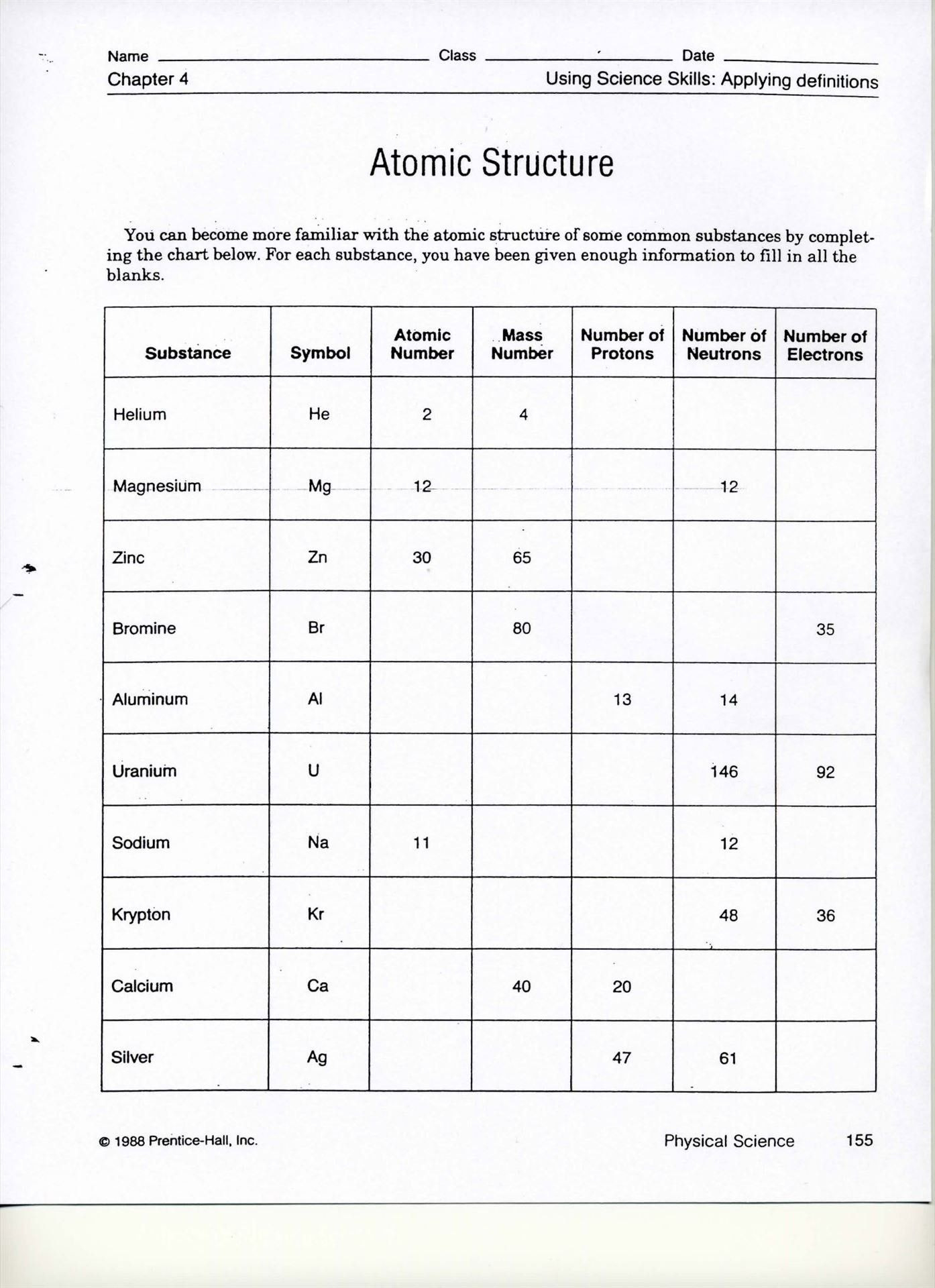
Isotopes, Ions & Atoms Worksheet Answers Explained

Isotopes, ions, and atoms form the fundamental building blocks of chemistry. Understanding their differences is crucial for students studying chemistry at any level. In this post, we will delve into these concepts, elucidate common worksheet problems, and provide comprehensive answers. This approach will aid in fostering a robust understanding of the differences between isotopes, ions, and atoms.
What are Atoms?

Atoms are the smallest units of an element that retain the chemical properties of that element. They consist of:
- Nucleus: Contains protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: Orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
Key Points:
- Protons give the atom its atomic number.
- The number of protons equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
- Neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom but do not affect its chemical behavior.
💡 Note: The term "atomic number" refers to the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which is unique for each element on the periodic table.
Understanding Isotopes

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This variation does not affect the chemical properties of the atom but changes its mass. Here’s what you need to know:
- Isotopes have the same atomic number (number of protons).
- They differ in mass number (sum of protons and neutrons).
- Isotopes are identified by their mass number. For example, Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
Example:
Consider oxygen:
| Isotope | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen-16 | 8 | 8 |
| Oxygen-18 | 8 | 10 |

🌐 Note: Isotopes can be used in fields like archaeology (radiocarbon dating) or medicine (radioactive tracers).
Ions: Charged Atoms

Ions are atoms that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electric charge:
- Cations: Positively charged ions that have lost electrons.
- Anions: Negatively charged ions that have gained electrons.
Key Points:
- The charge of an ion is the number of electrons gained or lost.
- Ions with the same charge or different charges interact through electrostatic forces.
Example Worksheet Questions:

Problem: An atom of sodium loses one electron. What is its resulting charge?
Answer: Sodium (Na) typically has 11 electrons. When it loses one, it becomes an ion with a charge of +1 (Na+).
Isotopes vs. Ions

Here’s a side-by-side comparison to clarify:
| Aspect | Isotopes | Ions |
|---|---|---|
| Protons | Same | Same |
| Neutrons | Different | Same or Different |
| Electrons | Same | Different (gained or lost) |
| Charge | Neutral | Charged |
🌟 Note: Understanding isotopes and ions is essential for grasping why chemical elements behave the way they do, especially in reactions and bonding.
Summary and Key Takeaways

Through this detailed exploration of atoms, isotopes, and ions, we’ve covered the core principles that define these entities:
- Atoms are fundamental units of matter with a defined nucleus and electron cloud.
- Isotopes are versions of the same element with differing neutron counts, affecting only mass.
- Ions are atoms with a net charge due to the gain or loss of electrons, altering their chemical behavior.
We’ve also reviewed how to identify and calculate charges for ions, along with an overview of isotopes’ properties. Here are some key takeaways:
- The atomic number defines an element, while the mass number accounts for the isotope.
- Chemical reactions involve the interaction of ions, not isotopes directly.
- The periodic table helps predict ion formation and valency.
What causes the formation of ions?

+
Ions form when atoms gain or lose electrons, often during chemical reactions. This can occur due to an element’s desire to achieve a full outer shell (noble gas configuration), through processes like ionization or electron transfer in ionic bonding.
Can isotopes turn into ions?
+
Yes, isotopes can become ions if they gain or lose electrons. The neutron count does not directly influence ion formation, but isotopes of the same element will form ions with the same charge.
Why is it important to differentiate between isotopes and ions in chemistry?

+
Isotopes and ions affect different aspects of chemistry. Isotopes are relevant in mass spectrometry and nuclear chemistry, whereas ions play a critical role in electrochemistry, acid-base theory, and biological processes.