5 Essential Tips for Alkanes Worksheet Answers

When it comes to understanding the structure, properties, and reactions of alkanes, practice is key. Working on alkane worksheets helps students to reinforce what they've learned in their chemistry classes. Here are five essential tips to help you navigate alkanes worksheet answers with confidence and accuracy:
1. Understand the Basics of Alkanes


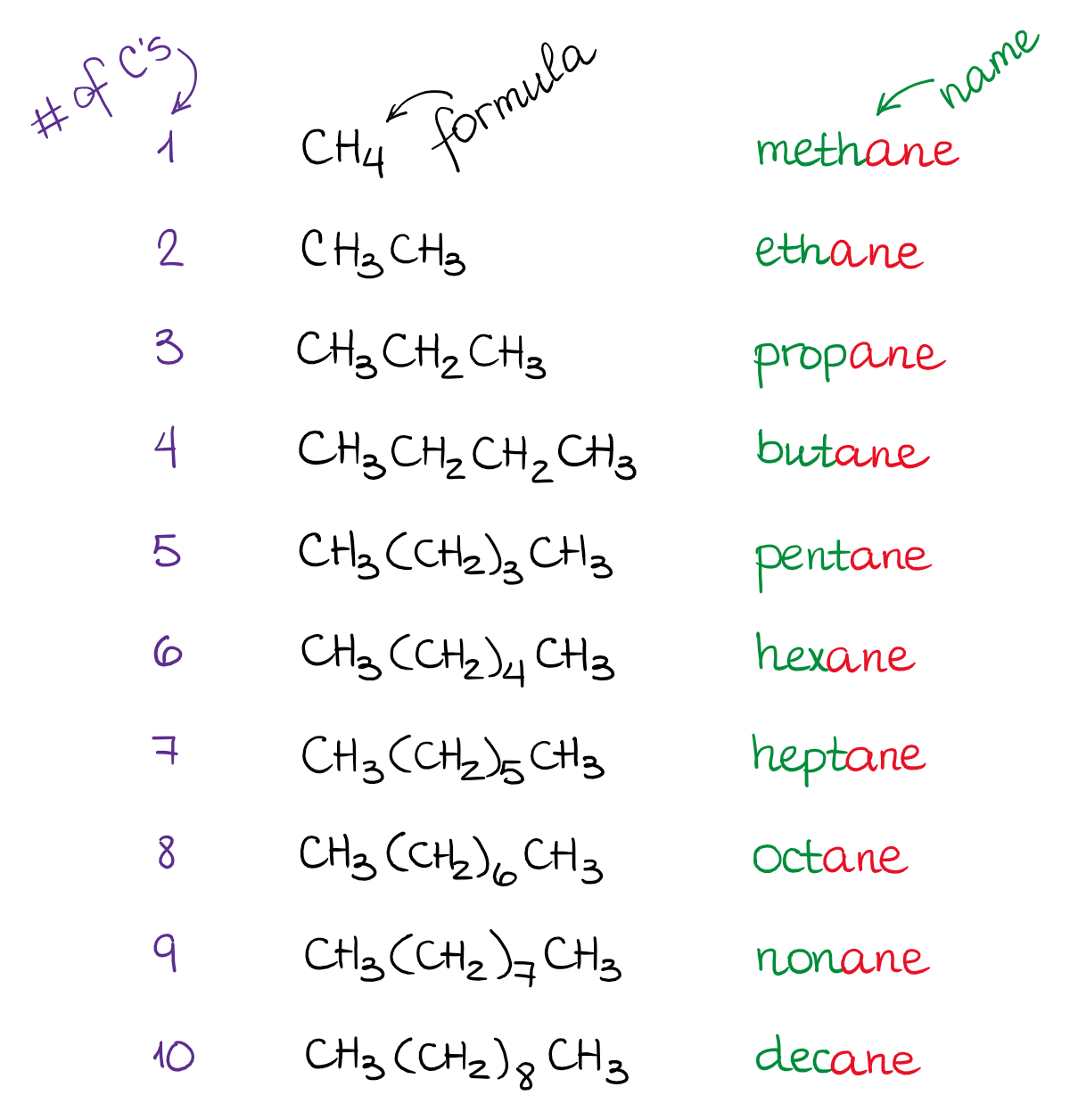
Alkanes, also known as paraffins, are hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the chain. Here’s what you need to know:
- Nomenclature: Learn the naming conventions for alkanes, including root names for different carbon chain lengths (e.g., methane for C1, ethane for C2, propane for C3, and so on).
- Structural Isomers: Understand that alkanes can have different structural isomers, which means the same molecular formula can represent different compounds. This is due to the possibility of branching in the carbon chain.
- Functional Groups: Alkanes are saturated, which means they have no functional groups or unsaturation. They don’t react readily, but substitution reactions can occur.
2. Familiarize Yourself with Common Reactions

Alkanes undergo a few specific reactions, the most common of which are:
- Combustion: The complete combustion of alkanes in oxygen yields carbon dioxide and water.
- Substitution: In the presence of ultraviolet light or high temperatures, alkanes can undergo halogenation reactions where hydrogen atoms are replaced by halogen atoms.
- Cracking: This industrial process breaks longer-chain alkanes into smaller, more useful ones, often for gasoline production.
⚠️ Note: In worksheet problems, make sure you identify the correct reaction taking place to answer the question accurately.
3. Recognize and Draw Structural Formulas

Being able to draw structural formulas of alkanes is vital. Here’s what you should focus on:
- Carbon Skeleton: Start by laying out the carbon backbone, taking into account any branching.
- Hydrogens: Add the appropriate number of hydrogen atoms to complete each carbon’s octet rule.
- Line-Wedge-Dash Notation: Understand the 3D representation of molecules using this notation for a better visualization.
Here’s a simple example of how to represent butane:
| Structural Formula | Line-Wedge-Dash Notation |
|---|---|
| CH3CH2CH2CH3 |  |

4. Practice Naming and Identifying Isomers

Naming alkanes and recognizing their isomers is a skill that improves with practice:
- Systematic Naming: Follow IUPAC rules for naming alkanes, including understanding prefixes for substituent groups and where they attach to the main chain.
- Isomer Identification: Draw all possible isomers for a given molecular formula, systematically considering all possible configurations.
🧪 Note: Pay special attention to the position of substituents and the longest continuous chain when naming alkanes with branches.
5. Solve Problems Methodically

When approaching alkane worksheet problems, here’s a structured approach:
- Read Carefully: Understand what the question is asking before you start working.
- Sketch if Needed: Draw out the molecules or reactions if it helps to visualize the problem.
- Check Work: Always recheck your answers, especially when dealing with isomer count or reaction products.
🧾 Note: Some problems might require you to calculate molecular weights or predict the physical properties like boiling points based on structure.
In summary, mastering alkanes in chemistry involves more than just memorizing facts; it requires an understanding of structural relationships, reaction mechanisms, and problem-solving strategies. With these tips in mind, you'll find yourself better prepared to tackle any alkane worksheet with precision and ease, making complex chemical concepts more accessible. Whether you're navigating through naming conventions, recognizing isomers, or determining reaction products, remember these essential strategies to excel in your chemistry studies.
How do you name branched alkanes?
+
Start by identifying the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms, which forms the root name. Then number the chain to give the lowest possible numbers to the substituents. Name the substituents alphabetically before the root name, followed by their positions.
What is the difference between alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes?

+
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds only. Alkenes have at least one double bond between carbon atoms, making them unsaturated, while alkynes have at least one triple bond, making them also unsaturated but with a higher degree of unsaturation than alkenes.
Can you list common reactions of alkanes?

+
Here are some of the common reactions of alkanes:
- Combustion - complete oxidation to CO2 and H2O
- Substitution with halogens - forming alkyl halides
- Cracking - breaking larger alkanes into smaller ones
What are structural isomers and why are they important in alkanes?

+
Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms. They are significant in alkanes because they demonstrate the complexity of organic chemistry, how different structures can have different physical and chemical properties.