Basic Chemistry Concepts Worksheet for Beginners

Learning basic chemistry concepts is like unlocking a key to understanding the world at its most fundamental level. Whether you're a student beginning your journey in the fascinating world of science or someone looking to refresh their memory, this guide will walk you through the essentials of chemistry, ensuring you grasp the foundational principles that are critical for deeper learning.
The Basics of Chemistry

Chemistry can be daunting at first glance, with its myriad of terms, theories, and processes. However, understanding the following basic concepts is crucial:
- Atoms and Molecules: The building blocks of all matter. Atoms are the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical identity, and molecules are groups of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound.
- Elements and Compounds: Elements are pure substances made up of one type of atom, while compounds are substances where two or more different elements are chemically bonded.
- Physical and Chemical Properties: Physical properties can be observed without changing the identity of the substance (like color, density, etc.), while chemical properties relate to how substances react chemically to form new substances.
Understanding Chemical Bonds

Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in molecules or compounds. Here's a quick look at the main types:
- Ionic Bonds: Formed when one atom transfers electrons to another, creating ions with opposite charges that attract each other.
- Covalent Bonds: Occur when atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer electron shell, forming stable molecules.
- Metallic Bonds: Unique to metals, where free electrons move within a lattice of positively charged metal ions.

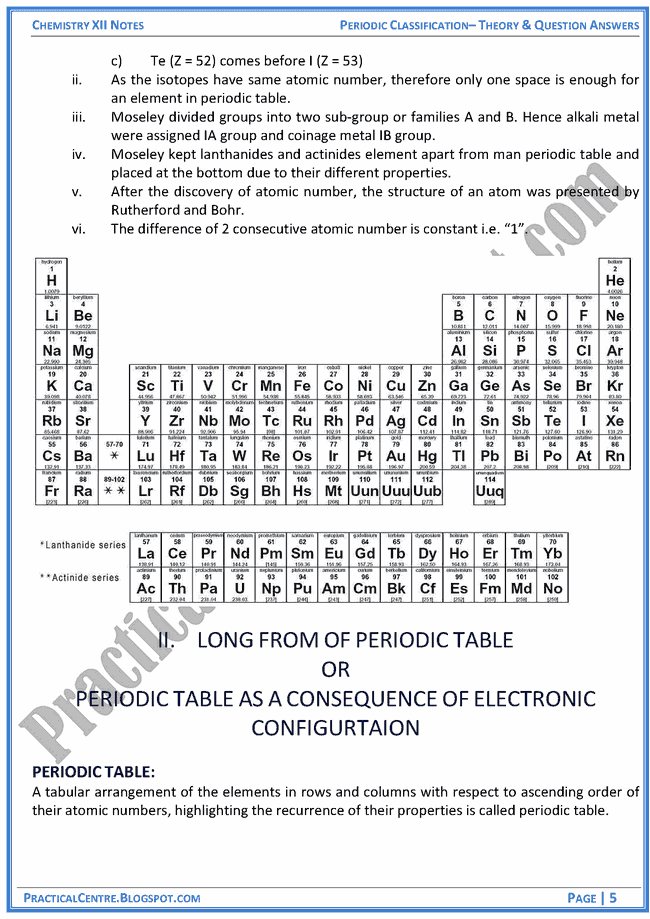
The Periodic Table
The periodic table is an organized chart of all the elements in a way that reflects their atomic structure and chemical properties:
- Groups (Columns): Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell, leading to similar chemical behavior.
- Periods (Rows): Each row corresponds to the number of electron shells in an atom of the element.
Here's a basic representation of the periodic table:
| Group | Element | Atomic Number | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen | 1 | H |
| 2 | Helium | 2 | He |
| 1 | Lithium | 3 | Li |
| 18 | Neon | 10 | Ne |

States of Matter

Matter exists in different states, each with unique properties:
- Solid: Fixed shape and volume. Particles are closely packed in a regular arrangement.
- Liquid: Fixed volume but no definite shape. Particles move around but are still close to each other.
- Gas: No fixed shape or volume. Particles are far apart and move freely.

Chemical Reactions

Chemical reactions involve the breaking or forming of chemical bonds, leading to new substances:
- Reactants: The starting materials which are transformed into products.
- Products: The new substances formed as a result of the reaction.
- Law of Conservation of Mass: States that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, only rearranged.
Common Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is crucial for understanding the stoichiometry of reactions:
- Example:
H2 + O2 → H2O
This equation shows the combination of hydrogen and oxygen to form water, but it's not balanced. Here's the balanced version:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
🔍 Note: Understanding how to balance chemical equations requires knowing the atomic mass and molar ratios of elements.
Remembering these foundational concepts will significantly ease the learning process as you delve into more complex chemistry topics. They serve as the basic building blocks for understanding more intricate chemical theories, processes, and reactions. By mastering these basics, you'll be equipped to explore the vast and fascinating world of chemistry with confidence and curiosity.
What is the difference between an element and a compound?

+
An element is made up of only one type of atom, whereas a compound consists of two or more different elements bonded together in fixed ratios.
Why do atoms form chemical bonds?

+
Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve stability, usually by filling or emptying their outermost electron shells. This gives them a stable electron configuration, similar to the noble gases.
What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry?

+
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic structure, which allows chemists to predict chemical properties and behaviors of elements and their compounds, facilitating research and education in chemistry.
Can you give an example of a physical property?

+
A physical property could be the melting point of water, which is 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit). This is observed without changing the substance’s chemical identity.



