5 Easy Steps to Master Protractor Angle Measurement

Understanding how to accurately measure angles with a protractor is essential for students, engineers, architects, and anyone involved in design or construction. Not only does it require precision, but also an understanding of angles and their significance in various fields. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the five easy steps to master protractor angle measurement, ensuring you can confidently tackle any angular measurement task with ease.
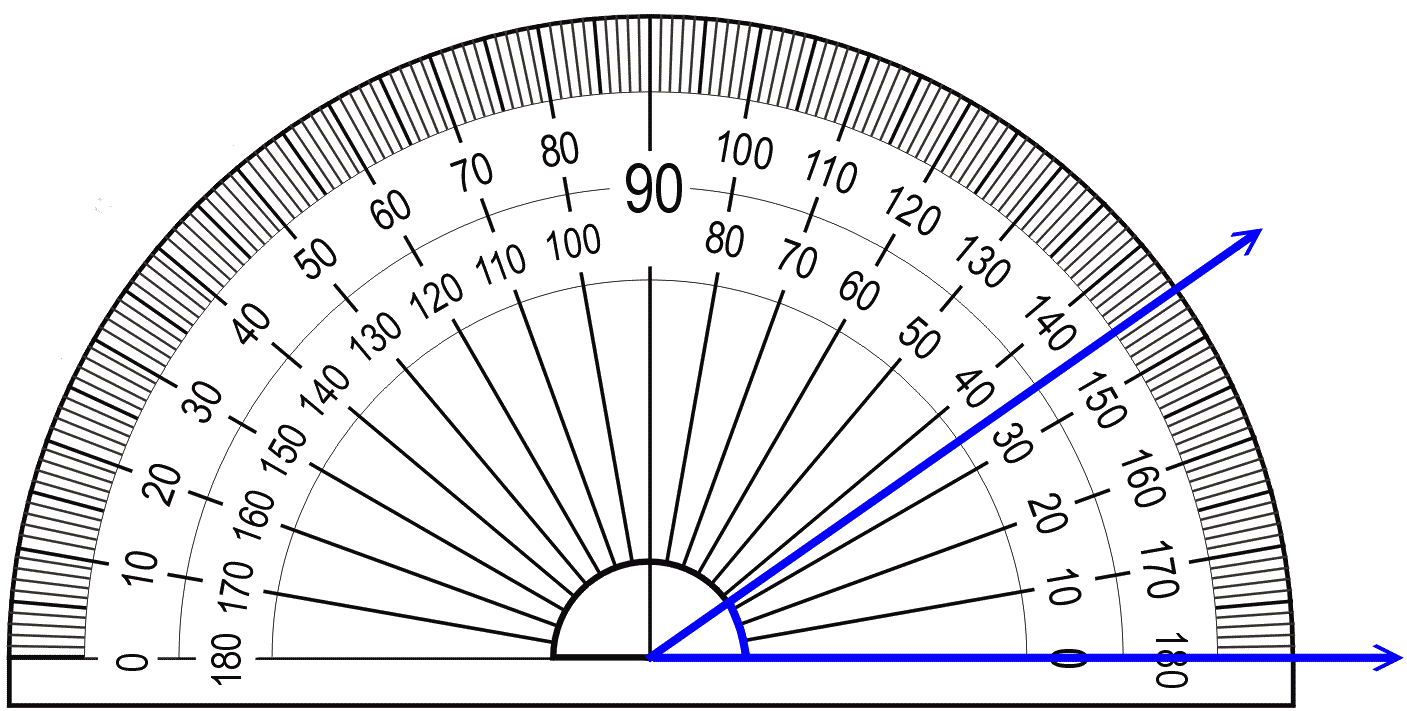
1. Understand Your Protractor

The protractor is a semicircular or circular measuring instrument with a scale divided into degrees. Here's how you can familiarize yourself with it:
- Know the Scale: The semicircular protractor starts from 0° at one end, goes up to 180° at the other. A full-circle protractor has 360°.
- Identify the Centre: Locate the small hole or dot at the center of the straight edge; this is where the vertex of your angle should align.
- Understand Dual Scales: Most protractors have two scales, one that reads clockwise from 0° at the right to 180° at the left, and another reading anticlockwise from 0° at the left to 180° at the right. Choose the one that aligns with your angle's direction.

2. Position the Protractor Correctly

Accurate measurement depends heavily on how well you position the protractor. Here are the steps to ensure you've got it right:
- Vertex Alignment: Place the protractor's center hole or dot directly over the vertex (the point where the two lines of the angle meet).
- Base Line Placement: Ensure the base line of the protractor (the straight edge) is along one of the angle's rays. If the angle isn't at a convenient location, use an adjustable set square or another straight edge to align it properly.
- Identify Reading Direction: Determine if your angle opens to the left or right to choose the correct scale on the protractor.
3. Read the Protractor Scale

Reading the protractor scale is where many people falter. Here’s how to do it without mistakes:
- Look for the Lines: Find where the second ray of the angle intersects with the protractor scale.
- Select the Scale: Use the scale that starts from the zero on the side where the angle opens. Ensure you're not reading from the opposite scale.
- Count Carefully: Count the degree markers to find the exact measurement. If it's between two markers, estimate where it falls.
4. Account for Errors and Adjust
Measurement might be off due to several common mistakes or equipment issues:
- Parallax Error: Your eye level should be in line with the protractor scale to avoid this error.
- Inaccurate Protractor: Ensure your protractor is well-made and its scale is precise.
- Rounding Errors: When the angle falls between two markers, you'll need to approximate. If accuracy is paramount, use a higher-resolution protractor or digital angle finder.
5. Practice and Refine

Like any skill, mastering angle measurement with a protractor takes practice:
- Construct Angles: Use a drawing set or software to create angles of known values and then measure them with a protractor.
- Group Measurement: Work in groups or pairs to compare measurements. This peer review can highlight any consistent mistakes.
- Real-World Application: Measure angles in your environment, like window frames or wall angles, to get practical experience.
💡 Note: When measuring obtuse angles or angles larger than 180°, extend your straight edge outside the circle to find the true measurement.
Mastering the art of using a protractor for angle measurement enhances your precision in various applications. Whether for academic assignments, architectural drafts, or technical drawings, these steps will empower you with the confidence to measure angles accurately. Practice these methods, keep refining your techniques, and remember that the protractor, while simple, can be a powerful tool when used correctly.
Why are there two sets of numbers on a protractor?

+
Protractors have two sets of numbers because they can measure angles in both directions. The outer set measures clockwise angles, and the inner set measures counter-clockwise angles from 0° at either end to 180° at the opposite end.
What if the angle falls between two degree markers on the protractor?

+
If the angle falls between two markers, you should estimate the measurement. A good rule is to split the difference or interpolate. For more accuracy, consider using a protractor with smaller degree divisions or a digital angle finder.
How do I measure reflex angles with a protractor?

+
To measure a reflex angle (over 180°), measure the smaller included angle and subtract it from 360°. For example, if the included angle is 135°, the reflex angle is 360° - 135° = 225°.



