5 Tips for Understanding Atomic Structure and Isotopes

Understanding the intricacies of atomic structure and isotopes is not only crucial for students of chemistry and physics but also for anyone interested in the workings of our universe. Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, and grasping their structure can unlock the door to understanding complex scientific concepts. Here are five key tips that can help you navigate through the atomic labyrinth:
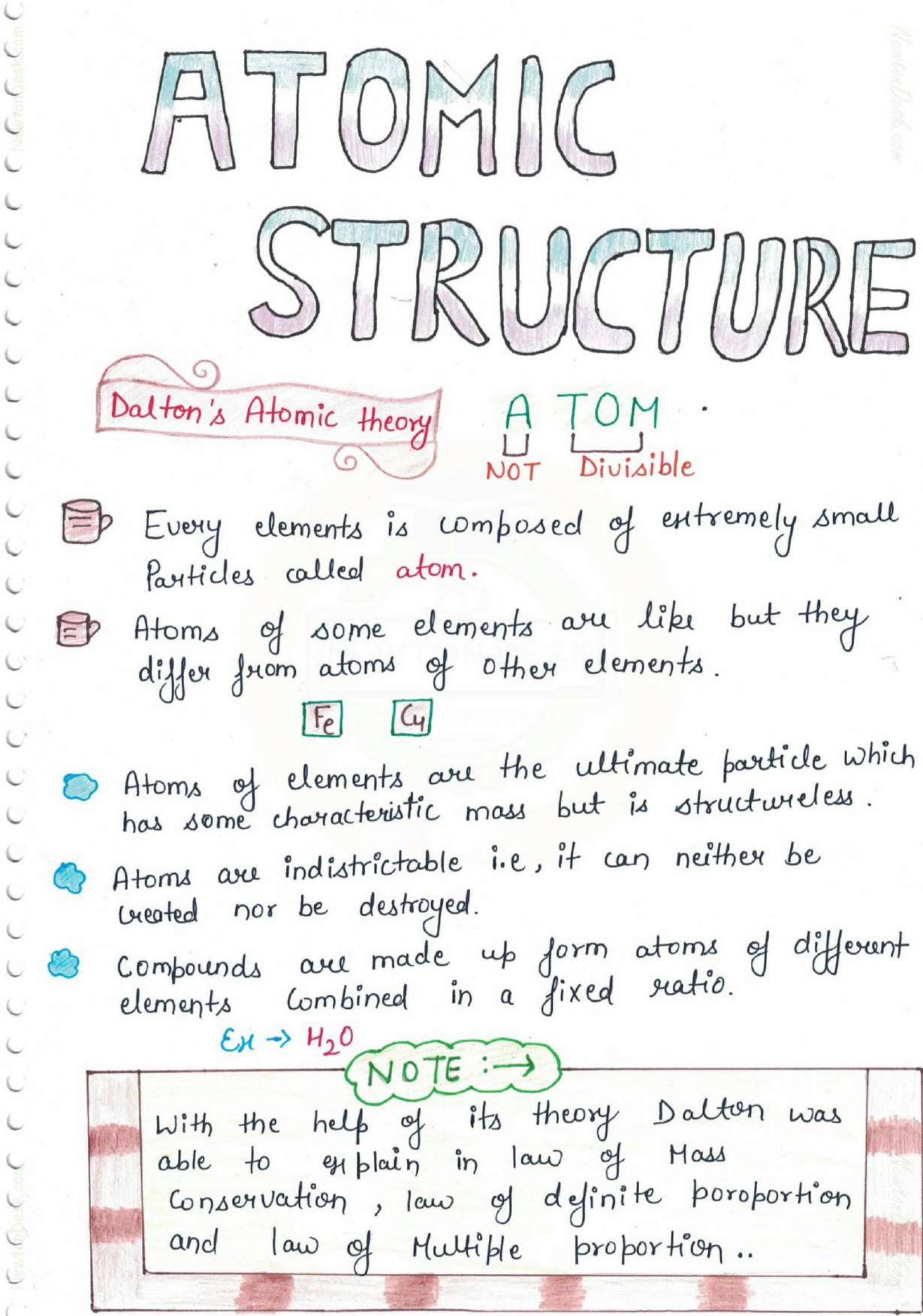
The Basics of Atomic Structure

At the heart of every atom is the nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons. Surrounding this nucleus are electrons, which orbit in various energy levels. Here’s what you need to know:
- Protons: Positively charged particles with a mass approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu). The number of protons determines the element’s atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles with a slightly larger mass than protons. The total of protons and neutrons gives the atomic mass.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles with negligible mass, contributing to the atomic size but not to the mass significantly.
These components define the characteristics and behaviors of each element in the periodic table, forming the foundation of atomic theory.
The Concept of Isotopes

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This variation results in differing atomic masses. Here’s what you should understand about isotopes:
- They have the same atomic number (same number of protons), hence the same chemical properties.
- Different isotopes can have significantly different physical properties due to the change in atomic mass.
- Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, decaying over time into different elements or isotopes.
An isotope's existence is often due to cosmic or natural processes, or in some cases, nuclear reactions. Understanding this diversity within elements can elucidate various phenomena, from carbon dating to medical isotopes in radiology.
Atomic Notation and Isotope Symbolism
Atomic notation provides a shorthand way to represent an isotope:
| Isotope Symbol | Protons | Neutrons | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 | 1 | 0 | 1 amu |
| H-2 (Deuterium) | 1 | 1 | 2 amu |
| H-3 (Tritium) | 1 | 2 | 3 amu |
Here's how you can interpret this:
- Atomic Mass: The sum of protons and neutrons.
- Mass Number: The integer close to atomic mass, used to label isotopes.
- Isotope Symbol: The element symbol followed by the mass number (e.g., C-12 for carbon-12).
💡 Note: Remember that the symbol for an element includes only the mass number, not the atomic mass, when denoting isotopes.
The Impact of Isotopes on Everyday Life

Isotopes might seem like an abstract concept, but they have real-world applications:
- Carbon Dating: C-14, an isotope of carbon, decays at a known rate, allowing us to date ancient artifacts.
- Medicine: Radioactive isotopes like Tc-99m are used in imaging techniques like PET scans.
- Industrial Applications: Neutron activation analysis uses stable isotopes to analyze the composition of various materials.
- Energy: Nuclear reactors use isotopes like U-235 for fission reactions to generate electricity.
Each of these applications showcases how a tiny variation in atomic structure can have significant technological and scientific implications.
Advanced Understanding: Electron Configurations

While understanding atomic structure typically involves protons, neutrons, and isotopes, delving into electron configurations adds another layer of complexity:
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting from 1s to the highest energy levels available.
- Hund's Rule: Electrons will occupy degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up, leading to maximum spin multiplicity.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers, leading to the unique electron configuration of each element.
This understanding helps predict the chemical behavior and reactivity of atoms, particularly when it comes to the formation of bonds.
Embarking on a journey through atomic structure and isotopes can seem daunting, but with these tips, you’re well on your way to a deeper understanding. From the microscopic world of particles to the macroscopic effects of isotopes, this knowledge will illuminate the foundations of our physical reality, connecting the dots from the quantum scale to the cosmos.
What is the difference between an atom and an isotope?
+
An atom is defined by its number of protons, which determines its identity as an element. An isotope, on the other hand, is an atom of an element with a different number of neutrons. This variation results in different atomic masses for isotopes of the same element.
Why are some isotopes radioactive?
+
Isotopes can be radioactive if their nucleus has an unstable ratio of protons to neutrons, which leads to spontaneous decay to achieve greater stability. This decay can release energy in the form of particles or radiation.
How can I remember the periodic table with all these isotopes?

+
Focusing on the elements’ atomic numbers and mass numbers is key. Remember that the periodic table primarily displays the most common isotopes in terms of abundance. For a detailed understanding, supplementary resources like a “Visual Periodic Table” can be quite helpful.