5 Essential Tips for Area and Perimeter Mastery

Whether you're a student tackling geometry problems, a hobbyist in design, or someone who enjoys brain teasers involving shapes, mastering the concepts of area and perimeter can be incredibly rewarding. These fundamental principles not only help in academic and professional pursuits but also in everyday situations like home renovation, gardening, or planning layouts for events. Here, we delve into the essentials that will help you conquer area and perimeter calculations with confidence.
1. Understand the Basics

Before diving into complex calculations, ensure you have a firm grasp of what area and perimeter really mean:
- Area: The measure of the space inside a shape, often expressed in square units like square meters (m²) or square inches (in²).
- Perimeter: The total length of the outer edge of a shape, typically measured in linear units like meters or feet.
📌 Note: While these concepts are related, understanding their differences is key to avoiding common mistakes in calculations.
2. Familiarize Yourself with Common Shapes

Knowing the basic formulas for common shapes will save you time and effort:
| Shape | Perimeter | Area |
|---|---|---|
| Square | 4s | s² |
| Rectangle | 2l + 2w | l × w |
| Circle | 2πr | πr² |
| Triangle | a + b + c | 0.5 × b × h |
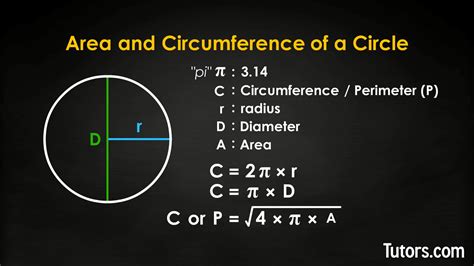
Memorizing these formulas will not only help with quick calculations but also with understanding how these quantities are derived.
3. Master the Use of Variables in Formulas

Mathematical formulas often use variables to represent unknown or variable quantities. Here’s how you can approach using variables:
- Use symbolic notation to represent side lengths, base, height, or radii.
- Understand that when variables change, the calculation of area or perimeter will also change accordingly.
📚 Note: Practice with multiple scenarios using variables to enhance your understanding of how alterations in one part of a shape can affect the others.
4. Apply Dimensional Analysis

Dimensional analysis, or the ‘unit factor method,’ is a powerful tool for ensuring that your calculations are dimensionally correct:
- Always verify that the units in your final calculation are consistent with the expected output.
- Convert units when necessary to maintain dimensional accuracy.
- For example, if you’re calculating the area of a room to determine how much carpet you need, you must ensure the units are in square meters, not just meters.
5. Solve Real-World Problems

The real test of understanding comes when you apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations:
- Calculate the perimeter of a garden to figure out how much fencing you need.
- Find the area of a floor to estimate flooring material.
- Determine the area of a poster board for a project, considering any decorative borders.
These practical applications not only reinforce the concepts but also help you to develop problem-solving skills that are useful in various aspects of life.
The journey to mastering area and perimeter is filled with both fundamental learning and practical application. By understanding the basics, memorizing key formulas, learning to use variables effectively, practicing dimensional analysis, and solving real-world problems, you'll become adept at handling these geometric properties. The skills you gain can enhance your problem-solving capabilities, making you more efficient in tasks that involve spatial reasoning and measurement. Keep practicing, explore different scenarios, and remember that every shape has its own unique set of rules and applications, making geometry both challenging and fascinating.
Why is it important to know the difference between area and perimeter?

+
Understanding the difference between area and perimeter is crucial because they measure different aspects of a shape. Area gives you the size or amount of space a shape covers, which is vital for tasks like painting, carpeting, or buying materials. Perimeter, on the other hand, is important for determining how much fencing, molding, or edging you need. Confusing the two can lead to errors in planning and material estimation.
How do you calculate the area of an irregular shape?

+
Calculating the area of an irregular shape can be approached in several ways:
- Decomposition: Divide the shape into simpler, known shapes like rectangles, triangles, or circles, calculate their areas, and sum them up.
- Grid Method: Overlay a grid on the shape, count the number of full and partial squares inside, and estimate the area based on the fraction of squares filled.
- Integration: For more complex shapes, calculus can be used to find the area under a curve or over an irregular boundary.
Can I find the perimeter without knowing all the side lengths?

+
Yes, you can estimate the perimeter of certain shapes without knowing all the side lengths by using properties specific to those shapes:
- Regular Polygons: If you know one side length, multiply it by the number of sides.
- Similarity: If a shape is similar to another where you know some of the side lengths, you can use proportion to calculate missing side lengths.
- Right Triangles: The hypotenuse can be found using Pythagorean theorem if you know two sides.



