Inside Attack Threats

Introduction to Inside Attack Threats
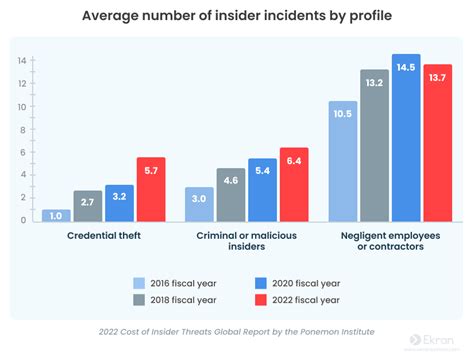
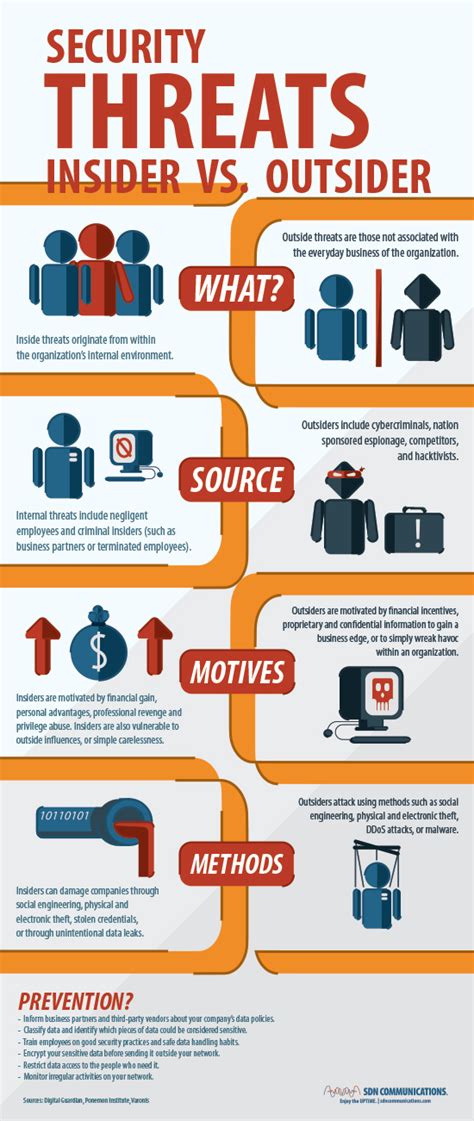
In the realm of cybersecurity, threats can originate from various sources, including both external and internal factors. While external threats, such as hacking and malware, are well-documented and widely discussed, inside attack threats pose a significant and often overlooked danger to an organization’s security and integrity. These threats emanate from within the organization itself, perpetrated by individuals with authorized access to the company’s assets, systems, and data. The insider threat landscape is complex, involving not just malicious actors but also accidental or negligent insiders whose actions, though unintentional, can still cause considerable harm.
Types of Inside Attack Threats
Inside attack threats can be categorized into several types based on the motivations and actions of the insiders: - Malicious Insiders: These are individuals who intentionally seek to cause harm to the organization. Their actions can range from stealing sensitive data to disrupting operational systems. - Accidental Insiders: These individuals unintentionally cause security breaches. This could be due to a lack of training, negligence, or simply making mistakes. - Negligent Insiders: Similar to accidental insiders, negligent insiders cause harm due to careless behavior. However, their actions might be more egregious due to a consistent pattern of neglect.
Causes and Motivations

Understanding the causes and motivations behind inside attack threats is crucial for mitigating them. Some common reasons include: - Financial Gain: Insiders might steal data or disrupt services for personal financial benefit. - Revenge: Employees who feel wronged by the organization might seek revenge through sabotage or data theft. - Lack of Awareness: Insiders might unintentionally cause security breaches due to a lack of training or awareness about security protocols. - Personal Issues: Personal problems, such as financial difficulties or emotional instability, can sometimes drive insiders to malicious behavior.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies

Preventing and mitigating inside attack threats require a multi-faceted approach that includes both technological solutions and human-centered strategies: - Implement Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive data and systems to only those who need it can reduce the risk of insider threats. - Monitor Activity: Regular monitoring of user activity can help in early detection of malicious behavior. - Training and Awareness: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and the importance of security can reduce accidental and negligent insider threats. - Incident Response Plan: Having a plan in place to respond quickly and effectively to insider threats can minimize damage.
Technological Solutions
Several technological solutions can aid in the prevention and detection of inside attack threats: - Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems can monitor network traffic for signs of unauthorized access or malicious activity. - Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: DLP tools can detect and prevent sensitive data from being exfiltrated. - User Activity Monitoring (UAM) Software: UAM software can track and analyze user behavior to identify potential insider threats.
Challenges in Mitigating Inside Attack Threats

Despite the importance of addressing inside attack threats, several challenges hinder effective mitigation: - Balancing Security with Privacy: Monitoring employee activities raises privacy concerns, making it challenging to balance security needs with respect for employees’ privacy. - Resource Constraints: Small and medium-sized organizations often lack the resources (financial, technological, and human) to implement comprehensive insider threat mitigation strategies. - Evolving Nature of Threats: Insider threats are dynamic, with new motivations and methods emerging continuously, requiring organizations to stay vigilant and adapt their strategies.
🚨 Note: Organizations must continually update their security protocols and awareness programs to keep pace with the evolving landscape of insider threats.
Best Practices for Organizations

To effectively manage and mitigate inside attack threats, organizations should adopt the following best practices: - Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Identify vulnerabilities and potential insider threats through regular assessments. - Implement a Culture of Security: Foster an organizational culture that prioritizes security and encourages employees to report suspicious activity. - Provide Ongoing Training: Offer regular training and updates to ensure employees are aware of the latest threats and best practices.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Control | Limit access to sensitive data and systems. |
| Monitoring | Regularly monitor user activity for suspicious behavior. |
| Awareness and Training | Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices and the importance of security. |

In essence, combating inside attack threats requires a holistic approach that combines technological measures with a deep understanding of human behavior and motivations. By fostering a culture of security, implementing robust access controls, and staying vigilant, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to insider threats.
The key points to consider when addressing inside attack threats include understanding the types of threats, recognizing the causes and motivations, implementing robust prevention and mitigation strategies, and continually updating security protocols to stay ahead of emerging threats. By prioritizing insider threat mitigation, organizations can protect their assets, maintain trust, and ensure operational continuity in an increasingly complex and risky cybersecurity landscape.



