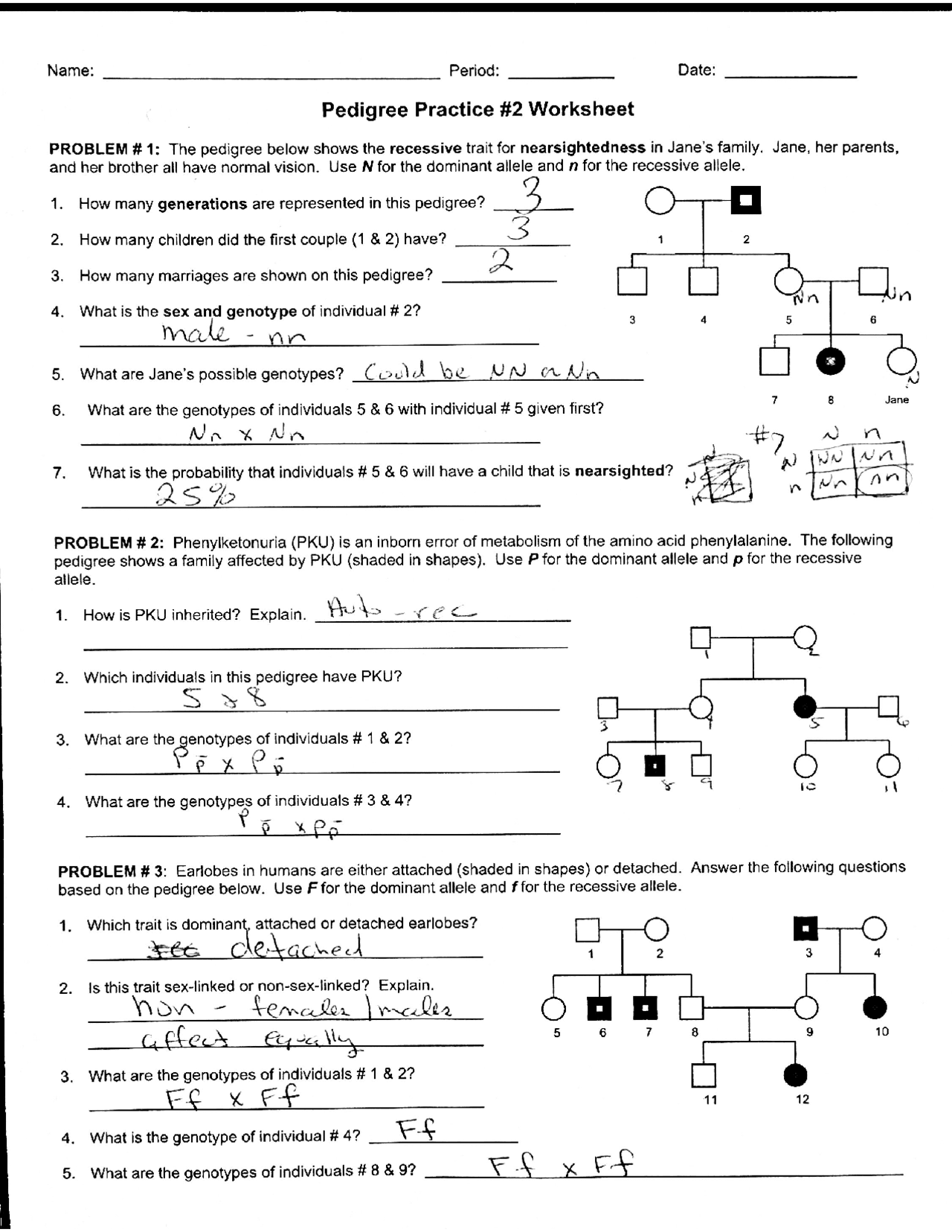
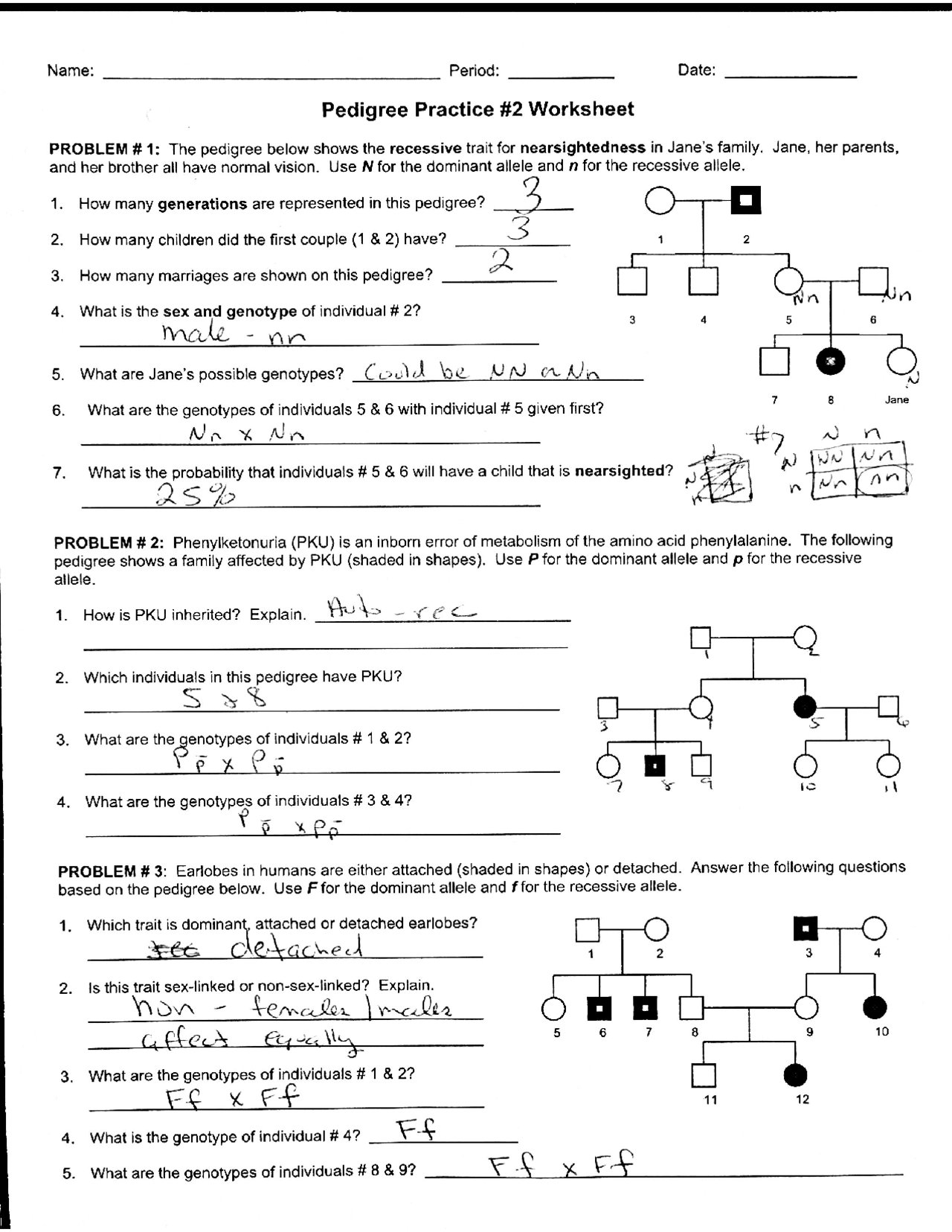
AP Biology Pedigree Worksheet: Master Genetics Now
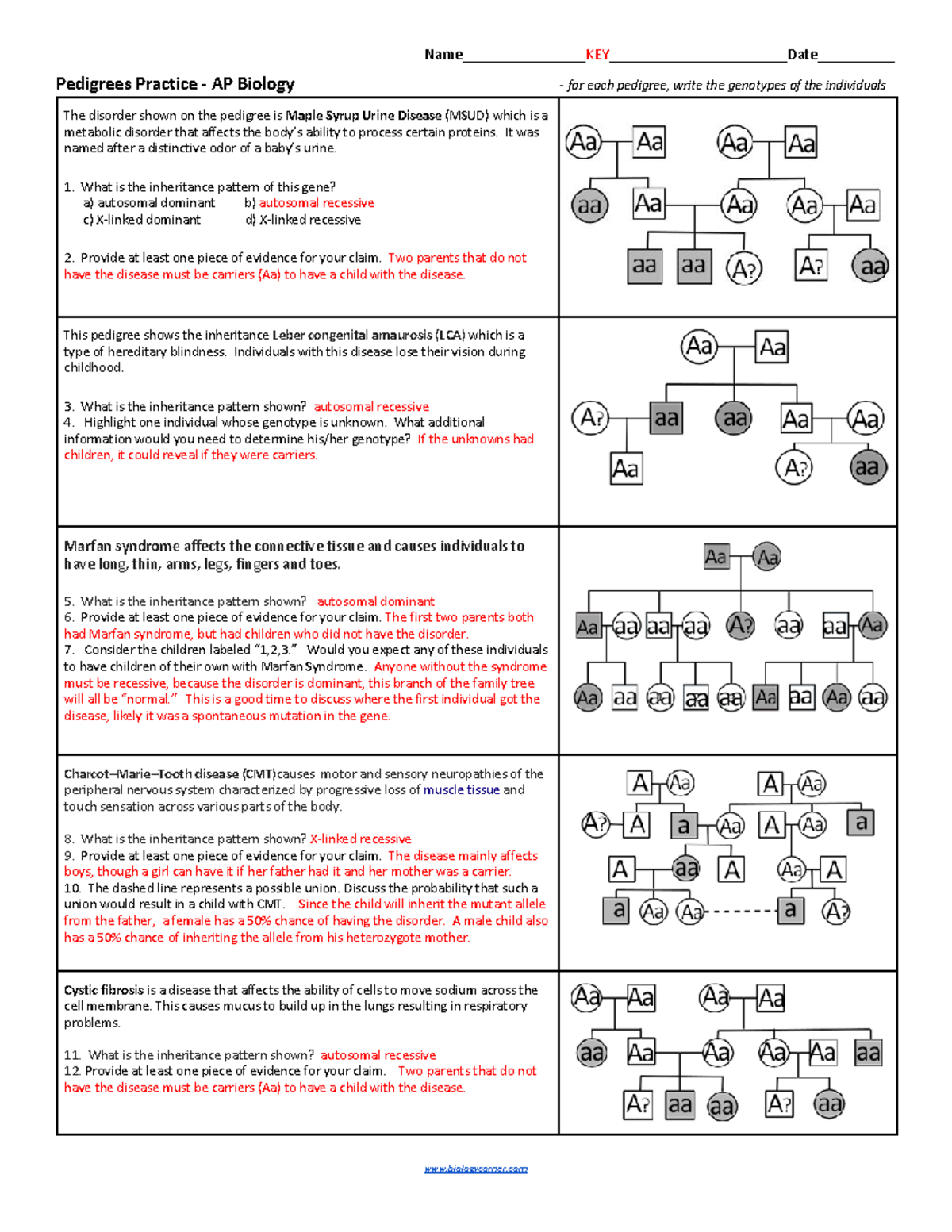
Pedigree Analysis in Advanced Placement (AP) Biology is more than just drawing family trees. It's an intricate way to uncover the patterns of inheritance for various traits, disorders, and genetic diseases. For high school students, understanding pedigree charts not only prepares them for college-level biology but also enriches their grasp of genetics. This blog post will guide you through the fundamentals, the practical application, and the importance of pedigree analysis in AP Biology, empowering you to master genetics like a pro.
What is Pedigree Analysis?
Pedigree analysis is the study of inheritance patterns within families. It involves:
- Analyzing genetic relationships and traits among family members.
- Visual representation of inheritance patterns using standardized symbols and lines.
Basics of Pedigree Symbols

| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Male Individual |
 |
Female Individual |
 |
Affected Individual |
 |
Carrier (Heterozygous) |
 |
Gender Unknown |
 |
Relationship (e.g., marriage, parent-child) |
📝 Note: Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting pedigrees correctly.
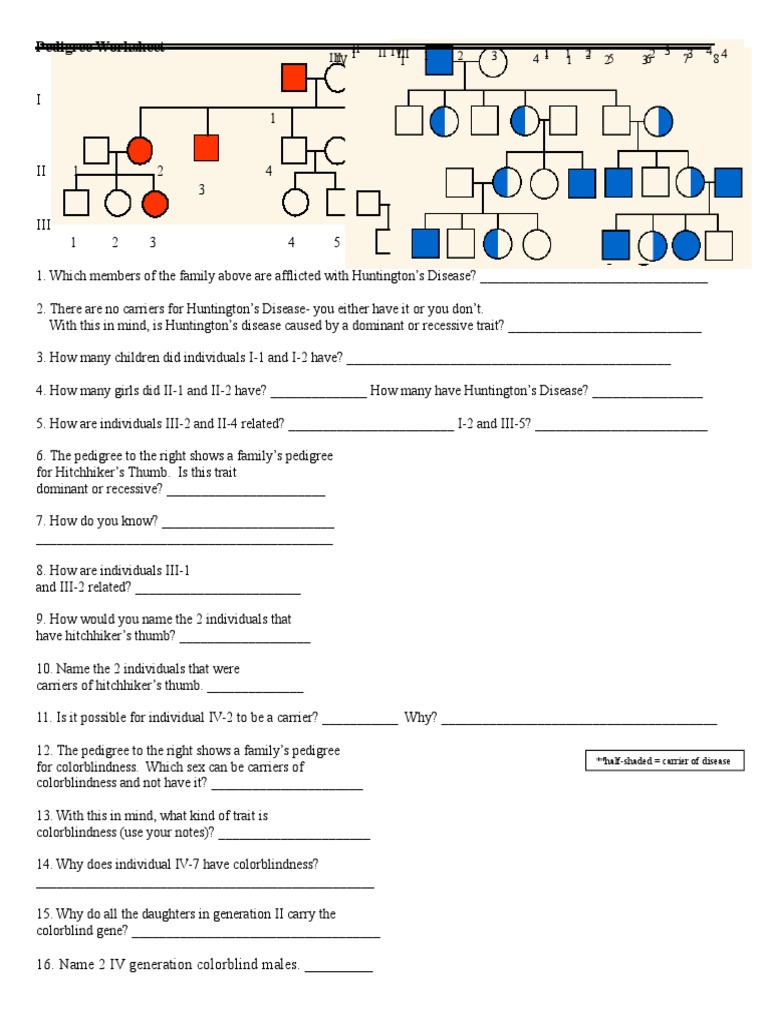
Why Pedigree Analysis Matters in AP Biology
Learning pedigree analysis in AP Biology provides several benefits:
- Understanding Inheritance: It showcases how traits pass from one generation to another, highlighting Mendelian genetics in real-world contexts.
- Genetic Disorders: Pedigrees allow students to see the spread of genetic disorders in families, from autosomal dominant to X-linked recessive traits.
- Preparation for Genetics: It's a foundation for more complex genetic analysis in college-level courses, research, or medical fields.
Practical Application in AP Biology

Pedigree analysis is not just theoretical; it has real-world applications:
- Predictive Medicine: It helps predict the likelihood of disease in future generations.
- Genetic Counseling: Provides essential information for families making reproductive choices.
- Research: Informs geneticists about the prevalence and inheritance patterns of diseases.
Interpreting Pedigree Charts

Pedigree charts are designed to be visually informative. Here's how to interpret them:
- Genotype vs. Phenotype: Distinguish between the genetic makeup (genotype) and the observed traits (phenotype) of individuals.
- Autosomal vs. X-linked: Differentiate traits inherited via autosomal chromosomes from those on the X chromosome.
- Dominant vs. Recessive: Understand how dominant traits express in every generation while recessive traits might skip.
- Probabilities: Calculate the probability of inheritance based on observed patterns.
Determining Genotypes from Phenotypes

To determine possible genotypes, follow these steps:
- Analyze each individual's phenotype.
- Consider both parents' phenotypes and the offspring's phenotypes to deduce genotype probabilities.
- Use Punnett squares or Bayesian analysis for detailed probability calculations.
📝 Note: When a dominant trait is not present in the offspring, one or both parents must be heterozygous.
Tips for Mastering Pedigree Analysis
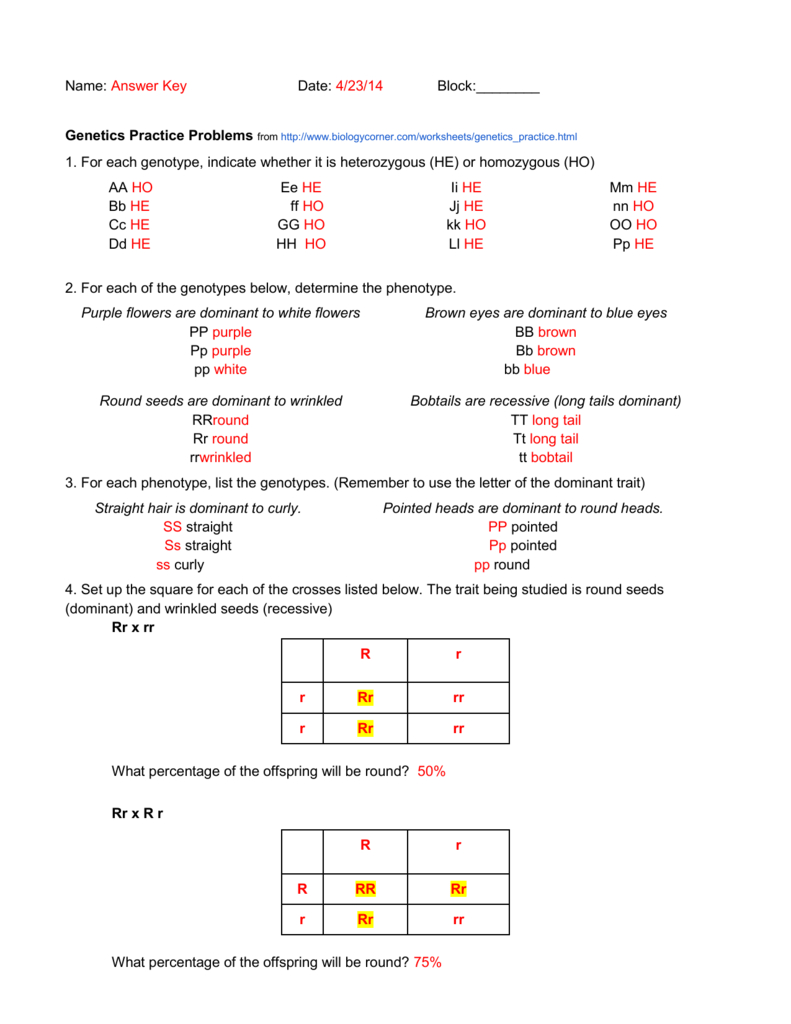
Here are some tips to become proficient in pedigree analysis:
- Practice: Work through as many pedigree problems as possible, starting with simple cases.
- Learn Patterns: Familiarize yourself with common inheritance patterns.
- Use Models: Visual aids or software can help visualize complex pedigrees.
- Know Your Terminology: Understand terms like "carrier," "affected," "unaffected," and "proband."
Real-World Application
Pedigree analysis isn't just for textbooks; it has practical uses:
- Medical Field: Doctors use pedigree analysis to understand the risk of genetic conditions in patients' families.
- Forensics: It can help in establishing familial relationships in legal or inheritance cases.
- Conservation: Breeding programs for endangered species rely on pedigree analysis to maintain genetic diversity.
Pedigree analysis is a fundamental tool in genetic education and research, offering insights into the mechanisms of inheritance, disease patterns, and the power of predictive genetic testing. As we delve into complex genetic topics, mastering pedigree analysis lays the groundwork for understanding more intricate genetic phenomena. It's a skill that not only enhances academic performance but also prepares you for a career in genetics, medicine, or related fields. By practicing, understanding patterns, and staying current with genetic research, you can become proficient in using pedigrees to unlock the secrets of heredity.
What is the difference between autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance?
+
Autosomal dominant traits are expressed if one copy of the mutated gene is present, appearing in every generation. Recessive traits require both copies of the gene to be mutated, often skipping generations when carriers are heterozygous.
Why is pedigree analysis important for genetic counseling?
+
Pedigree analysis allows genetic counselors to assess the likelihood of a person passing on a genetic condition, inform family planning decisions, and predict the risk of genetic disorders in future generations.
How does pedigree analysis help in conserving endangered species?

+
It assists in managing the genetic diversity of captive populations by avoiding inbreeding and ensuring genetic variability, which is crucial for the health and survival of the species.