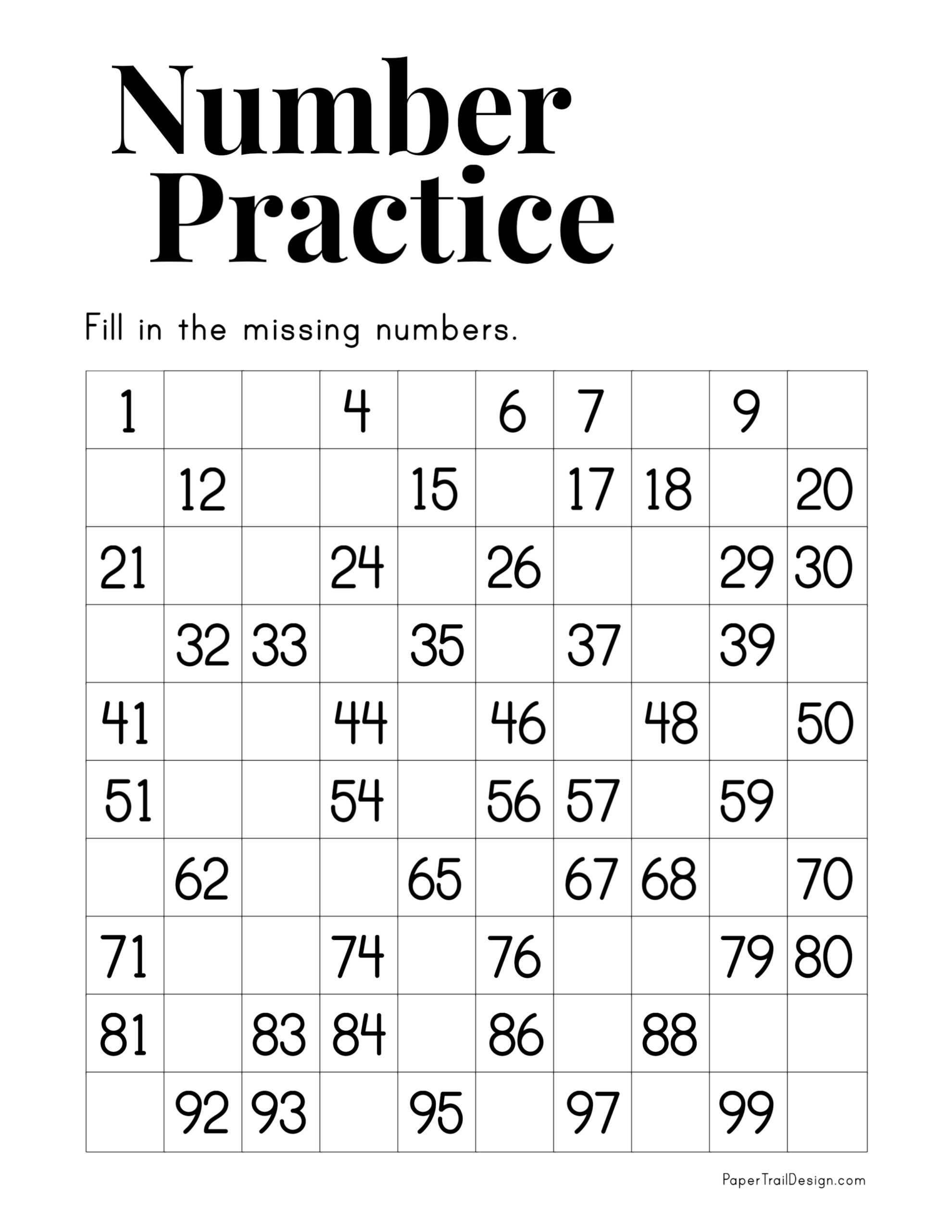
5 Must-Know Answers from Bill Nye's Sound Worksheet

Introduction to Sound

Did you ever wonder what makes sounds so diverse and complex? It's all thanks to the fascinating world of physics, particularly how sound waves travel and interact with our environment. In this blog post, we'll explore the essential insights from Bill Nye the Science Guy, a beloved figure in the world of science education, specifically focusing on his worksheet on sound. This guide will not only deepen your understanding of the physics behind sound but also enrich your appreciation of how sound science applies in everyday life.
What is Sound?

Sound is not just a result of noises around us; it's a physical phenomenon involving the propagation of vibrations through a medium like air, water, or even solids. Here’s a detailed look at what sound really is:
- Vibrations: Sound begins when something vibrates, causing the surrounding air particles to move back and forth.
- Wave Motion: These vibrations create waves of pressure, known as sound waves, which travel through the medium.
- Travel Through Mediums: Sound can travel through different mediums, but its speed varies - fastest through solids, then liquids, and slowest through gases.
How Does Sound Travel?

Sound travels as a wave of pressure, but understanding the specifics can enhance our appreciation of this phenomenon:
- Wave Compression and Rarefaction: Sound waves consist of areas where particles are closer together (compression) and further apart (rarefaction).
- Speed of Sound: The speed at which sound travels depends on the properties of the medium it's moving through; for instance, at sea level, sound travels at approximately 343 meters per second in air.
- Frequency and Pitch: The frequency of these waves determines the pitch of the sound, with higher frequencies yielding higher pitches.
Bill Nye's Sound Worksheet

Bill Nye’s approach to teaching sound combines educational content with an entertaining twist. Here’s how his worksheet educates students about sound:
1. Identify Sources of Sound

The worksheet prompts students to recognize everyday sources of sound, from natural phenomena like thunder to the human voice, emphasizing the wide range of vibrations that generate sound:
| Source of Sound | Description |
|---|---|
| Thunder | Rapid expansion and contraction of air surrounding a lightning bolt |
| Human Voice | Vibrations in the vocal cords |
| Musical Instruments | Various types of vibrations created through different mechanisms |

2. Explore Pitch and Frequency

Students delve into the relationship between pitch, frequency, and how our perception of these elements changes sound:
🎼 Note: Pitch is not the same as loudness; it's about how high or low the tone of sound is.
3. Understand Amplitude and Volume

Here, the concept of amplitude or the intensity of the sound wave is explained, directly correlating with the volume of the sound:
- Greater Amplitude: Leads to louder sound
- Lesser Amplitude: Results in quieter sound
4. The Doppler Effect

A key concept covered is the Doppler Effect, which explains why the sound of a passing ambulance changes in pitch:
- As the ambulance approaches, the frequency increases, resulting in a higher pitch.
- As it moves away, the frequency decreases, lowering the pitch.
5. Sound in Different Environments

Bill Nye's worksheet also touches on how sound behaves differently in various environments:
- Reflection: Sound waves bouncing off surfaces.
- Diffraction: Bending of sound waves around obstacles.
- Refraction: Change in direction due to a change in the medium.
Wrapping Up

In summary, understanding sound through Bill Nye’s engaging methods not only makes learning physics fun but also deeply educational. By exploring the origins of sound, its properties, and behaviors, we've gained a comprehensive view of this acoustic science. From identifying everyday sound sources to understanding complex phenomena like the Doppler Effect, these insights are both fascinating and practically applicable in fields ranging from music to engineering.
What is the difference between pitch and volume?

+
Pitch relates to the frequency of sound waves, determining whether a sound is high or low. Volume, on the other hand, is related to the amplitude of the wave, affecting how loud or quiet the sound is.
Why does sound travel faster in solids than in gases?

+
In solids, particles are closely packed, allowing sound waves to travel quickly as they can compress and expand the medium more efficiently. Gases have particles that are much farther apart, reducing the speed at which sound can travel.
Can sound travel through space?

+
No, sound cannot travel through the vacuum of space because there are no molecules to vibrate and carry the sound waves. However, sound can travel in some environments like inside spacecraft where there’s atmosphere.