compensation and benefits. These codes can include: * Code A: Uncollected Social Security or RRTA tax on tips * Code B: Uncollected Medicare tax on tips * Code C: Taxable cost of group-term life insurance over 50,000 * Code D: Elective deferrals to a 401(k) or other qualified plan * Code E: Elective deferrals to a 403(b) plan * Code F: Elective deferrals to a 408(k)(6) SEP plan * Code G: Elective deferrals and employer contributions to a 457(b) plan * Code H: Elective deferrals to a 501(c)(18)(D) plan * Code J: Nontaxable sick pay (information only, not included in Box 1) * Code K: 20% excise tax on excess golden parachute payments * Code L: Substantiated employee business expense reimbursements * Code M: Uncollected Social Security or RRTA tax on taxable cost of group-term life insurance over 50,000 (for former employees) * Code N: Uncollected Medicare tax on taxable cost of group-term life insurance over $50,000 (for former employees) * Code P: Excludable moving expense reimbursements paid directly to a qualified moving company (not included in Box 1) * Code R: Employer contributions to an Archer MSA * Code S: Employee salary reduction contributions under a Section 408(p) SIMPLE plan * Code T: Adoption benefits (amounts are not included in Box 1, but are reported for information only) * Code V: Business expense reimbursements for a qualified nonpersonal use vehicle (not included in Box 1) * Code W: Employer contributions to an employee’s health savings account (HSA) * Code Y: Deferrals under a Section 409A on behalf of the employee * Code Z: Income under Section 409A on behalf of the employee * Code AA: Designated Roth contributions under a Section 401(k) plan * Code BB: Designated Roth contributions under a Section 403(b) plan * Code CC: Hires exempt from OASDI and/or Medicare tax * Code DD: Cost of employer-sponsored health coverage * Code EE: Designated Roth contributions under a governmental Section 457(b) plan📝 Note: The codes listed in Box 12 can be complex and subject to change, so it's essential to consult the IRS instructions or a tax professional for guidance.
The 12 W2 box codes provide essential information for employees and employers, and are used to determine tax liability, Social Security benefits, and other vital benefits. By understanding what each box represents, individuals can better navigate the tax filing process and ensure accurate reporting of their income and benefits.
To summarize, the 12 W2 box codes are: * Box 1: Wages, tips, other compensation * Box 2: Federal income tax withheld * Box 3: Social Security wages * Box 4: Social Security tax withheld * Box 5: Medicare wages and tips * Box 6: Medicare tax withheld * Box 7: Social Security tips * Box 8: Allocated tips * Box 9: Advance EIC payment * Box 10: Dependent care benefits * Box 11: Nonqualified plans * Box 12: Codes
In conclusion, the 12 W2 box codes are a critical component of the tax filing process, providing essential information for employees and employers. By understanding what each box represents, individuals can better navigate the tax filing process and ensure accurate reporting of their income and benefits.
What is the purpose of the W2 form?

+
The W2 form is used to report an employee’s annual wages and taxes withheld to the IRS and the employee.
What is the difference between Box 1 and Box 3 on the W2 form?

+
Box 1 reports the total amount of wages, tips, and other compensation, while Box 3 reports the total amount of wages subject to Social Security tax.
What are the codes listed in Box 12 on the W2 form?

+
The codes listed in Box 12 include various amounts and codes related to the employee’s compensation and benefits, such as elective deferrals, employer contributions, and taxable benefits.



