5 Engaging WW2 Worksheets with Answer Keys

Introduction to World War II Education

World War II remains one of the most significant events in modern history, shaping geopolitical landscapes, economies, and cultures around the globe. For educators, teaching WW2 not only involves historical facts but also fosters critical thinking, empathy, and a nuanced understanding of humanity’s potential for both great evil and tremendous courage. To engage students effectively, incorporating diverse teaching methods is essential, which includes the use of worksheets. Here are five engaging WW2 worksheets with answer keys designed to enhance students’ understanding of this complex era.
Worksheet 1: Major Events Timeline

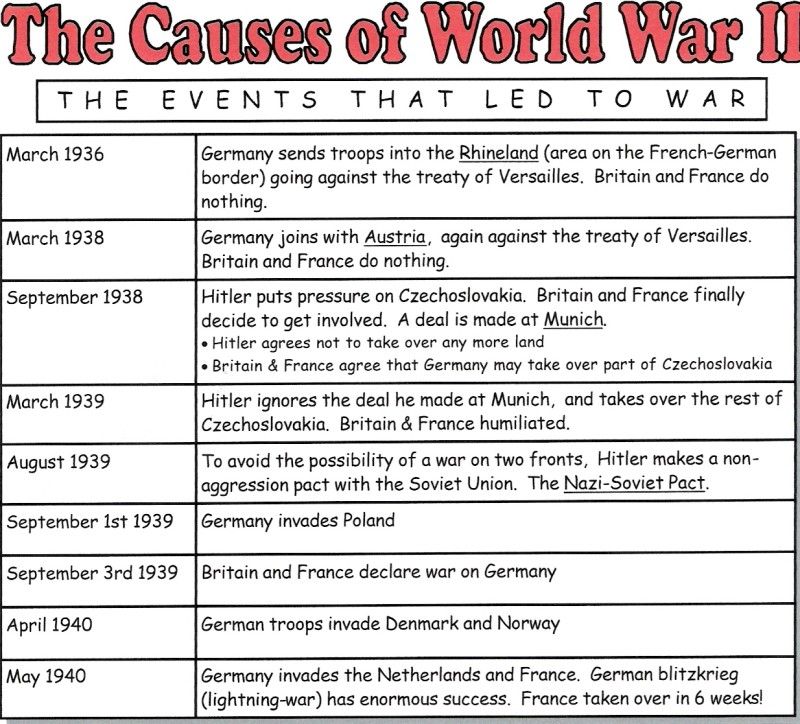
Creating a timeline of key events during WW2 can help students understand the sequence of events and their interconnectedness.
Objective:

- To comprehend the chronological flow of WW2, its key battles, and turning points.
Activity:

- Provide a blank timeline to students. - Ask them to fill in the following events with their dates: - Invasion of Poland (September 1, 1939) - Attack on Pearl Harbor (December 7, 1941) - D-Day (June 6, 1944) - Battle of Stalingrad (July 17, 1942 – February 2, 1943) - Surrender of Germany (May 7, 1945) - Atomic bombing of Hiroshima (August 6, 1945) - Include spaces for students to add brief descriptions or consequences for each event.
🔍 Note: Encourage students to research beyond these major events for a more comprehensive understanding.
Answer Key:

| Event | Date | Description/Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Invasion of Poland | September 1, 1939 | Marks the beginning of WW2, leading to Britain and France declaring war on Germany. |

Worksheet 2: Leaders of World War II

This worksheet will delve into the leaders who shaped the course of WW2, highlighting their policies, decisions, and the impact on the war.
Objective:

- To explore the personalities and decision-making processes of key WW2 figures.
Activity:

- Provide brief biographies of leaders like Adolf Hitler, Franklin D. Roosevelt, Winston Churchill, and Joseph Stalin. - Ask students to analyze and answer: - What was this leader's primary war strategy? - How did their personal beliefs influence their wartime decisions? - What was the most significant contribution or mistake they made during WW2?
👉 Note: Consider the complexity of these leaders' actions; they are not one-dimensional figures.
Answer Key:

- Adolf Hitler:
- Strategy: Blitzkrieg tactics and expansionist policies.
- Influence: Driven by racial superiority ideology, which led to the Holocaust and aggressive warfare.
- Significance: Initiated WW2; his underestimation of Soviet resolve led to his downfall.
Worksheet 3: Propaganda and Communication

Studying propaganda during WW2 provides insight into how governments manipulated information to sway public opinion and boost morale.
Objective:

- To examine the role of propaganda and its impact on society during WW2.
Activity:

- Show students examples of WW2 propaganda from different countries. - Ask them to analyze: - What message does the propaganda convey? - How does it aim to influence the audience? - What techniques were used (e.g., visual elements, slogans)?
📢 Note: Discuss ethical considerations regarding propaganda and freedom of speech.
Answer Key:

- Nazi Propaganda:
- Message: Superiority of the Aryan race, demonization of enemies.
- Influence: Aimed at creating a consensus for war and genocide.
- Techniques: Strong visual symbols, repetition, and emotional appeals.
Worksheet 4: The Home Front

Understanding the ‘home front’ is crucial to comprehending the broader impact of WW2 on societies.
Objective:
- To explore how civilians contributed to the war effort and experienced WW2.
Activity:
- Provide students with brief descriptions of various home front roles like rationing, war production, and women's contributions. - Ask them to complete: - How did this aspect of the home front support the war effort? - What were the long-term social changes as a result?🏡 Note: Highlight the diverse roles civilians played, including children, the elderly, and minorities.
Answer Key:
- Rationing:
- Support: Ensured resources were available for military use.
- Changes: Fostered a culture of frugality and the "victory garden" movement.
Worksheet 5: Effects of WW2 on the World

Examining the consequences of WW2 allows students to understand its long-lasting impact.
Objective:
- To analyze the political, economic, and social changes post-WW2.Activity:
- Give students a list of post-war outcomes (e.g., UN formation, Cold War, decolonization). - Ask them to explain: - How did WW2 contribute to this outcome? - What are the implications today?🌍 Note: Remind students that WW2's effects are still relevant, influencing modern geopolitics.
Answer Key:
- United Nations:
- Contribution: WW2 highlighted the need for international cooperation to maintain peace.
- Implications: Today's global governance and efforts towards human rights and disarmament.
In wrapping up our exploration of World War II through educational activities, we’ve provided a structured approach to engage students with the multifaceted history of this period. Through these WW2 worksheets, students can understand the sequence of events, analyze leadership decisions, consider the influence of propaganda, examine the role of civilians, and appreciate the enduring consequences of the war. Each worksheet brings a unique perspective to learning, fostering critical thinking, historical empathy, and a deeper understanding of one of the most tumultuous periods in human history.
Why is it important to study World War II in school?
+Studying World War II in school helps students understand pivotal historical events, the consequences of war, the rise and fall of political ideologies, and the importance of peace, democracy, and international cooperation. It also fosters critical thinking, empathy, and a sense of historical continuity.
How can teachers make WW2 lessons more engaging for students?
+Teachers can engage students by incorporating various media like films, documentaries, primary sources, interactive simulations, and role-playing activities. Using worksheets like those outlined above can also make learning interactive, encouraging active participation and personal reflection on the historical events.
What are the key themes to focus on when teaching about World War II?
+Key themes include the rise of totalitarian regimes, the causes and consequences of war, the Holocaust, the role of civilians, international alliances and diplomacy, technological advancements in warfare, and the societal changes post-war.