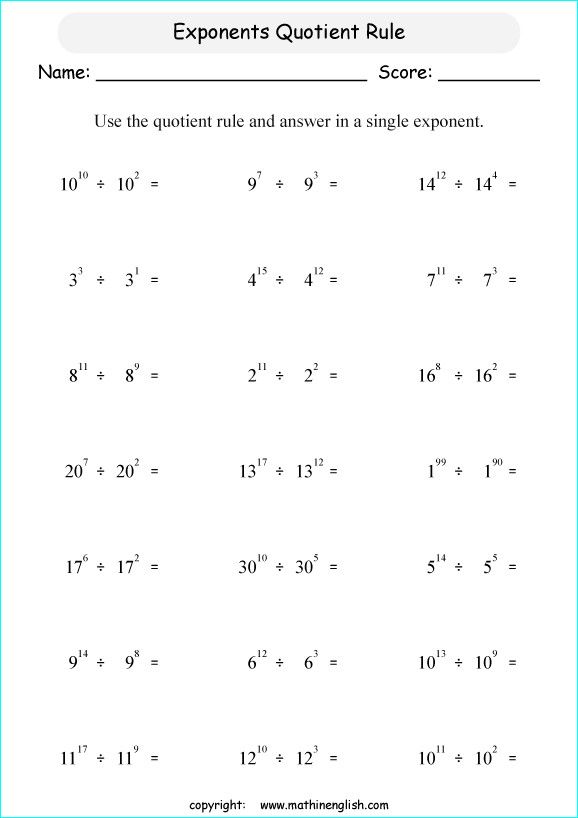
Relative Dating Worksheet: Your Answer Key Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on mastering the art of relative dating in geology. Relative dating is a fundamental concept that allows us to understand the sequence in which geologic events occurred without knowing the actual date of those events. In this guide, we'll walk through the principles and techniques used in relative dating, provide step-by-step answers to common worksheet questions, and offer insights into how these methods shape our understanding of Earth's geological history.
The Principles of Relative Dating

To grasp how geologists determine the relative ages of rock formations and fossils, we need to understand several key principles:
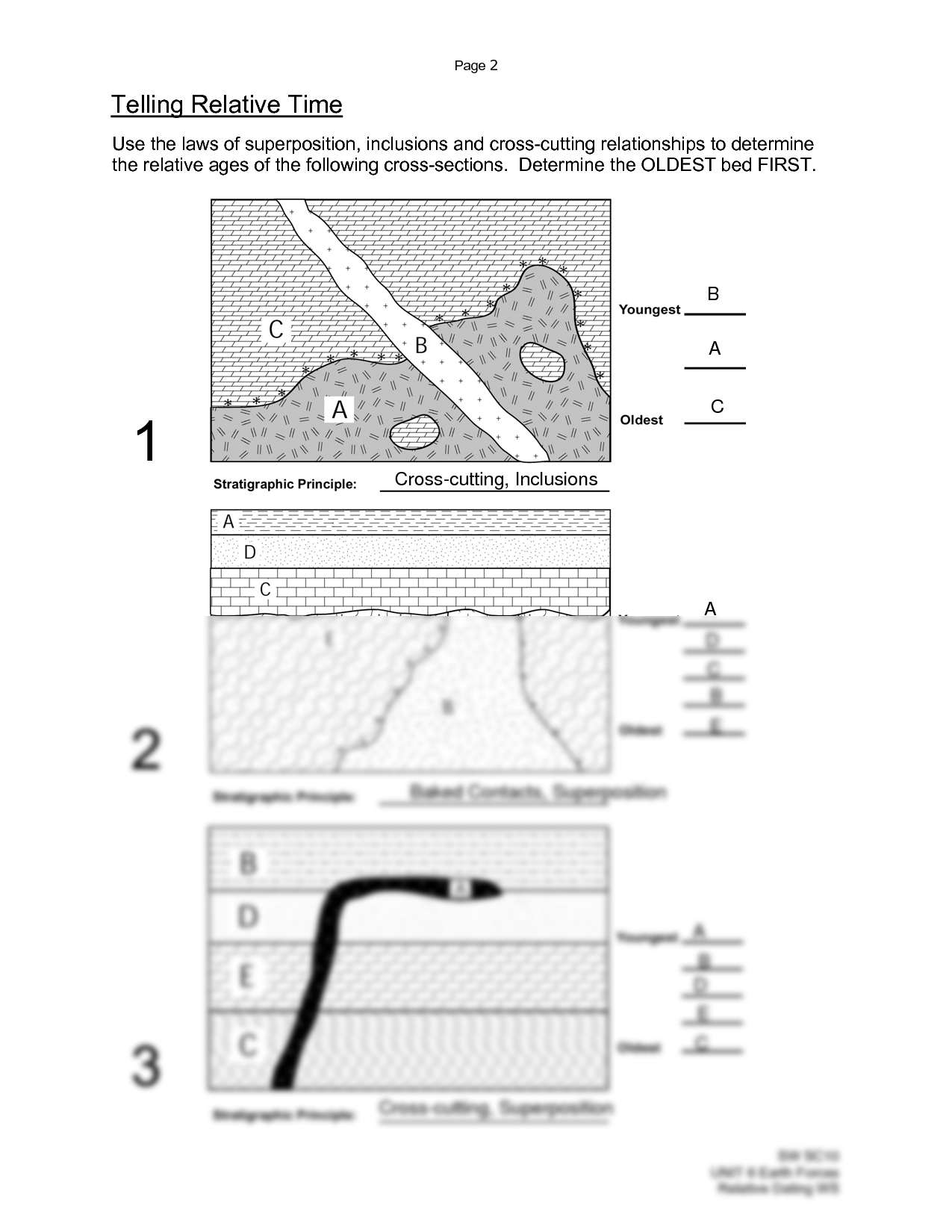
- Law of Superposition: In an undisturbed sedimentary sequence, the oldest layers are at the bottom, and the youngest are at the top.
- Principle of Original Horizontality: Layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally. Tilted or folded layers indicate that tectonic forces have acted upon them after deposition.
- Principle of Lateral Continuity: Layers of sediment initially extend in all directions and are continuous unless later broken by erosion or faulting.
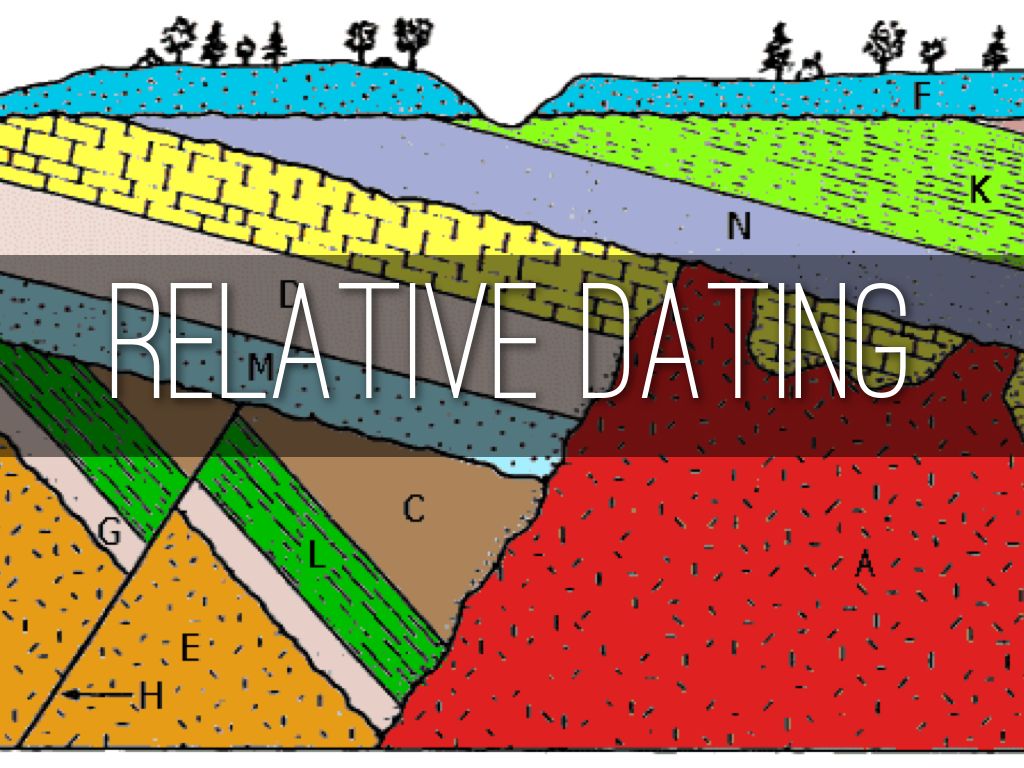
- Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships: Any rock or feature that cuts across another is younger than what it cuts through.
- Inclusions: Pieces of one rock (called inclusions) found within another rock are older than the rock containing them.
- Unconformities: Gaps in the rock record due to erosion or non-deposition, which can represent significant time periods not captured by the rocks present.
Relative Dating Worksheet Answer Key
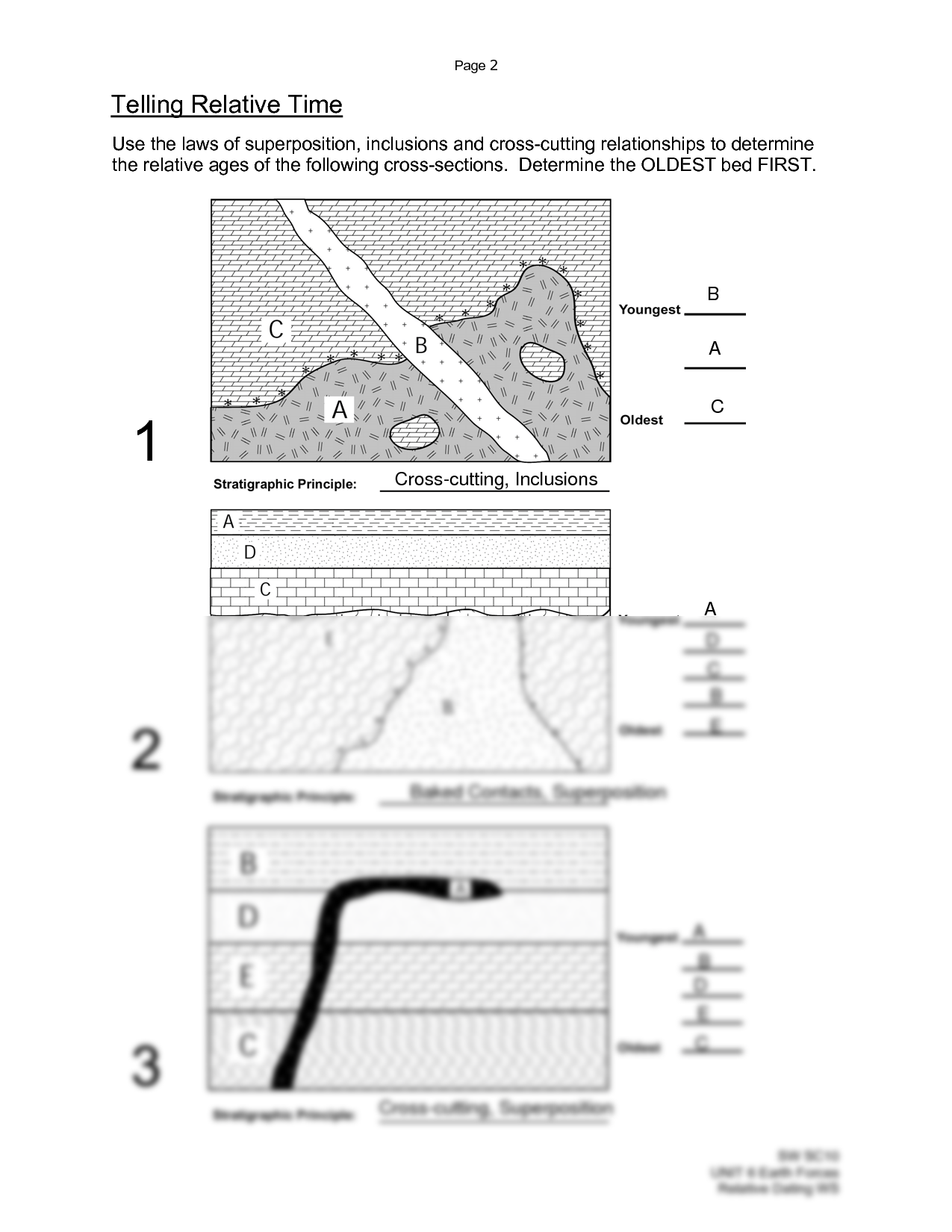
Let's dive into common questions found in relative dating worksheets, providing detailed answers:
Question 1: Use the Law of Superposition to Determine the Order of Rock Layers
In a hypothetical cross-section:
- Layer A is on the bottom.
- Layer B is above A.
- Layer C is above B.
According to the Law of Superposition, the order from youngest to oldest would be C, B, then A.
Question 2: Identify Faults and Unconformities
Analyze the following scenario:
- There's a layer of limestone (Layer 1) intruded by a dike (Dike A).
- A major unconformity separates this limestone from overlying sedimentary layers (Layers 2, 3, and 4).
- A fault crosses all layers, but it does not cross the dike.
Based on this information:
- The unconformity represents a time gap in rock deposition, where rocks from below the unconformity are older than those above it.
- The dike (Dike A) is younger than the limestone it intrudes but older than the layers above the unconformity.
- The fault cuts through all layers, indicating it's the youngest feature in the sequence.
Question 3: Determine the Relative Age of Inclusions
Given the following:
- Layer X contains inclusions of rocks from Layer Y.
- Layer X is directly above Layer Z, which does not contain these inclusions.
The answer is:
- Layer Y is older than Layer X because the inclusions are older than the rocks that contain them.
- The relative age of Layer Z cannot be determined without more information.
Practical Applications of Relative Dating
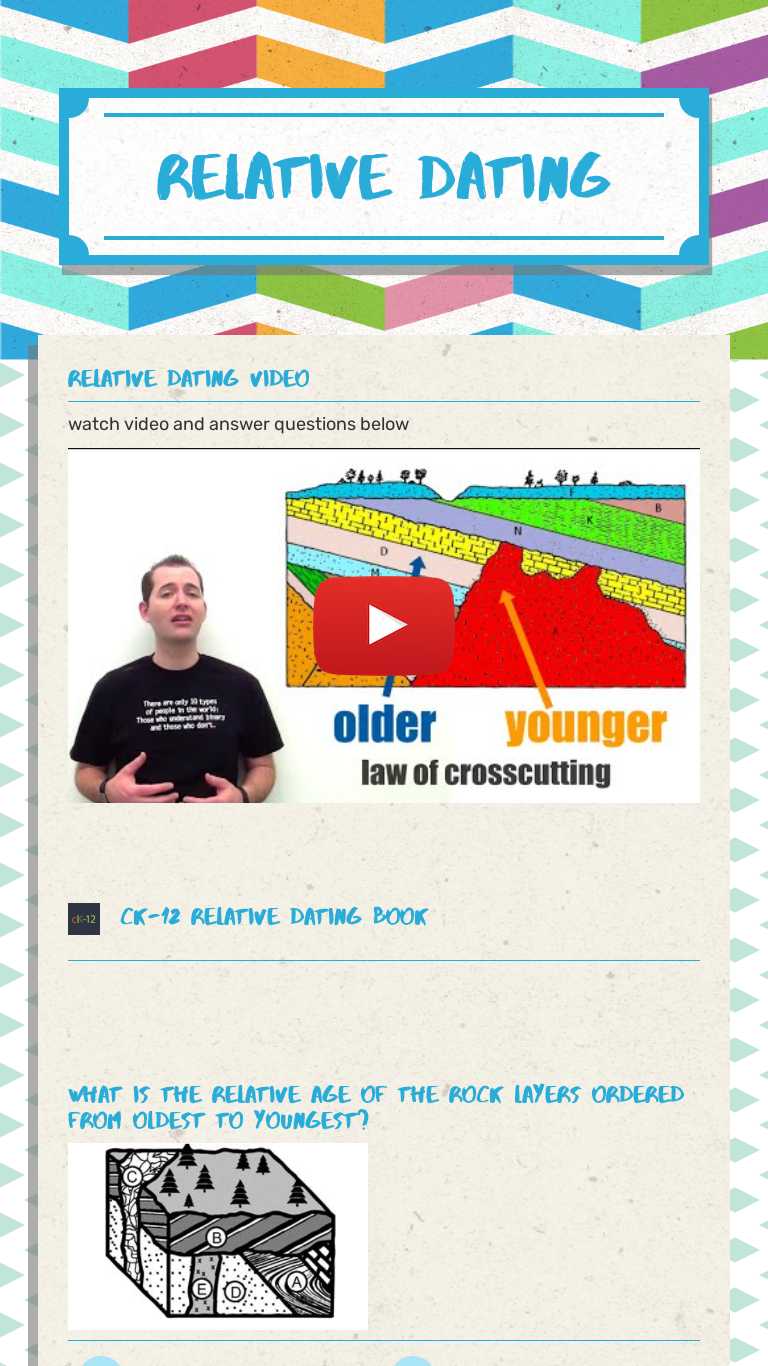
Beyond academic worksheets, understanding relative dating has practical implications in:
- Petroleum Geology: Determining the relative ages of rock layers to find and extract fossil fuels.
- Mineral Exploration: Identifying likely zones of ore deposition based on the relative ages of rock formations.
- Paleontology: Dating the fossils to understand evolutionary changes and environmental conditions through time.
By applying these principles, geologists can piece together the Earth's complex history, uncover ancient climates, and understand how life has evolved on our planet.
Why is relative dating important in geology?

+
Relative dating is crucial because it provides a framework for understanding the Earth’s geologic history in the absence of absolute dating methods. It helps in correlating rock sequences, understanding the sequence of geological events, and reconstructing ancient environments and life forms.
How do geologists handle uncertainties in relative dating?
+
Geologists use multiple principles together with other evidence like fossils, isotopic dating when possible, and tectonic events to refine and validate their relative dating conclusions. Uncertainty is managed through cross-verification with independent data sources.
Can relative dating provide accurate age estimates?

+
Relative dating does not provide an actual numerical age; instead, it establishes the sequence of events. For accurate ages, geologists turn to radiometric dating. However, relative dating sets the stage for these calculations by giving a context for the events being dated.