Anatomical Directions Made Easy: Body Planes Worksheet

Understanding the human body's anatomy can be a daunting task, especially when you're first introduced to the myriad of terms and directions used to describe its structure. One fundamental aspect of anatomy is understanding the body planes, which are imaginary flat surfaces that run through the body to separate it into various sections for study and reference. This guide aims to simplify the concept of body planes and how they are used in anatomical studies, offering a handy worksheet for those looking to master this aspect of anatomy.
The Basics of Body Planes
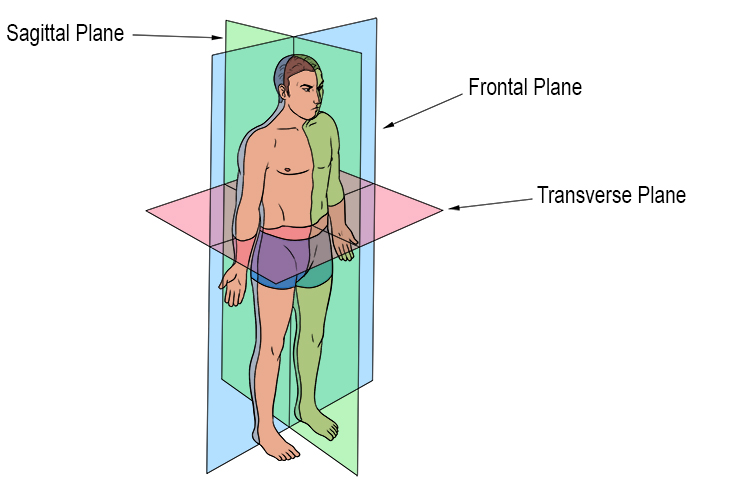
In anatomical studies, three main body planes are recognized:
- Sagittal Plane: This plane divides the body into left and right sections. If this division is exact, splitting the body into equal halves, it is called a mid-sagittal or median plane. A sagittal plane that doesn’t split the body into equal halves is called a parasagittal plane.
- Frontal (or Coronal) Plane: This plane divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions. It’s particularly useful for understanding structures like the limbs or the organs in the torso in a way that shows their depth.
- Transverse (or Horizontal) Plane: Also known as the axial plane, this divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) segments. It’s commonly used for imaging scans to get horizontal cross-sections of the body.
Why Body Planes are Important

Body planes serve several critical purposes in anatomy:
- Communication: They provide a universal language for describing body parts and their relationships to one another.
- Analysis: They allow for systematic study and observation of structures, diseases, and physiological processes.
- Imaging: MRI, CT scans, and other medical imaging technologies often produce images aligned with these planes, making it easier for medical professionals to interpret results.
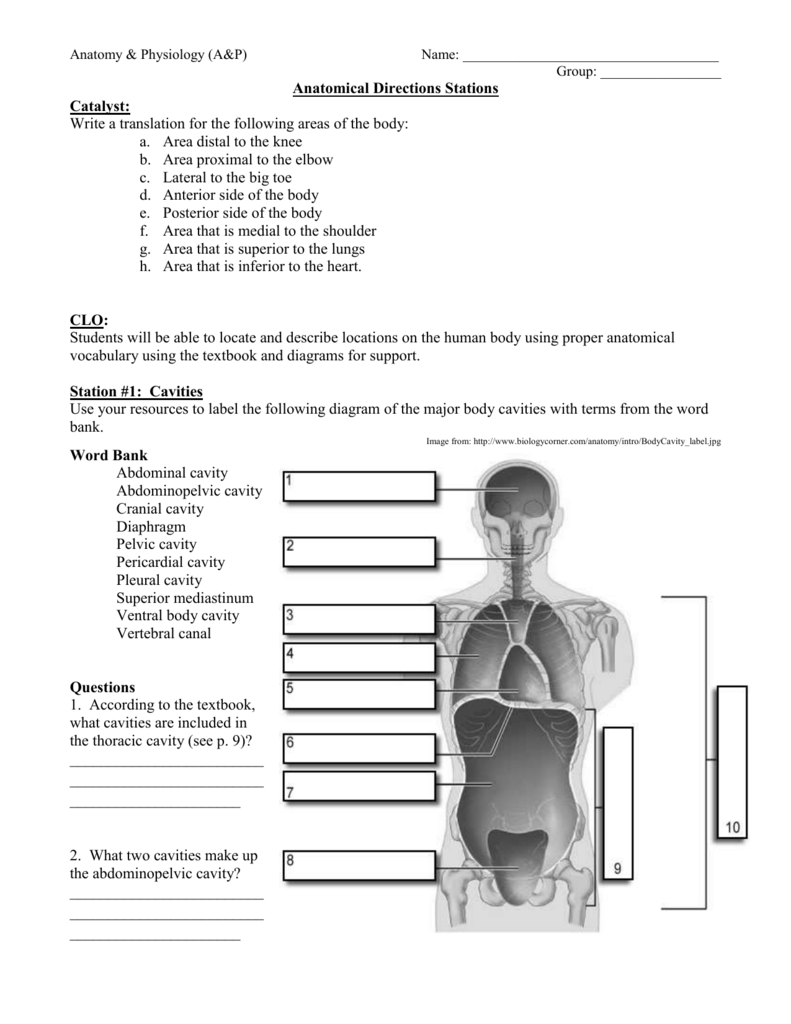
Anatomy Body Planes Worksheet

To help you better understand and visualize these planes, here’s a simple worksheet:
| Body Plane | Illustration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sagittal Plane |  |
Divides the body into left and right sections. |
| Frontal Plane |  |
Divides the body into front and back portions. |
| Transverse Plane |  |
Divides the body into upper and lower parts. |

✍️ Note: These planes are essential for understanding how organs and structures relate to each other in 3D space. Remember, while planes are fixed lines of reference, the human body can move through various positions which might alter the way structures appear in relation to these planes.
Exploring Each Plane in Depth

- Sagittal Plane: Imagine cutting an apple vertically through the middle. This would represent a sagittal cut. Key structures often seen in a sagittal view include:
- The spine
- The brain
- The digestive tract
- Frontal Plane: Think of slicing a loaf of bread through the side. This gives you a front-back perspective, which can show:
- The chest cavity
- The ribcage
- Muscles of the limbs
- Transverse Plane: Picture cutting a horizontal slice from the middle of a log. This view can reveal:
- The organs at different levels, like the liver and the stomach
- The spinal cord cross-section
- The internal structure of bones
Each plane has its unique value in the study of anatomy, allowing students and professionals to dissect, observe, and understand complex human structures in more manageable segments.
Applications in Medical Practice

The use of body planes extends beyond learning into practical applications:
- Surgery: Surgeons use these planes as guides to understand the best approach for operations, reducing unnecessary tissue damage and improving surgical outcomes.
- Radiology: Radiologists orient scans along these planes to make observations and diagnose conditions accurately.
- Rehabilitation: Understanding planes helps in designing physical therapy protocols that respect the body’s natural alignment and movement patterns.
By mastering these anatomical directions, medical professionals can communicate effectively, plan treatments, and understand the body's complex architecture. Here's a summary of how body planes facilitate this:
- They provide a structured approach to analyzing the body, simplifying the vast complexity of human anatomy.
- They help in visualizing how different body structures relate in space, especially when movement or pathological changes occur.
In conclusion, the study of body planes is not just a theoretical exercise but an indispensable tool for anyone interested in human anatomy, medicine, or health-related fields. This worksheet, along with the explanations provided, should serve as a valuable resource for understanding and applying these concepts in both education and practice.
Why are sagittal, coronal, and transverse planes used in anatomy?

+
These planes help divide the body into comprehensible segments, making it easier to study, communicate about, and understand the relationships between body structures.
What’s the difference between a mid-sagittal and a parasagittal plane?

+
A mid-sagittal plane divides the body into equal left and right halves, while a parasagittal plane creates unequal sections.
How do body planes influence medical imaging?
+
Medical imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans are often aligned with these planes to produce cross-sectional views that help in diagnosis and treatment planning.


