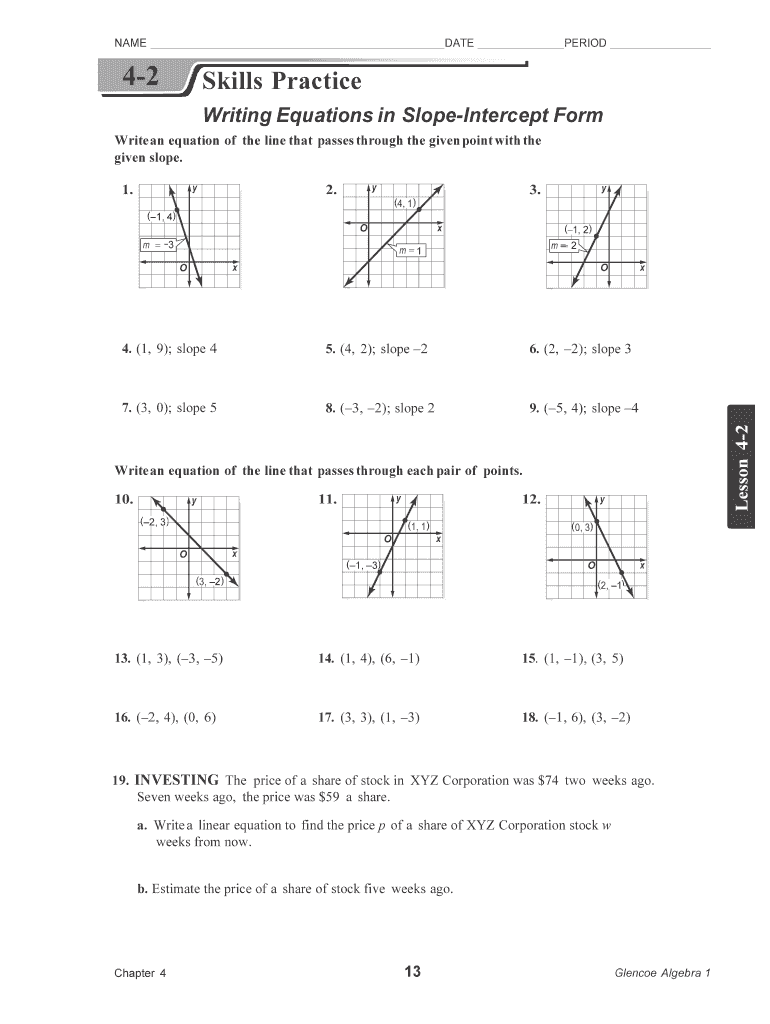
5 Essential Multiplication Facts for Quick Learning
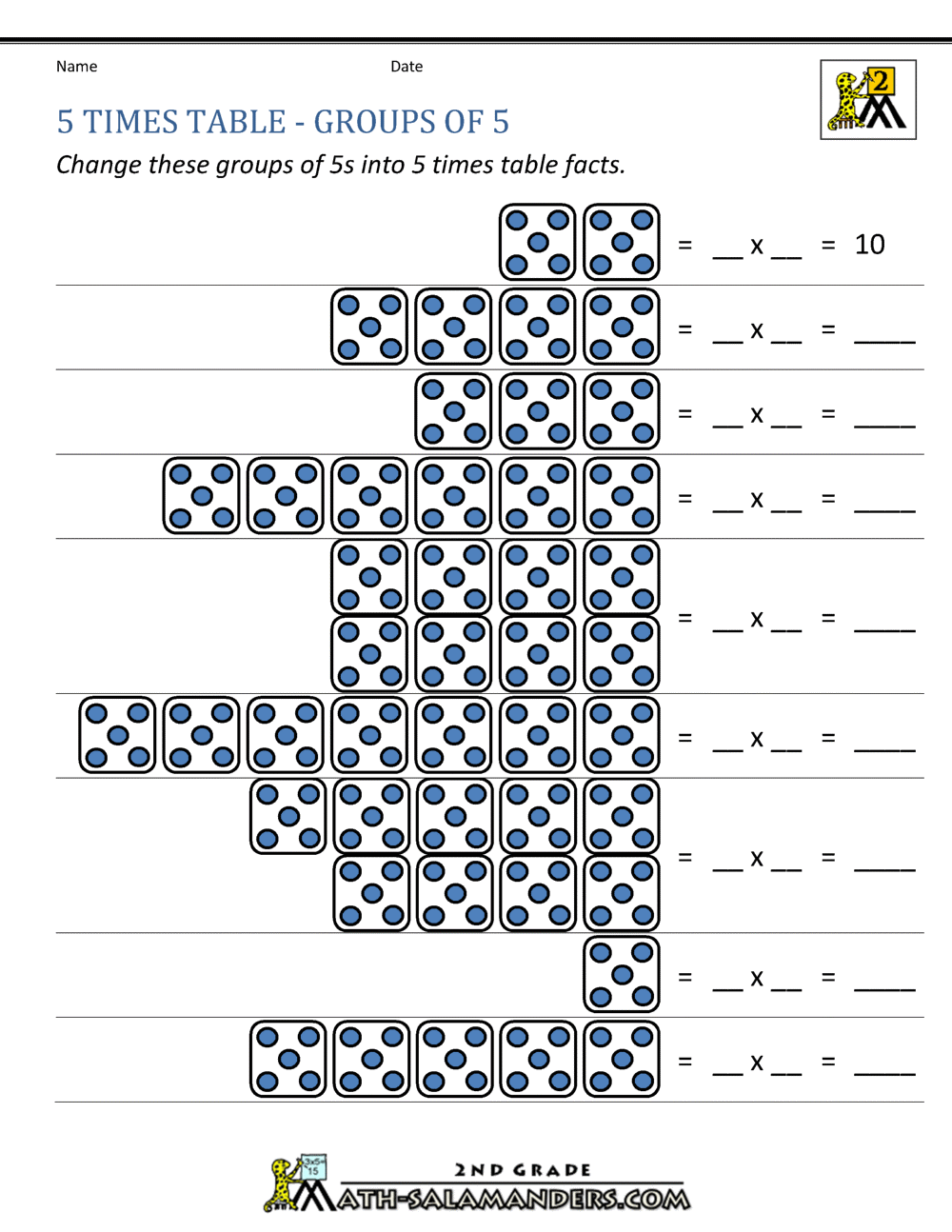
Mastering multiplication is a fundamental part of every student's mathematical journey. As they progress through their education, understanding and quick recall of multiplication facts can significantly enhance their ability to solve complex problems effortlessly. Here are five essential multiplication facts that not only aid in quick learning but also form the cornerstone of arithmetic proficiency:
1. The Commutative Property

The first and perhaps most critical fact to internalize is the commutative property of multiplication. This principle states that the order of the numbers in a multiplication equation does not change the product.
- Equation: a × b = b × a
- Example: 2 × 3 = 3 × 2, both equal 6
Understanding this property can:
- Reduce the number of facts to memorize.
- Help students recognize patterns and connections between numbers.
✨ Note: This property can be used creatively in problem-solving, making equations easier to manage.
2. The Associative Property

The associative property of multiplication allows for grouping the factors differently without altering the result. This is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or when simplifying multiplication strings.
- Equation: (a × b) × c = a × (b × c)
- Example: (2 × 3) × 4 = 2 × (3 × 4), both equal 24
By recognizing this property, students can:
- Simplify the multiplication process.
- Break down complex multiplication problems into smaller, more manageable steps.
3. The Zero Property

One of the simplest multiplication rules to grasp is the zero property: any number multiplied by zero is zero. This fundamental fact is essential for:
- Understanding the role of zero in mathematics.
- Helping students quickly identify when an equation will result in zero.
Equation:
- 0 × a = a × 0 = 0
🔴 Note: This rule is not just a mathematical fact; it's a window into understanding the concept of nothing or absence in math.
4. The One Property

The multiplicative identity, or the one property, states that any number multiplied by one remains unchanged. This property is key for:
- Introducing the concept of identity elements in math.
- Helping students understand why certain numbers do not change in some calculations.
- Equation: 1 × a = a × 1 = a
- Example: 1 × 7 = 7 × 1 = 7
Recognizing this property can also aid in:
- Verifying mathematical operations.
- Understanding the role of unity in mathematical systems.
5. The Doubling and Halving

Understanding how to double or halve numbers can dramatically speed up multiplication. This technique leverages the idea that multiplication can be approached through repetitive addition:
- Multiplying by 2 is just doubling the number.
- Multiplying by 4 can be seen as doubling twice.
- Multiplying by 8 can be viewed as doubling three times.
This strategy not only:
- Makes multiplication faster.
- Helps students recognize patterns and relationships between numbers.
Here's an example of doubling:
| Number | Multiplication by 2 |
|---|---|
| 5 | 10 (5×2) |
| 10 | 20 (10×2) |

🌟 Note: This technique can be particularly useful for larger numbers where traditional memorization of multiplication tables might falter.
In summary, the essential multiplication facts discussed here - commutative property, associative property, zero property, one property, and doubling/having - provide a solid foundation for quick learning. These facts not only streamline calculations but also deepen the understanding of mathematical relationships. Students who master these principles will find that the path to mathematical fluency becomes much smoother and more logical.
How can the commutative property simplify learning multiplication tables?

+
By understanding that the order of factors doesn’t change the product, students only need to memorize half of the multiplication table, as 4×3 is the same as 3×4.
Why is the zero property important in mathematics?

+
The zero property helps students understand that zero can’t contribute to a product, offering insights into the nature of zero and its implications in mathematical equations.
Can the one property be applied outside of basic multiplication?

+
Absolutely, the one property is a fundamental concept in group theory and algebra, where it serves as the identity element in various structures.
How does understanding doubling and halving help with multiplication?

+
It breaks down multiplication into simpler steps. Doubling numbers is essentially adding the number to itself, which can simplify complex calculations by reducing the mental load.
Are there any other multiplication strategies besides the ones mentioned?

+
Yes, there are many strategies, like the distributive property, where you split numbers into parts for easier multiplication, or using patterns in numbers like the square root for perfect squares.