5 Essential Tips for Solving Momentum and Force Problems

Are you struggling with understanding the complexities of momentum and force in physics? Whether you're a student or a professional, knowing how to handle these concepts is key in solving physics problems effectively. Here are five essential tips to help you navigate through momentum and force problems with ease.
1. Understand the Definitions Clearly
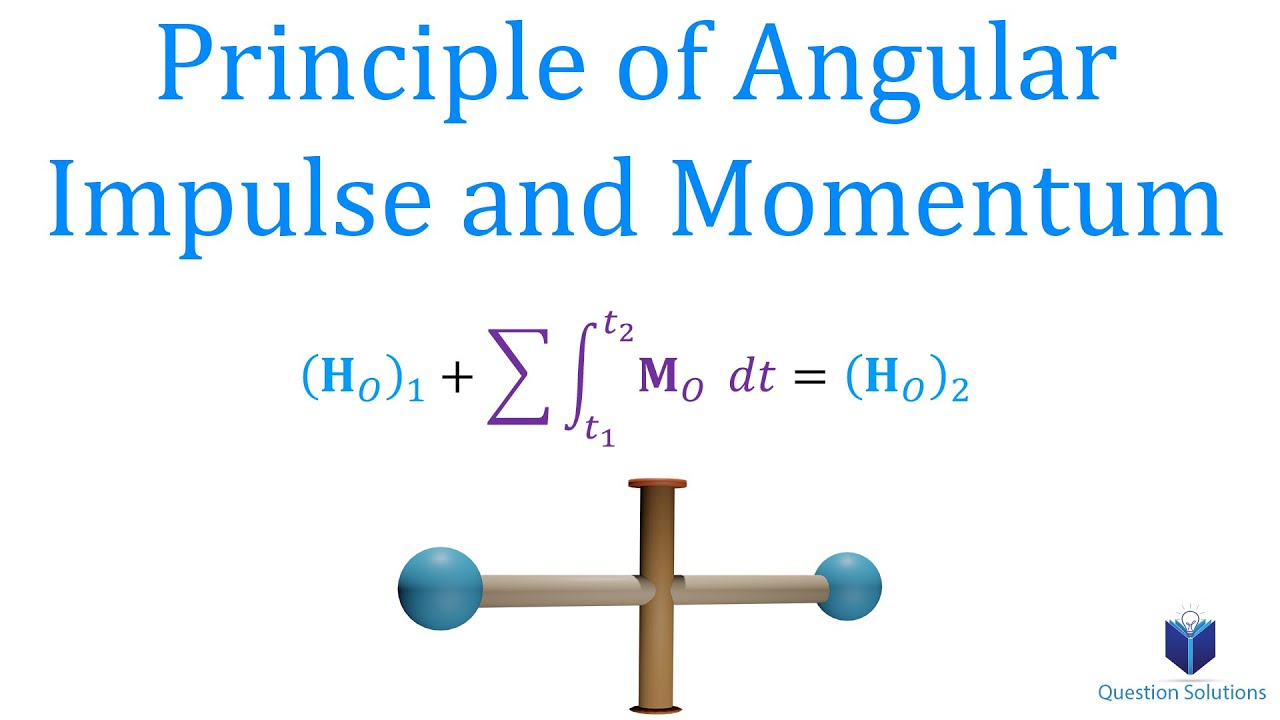

Before diving into complex problems, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental definitions:
- Momentum: Defined as the product of an object’s mass (m) and its velocity (v). Mathematically, it is p = m * v.
- Force: Force is what causes a change in momentum. It’s calculated using Newton’s second law of motion, F = m * a, where ‘a’ is acceleration.
Understanding these definitions and their units (SI units for momentum is kg⋅m/s, and for force, it’s Newton, or N, which equals kg⋅m/s²) will set a strong foundation for your problem-solving approach.
2. Use the Principle of Conservation of Momentum

The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act on it. Here’s how you can apply this principle:
- Identify the system and ensure there are no significant external forces acting on it.
- Set up an equation where the initial momentum equals the final momentum.
- Solve for unknown variables like velocity or mass.
This principle is particularly useful in collision problems where objects can bounce off each other or stick together.
3. Apply Newton’s Second and Third Laws

Understanding how these laws work together can simplify your calculations:
- Newton’s Second Law (F = ma) helps calculate the force needed to change an object’s momentum.
- Newton’s Third Law: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means forces come in pairs, which is vital when solving problems involving multiple objects.
📝 Note: Remember that when two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, even if one object is much larger than the other.
4. Diagram Your Problem

Visual aids can significantly clarify your understanding:
- Draw free-body diagrams to visualize all forces acting on an object.
- Use vectors to represent velocity, force, and momentum directions.
- Consider motion diagrams to track changes in motion over time.
| Diagram Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Free-body Diagram | To isolate and analyze forces on an object |
| Vector Diagram | To show directions and magnitudes of vectors |
| Motion Diagram | To depict changes in velocity or acceleration |

5. Solve with Systematic Steps

Approach every problem methodically:
- Identify known variables: Mass, velocity, time, distance, etc.
- Set up equations: Use conservation of momentum, Newton’s laws, or work-energy theorem if applicable.
- Simplify and solve: Substitute known values, simplify the equations, and solve for the unknown.
- Check the units: Ensure that the units on both sides of your equation match.
- Re-evaluate: After solving, recheck your logic and calculations to ensure there are no mistakes.
💡 Note: Always consider whether your solution makes sense physically. If an answer seems illogical or violates basic principles like conservation of momentum or energy, revisit your steps.
By following these tips, you'll be able to tackle momentum and force problems more efficiently. Each concept builds upon the others, creating a comprehensive understanding that can be applied to real-world physics scenarios. Remember, practice is key. The more problems you solve, the more intuitive these principles will become. Your ability to analyze and solve these problems will not only improve your problem-solving skills but also enhance your understanding of how the physical world operates.
What if the mass of objects changes in a problem?

+
When mass changes due to reasons like rockets expelling mass, you might need to use variable mass equations or consider the impulse of ejected mass. The equation for this scenario would be modified to account for the change in mass over time.
How do you handle problems with multiple collisions?

+
In problems with multiple collisions, consider each collision separately. You can use conservation of momentum for each event, tracking changes in momentum to find final velocities.
Can momentum be conserved in open systems?
+
Momentum is typically conserved in closed systems. In open systems, if external forces are present, they can change the total momentum. However, within the system, the momentum can still be conserved if the net external force is zero over the time of interest.
What are common mistakes when solving force and momentum problems?

+
Common errors include: - Forgetting to account for direction in vector quantities, - Neglecting to consider all forces in a free-body diagram, - Incorrect application of Newton’s laws, - Misinterpreting or missing conservation principles, - Calculation errors in algebra or unit conversion.