7.2 Cell Structure Worksheet: Key Answers and Insights

In the bustling world of biology, understanding the intricate structures within cells is fundamental to grasping how life operates at the most basic level. Cell Structure Worksheets serve as an excellent tool for students to learn about the various components that make up plant and animal cells. This post will delve into the key answers and provide insights into the cell structure, ensuring that learners are well-equipped with both the necessary knowledge and understanding for better academic results and a deeper appreciation of biological sciences.
What is a Cell?
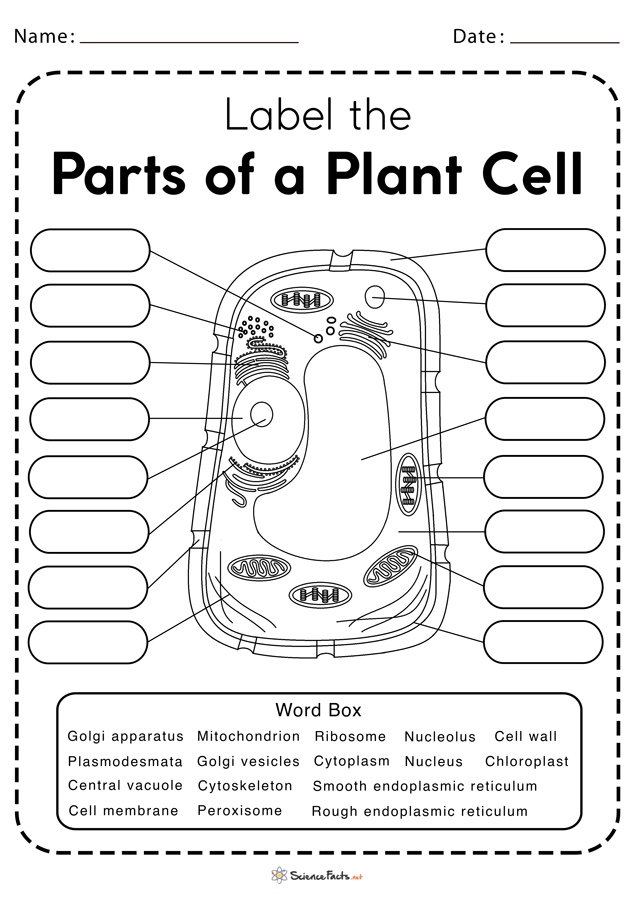
At its core, a cell is the smallest unit of life capable of independent functioning. Cells are the fundamental units from which all living organisms are built. Here are some key points about cells:
- All living things are composed of cells.
- Cells carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
- They can perform all the processes that sustain life.
Cell Structure Basics

Cells can be categorized into two main types:
- Prokaryotic cells - Simple, lack a distinct nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells - More complex, with a distinct nucleus and organelles separated by membranes.
Cell Structure Worksheet Answers

Animal Cell Structure
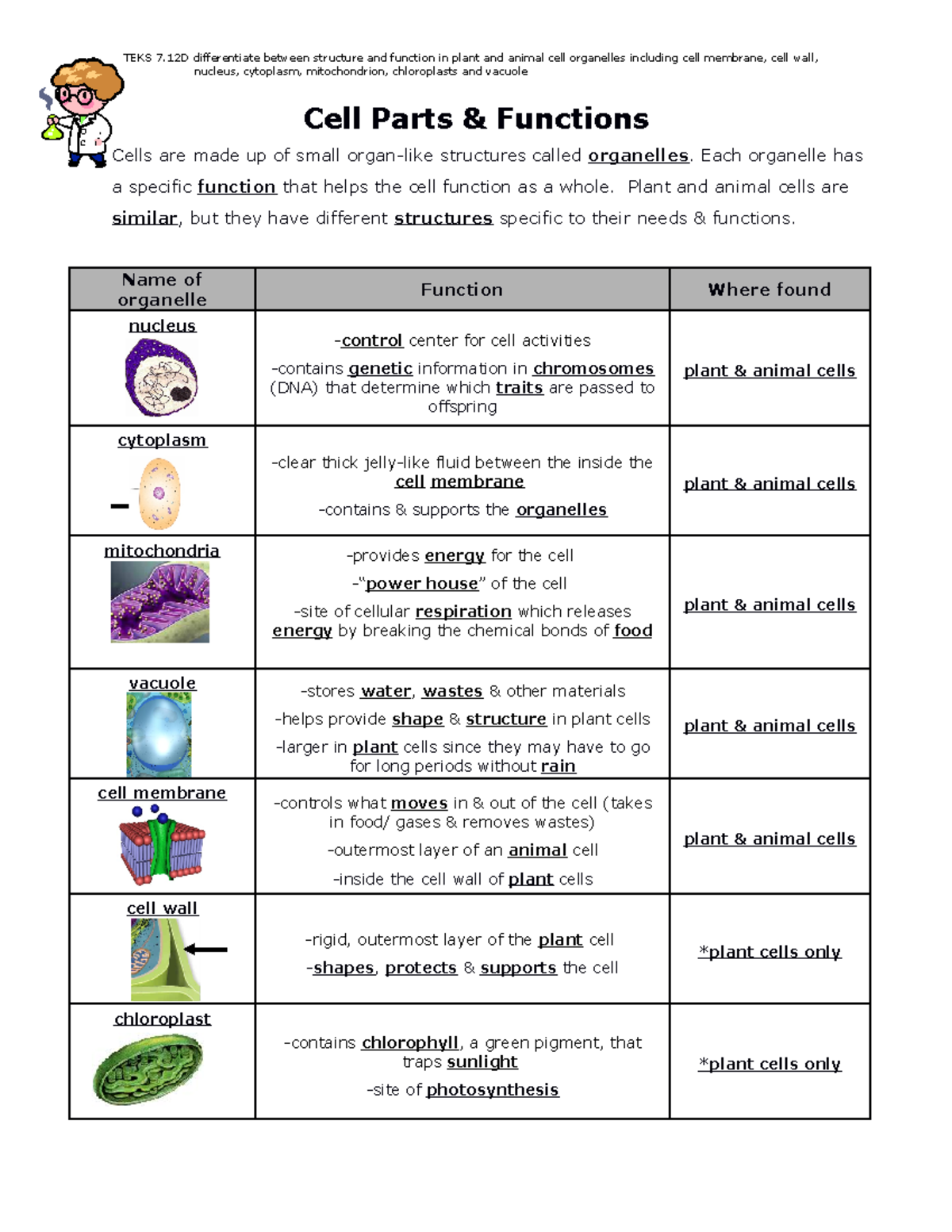
Here are some common elements and answers found in animal cell structure worksheets:
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Controls cell functions, contains genetic material |
| Mitochondria | Generates energy through cellular respiration |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Protein and lipid synthesis (Rough ER), lipid synthesis (Smooth ER) |
| Golgi Apparatus | Processes, packages, and sorts proteins and lipids |
| Ribosomes | Site of protein synthesis |

Plant Cell Structure

In addition to the organelles found in animal cells, plant cells have:
- Cell Wall - Provides structural support
- Chloroplasts - Conduct photosynthesis
- Large Central Vacuole - Stores water, nutrients, and waste
🌱 Note: While both plant and animal cells contain many of the same organelles, plant cells are unique in having cell walls and chloroplasts, which are vital for their specific functions.
Insights into Cell Structure

Understanding the cell structure goes beyond just memorizing the parts; it’s about recognizing how each part contributes to the cell’s overall function:
- Cell Membrane: Acts as a selective barrier, allowing essential nutrients in and waste products out. It’s essential for maintaining the integrity of the cell.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: The rough ER modifies proteins which are then sent to the Golgi apparatus. The smooth ER synthesizes lipids and detoxifies harmful substances.
- Golgi Apparatus: Here, proteins and lipids are modified, sorted, and packed into vesicles for transport.
- Mitochondria: Known as the powerhouse of the cell, they produce ATP, which is vital for energy processes within the cell.
- Chloroplasts in Plant Cells: Through photosynthesis, chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy, making plants autotrophs.
- Vacuoles: Plant cells have large central vacuoles that store substances and can expand to help maintain turgor pressure, keeping the cell rigid.
Common Misconceptions

When studying cell structures, students often encounter several misconceptions:
- All cells are the same: While cells share some basic features, their structures and functions can be quite diverse.
- Mitochondria are only in animal cells: Mitochondria are present in both animal and plant cells, but chloroplasts are exclusive to plants.
- Endoplasmic reticulum is just for transport: It’s involved in protein synthesis as well.
💡 Note: Clarifying these misconceptions early on helps in building a robust understanding of cellular biology.
The Importance of Learning Cell Structure

Mastering cell structure is not just about passing exams; it has practical implications:
- Understanding cellular processes aids in health-related sciences, like how cells multiply, repair, or mutate.
- Cell biology knowledge is fundamental for genetic engineering, biotechnology, and medical research.
- It provides a foundation for further studies in biology and related fields.
By now, you've explored the intricacies of cell structure, from the basic function of each organelle to the differences between plant and animal cells. The cell's complexity reflects the elegance of life at its most fundamental level. Whether you're studying for an exam or simply curious about biology, understanding these building blocks of life is key to appreciating the broader picture of living systems.
Why do plants have cell walls, but animals don’t?

+
Plant cells have cell walls made of cellulose which provide structural support and protection against environmental pressures, like osmotic pressure changes. Animal cells rely on other mechanisms for support, like cytoskeletons and the extracellular matrix.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus?

+
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from the ER into vesicles for transport. It’s akin to a cellular post office, ensuring that substances go where they need to within or outside the cell.
How does photosynthesis in chloroplasts benefit plant cells?

+
Photosynthesis transforms light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This provides energy for growth, reproduction, and other cellular activities. It also releases oxygen, a byproduct, contributing to Earth’s atmosphere.
Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell?

+
Mitochondria produce ATP through cellular respiration, providing most of the cell’s energy needs. This energy is used for various metabolic activities, making them the ‘powerhouse’ or energy generators of the cell.