ATP-ADP Cycle Worksheet Answers: Unlock Energy Secrets

In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the ATP-ADP cycle, exploring how cells harness and recycle energy. By understanding this process, we unlock one of the most crucial secrets of cellular function, the energy that keeps life running. Here's everything you need to know about ATP-ADP worksheet answers, its significance, and the science behind it.
Understanding ATP and ADP

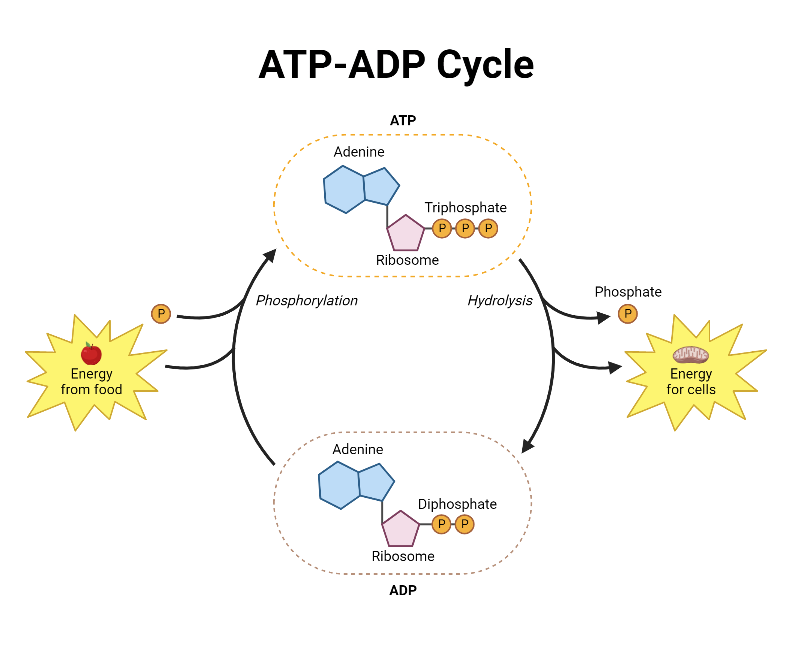
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is often dubbed the ‘energy currency’ of cells. It’s a small molecule with a massive role in living organisms. Here’s a breakdown of its components and structure:
- Adenine: A nitrogenous base, part of DNA and RNA.
- Ribose: A five-carbon sugar that serves as the backbone.
- Three Phosphates: The defining feature of ATP. When the bond between the second and third phosphate is broken, energy is released.
ADP, or adenosine diphosphate, is ATP’s less energetic cousin, consisting of the same adenine and ribose with only two phosphate groups instead of three.
Key Takeaway: The conversion between ATP and ADP is what fuels cellular processes.

The ATP-ADP Cycle

The ATP-ADP cycle represents the continuous interchange between these two molecules, pivotal for energy transfer:
- Phosphorylation: ATP is generated when ADP gains an additional phosphate group from the energy-releasing reactions, such as glycolysis or the Krebs cycle.
- Dephosphorylation: When ATP loses a phosphate, it becomes ADP, and energy is released for cellular work.
- Regeneration: ADP can be recharged back to ATP by processes like oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria.
⚠️ Note: ATP-ADP cycle maintains homeostasis by ensuring a constant supply of energy for metabolic activities.
How to Solve ATP-ADP Cycle Worksheet Problems

When working through ATP-ADP cycle worksheet answers, consider these steps:
- Identify the Process: Determine whether you’re dealing with energy storage or release.
- Understand Cellular Pathways: Recognize where ATP is produced or used in pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain.
- Track Energy Flow: Follow the movement of energy within cells, noting how ATP is both synthesized and consumed.
| Process | Change | Energy Status |
|---|---|---|
| ATP to ADP | Loses a phosphate | Energy released |
| ADP to ATP | Gains a phosphate | Energy stored |

💡 Note: ATP can be synthesized from other nucleoside triphosphates like GTP under certain conditions.
The Importance of the ATP-ADP Cycle

The ATP-ADP cycle is critical for several reasons:
- Energy Transfer: It ensures energy can be moved from where it is made to where it is needed.
- Cellular Regulation: ATP levels play a significant role in signaling pathways, influencing cell growth, division, and death.
- Homeostasis: The balance between ATP and ADP regulates metabolic processes, maintaining a stable internal environment.

Common Misconceptions about ATP
Here are a few misunderstandings often found when tackling ATP-ADP cycle worksheet answers:
- ATP is a long-term energy storage molecule: It’s not. ATP is a short-term energy carrier, unlike fats or glycogen.
- ATP is an energy source in itself: It’s better described as an energy courier.
- The ATP-ADP cycle is unidirectional: It’s a reversible process, constantly balancing energy needs and supply.
In sum, the ATP-ADP cycle is a fascinating and indispensable aspect of cellular metabolism. The interconversion of ATP to ADP and back again is an essential process that underpins all forms of life, ensuring the dynamic balance of energy supply and demand. Whether you're studying biology or just intrigued by life's energy secrets, understanding this cycle provides a foundational insight into how organisms sustain themselves and adapt to their environment.
Why is ATP considered the energy currency of the cell?

+
ATP is often referred to as the energy currency because it’s the immediate source of energy for most cellular processes. It provides a readily available form of chemical energy that can be quickly utilized when needed.
Can ATP be synthesized outside of mitochondria?

+
Yes, ATP synthesis can occur in other organelles like the chloroplasts in plants during photosynthesis and through glycolysis in the cytoplasm, which does not require mitochondria.
How does the ATP-ADP cycle impact muscle function?

+
Muscles contract using energy from ATP hydrolysis. As muscles work, ATP is converted to ADP, and the cycle of ATP regeneration is crucial for sustained muscle activity. Low ATP levels can lead to muscle fatigue.