Master the Art of Line Equations: Worksheet Guide

Understanding line equations is a fundamental skill in mathematics and physics, pivotal for everything from plotting simple graphs to engineering advanced structures. Line equations provide a powerful tool for describing relationships, allowing us to visualize trends, predict future values, and solve real-world problems. This comprehensive guide will not only walk you through the steps of mastering line equations but also offer insights on how to effectively use them in educational settings or personal study. Whether you're a student, teacher, or simply a math enthusiast, this worksheet guide will equip you with the skills needed to master the art of line equations.
Understanding Line Equations


The equation of a line in its most common form is the slope-intercept form: y = mx + b, where:
- m represents the slope or the steepness of the line,
- b is the y-intercept, where the line crosses the y-axis.
The slope describes how much the y-value changes for each unit increase in x:
- Positive slopes indicate lines that go upward from left to right.
- Negative slopes mean the line moves downward.
- A slope of zero indicates a horizontal line.
- An undefined slope corresponds to a vertical line.
The y-intercept gives you a starting point on the y-axis, enabling you to start drawing the line from that point.
Types of Line Equations

Here are the different forms in which a line equation can be written:
- Slope-Intercept Form (y = mx + b) - The most straightforward form for plotting a line.
- Point-Slope Form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)) - Useful when you have a point and the slope.
- Standard Form (Ax + By = C) - Commonly used in algebra, especially when solving systems of equations.
🎓 Note: These forms are interchangeable, and it's valuable to know how to convert between them for various applications.
Worksheet Steps to Master Line Equations
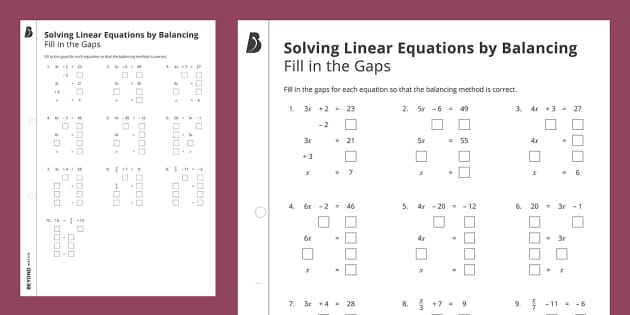
Mastering line equations involves a structured approach to learning:
Step 1: Identify the Equation Type

Understand the context in which the equation is given. If you know the slope and y-intercept, use the slope-intercept form. If you have a point and the slope, opt for point-slope form. If you’re given coordinates of two points, calculate the slope and then proceed.
Step 2: Practice Finding Slope

Use this formula to find the slope between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2):
[ m = \frac{y2 - y1}{x2 - x1} ]This formula gives you the change in y over the change in x, which is the essence of slope.
Step 3: Graphing Lines

Using your equation, plot points or use the y-intercept as the starting point and move along the slope to graph the line. Here’s a simple method:
- Plot the y-intercept (b) on the y-axis.
- Move horizontally by the change in x (the denominator of the slope).
- Move vertically by the change in y (the numerator of the slope).
✏️ Note: Visualizing the line helps solidify your understanding of how the equation works graphically.
Step 4: Conversion and Calculation
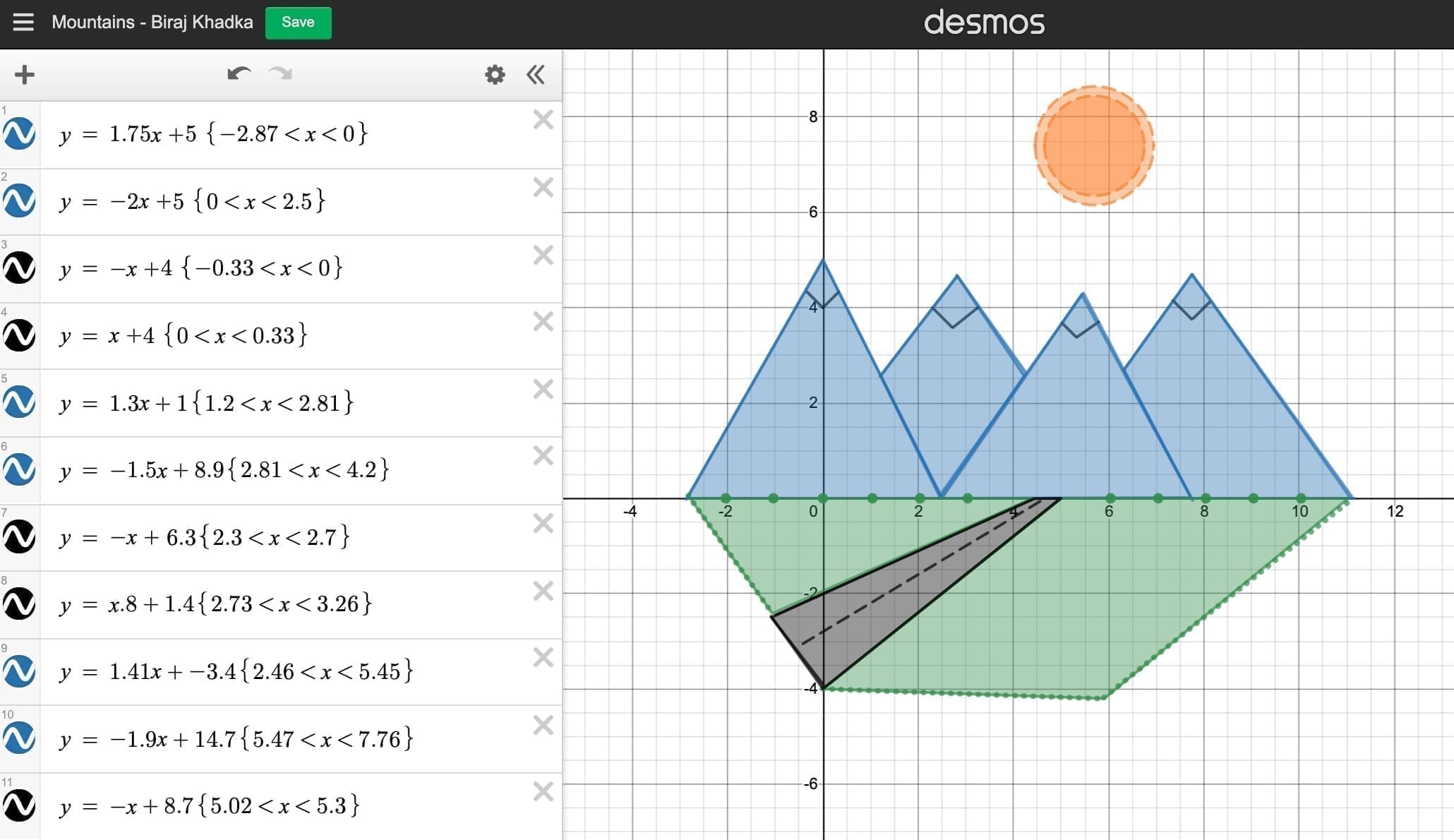
Convert equations between forms for flexibility:
- To convert from slope-intercept to standard form, rearrange to Ax + By = C.
- To move from point-slope to slope-intercept, distribute and simplify to isolate y.
| Form | Conversion |
|---|---|
| Slope-Intercept (y = mx + b) | To Standard: Multiply by -A/B if necessary |
| Point-Slope (y - y1 = m(x - x1)) | To Slope-Intercept: Distribute and simplify |
| Standard (Ax + By = C) | To Slope-Intercept: Solve for y |

Applications of Line Equations

Line equations are not merely academic; they have numerous practical applications:
- Physics: Determining speed and trajectories.
- Economics: Demand and supply curves.
- Engineering: Designing paths or slopes in construction projects.
- Finance: Predicting stock trends or calculating depreciation.
Understanding these applications can motivate learning by showing the real-world relevance of mastering line equations.
Summary

By following the steps in this guide, you’ll gain a deep understanding of line equations, moving from simple identification and graphing to complex conversions and real-world applications. Remember, mastering these equations involves:
- Identifying the type of equation,
- Practicing slope calculation,
- Graphing lines accurately,
- Converting between equation forms,
- Applying the concepts to practical scenarios.
This guide has provided you with the tools necessary to navigate the intricacies of line equations with confidence. Whether you're using these equations for academic purposes, professional problem-solving, or personal enrichment, you're now equipped with the knowledge to approach any line equation with precision and understanding.
Why is it important to learn about line equations?

+
Line equations are foundational in math, physics, engineering, and other STEM fields. They help in understanding the relationship between variables, predicting trends, and solving problems involving linear relationships.
What is the significance of the slope in a line equation?

+
The slope of a line equation tells us how steep the line is, which indicates the rate of change between the variables (x and y). It’s crucial for analyzing trends, understanding growth rates, and interpreting data.
Can I graph a line without knowing its equation?

+
Yes, you can graph a line if you know at least two points through which the line passes. Plot these points and draw a line through them to approximate the line equation.
How can I convert between different forms of line equations?
+
Conversion between different forms requires algebraic manipulation. For example, from point-slope to slope-intercept, distribute the slope, then isolate y. From slope-intercept to standard form, rearrange the terms to get Ax + By = C.