7 WW2 Facts

Introduction to WW2

The Second World War, often abbreviated as WW2, was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved most of the world’s nations, including all of the great powers, and is widely considered the deadliest conflict in human history. The war was fought between two main alliances: the Allies, which consisted of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union, among others, and the Axis powers, which included Germany, Italy, and Japan. In this blog post, we will explore seven fascinating facts about WW2 that highlight the complexity and scale of the conflict.
Fact 1: The War Began with the Invasion of Poland

The war began on September 1, 1939, when Nazi Germany, led by Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland. This act of aggression prompted the United Kingdom and France to declare war on Germany, which marked the beginning of the conflict in Europe. The invasion of Poland was a strategic move by Hitler to expand Germany’s territory and resources, but it ultimately led to the escalation of the war.
Fact 2: The Holocaust Was a Systematic Genocide

One of the most horrific aspects of WW2 was the Holocaust, a systematic genocide carried out by the Nazi regime against six million Jews and millions of others deemed undesirable, including Romani people, homosexuals, and individuals with disabilities. The Holocaust was a brutal and inhumane campaign that was carried out in concentration camps and ghettos across Europe. The atrocities committed during the Holocaust are a stark reminder of the dangers of racism, xenophobia, and hatred.
Fact 3: The Soviet Union Suffered the Highest Number of Casualties

The Soviet Union suffered the highest number of casualties during WW2, with estimates suggesting that between 26 and 30 million people lost their lives. The Soviet Union played a crucial role in the defeat of Nazi Germany, and its sacrifices were instrumental in the Allied victory. The Soviet Union’s contribution to the war effort is often overlooked, but it is essential to recognize the significant losses they suffered.
Fact 4: The United States Dropped Atomic Bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki

In August 1945, the United States dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing hundreds of thousands of people and leading to Japan’s surrender. The use of atomic bombs was a controversial decision that marked the end of the war in the Pacific. The bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki were a devastating conclusion to the conflict and had far-reaching consequences for international relations and global security.
Fact 5: The Lend-Lease Act Was a Crucial Factor in the Allied Victory

The Lend-Lease Act, signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1941, allowed the United States to supply the United Kingdom and other Allied nations with military equipment and supplies without requiring immediate payment. The Lend-Lease Act was a crucial factor in the Allied victory, as it enabled the United Kingdom and other nations to continue fighting against the Axis powers. The act marked a significant shift in U.S. foreign policy and demonstrated the country’s commitment to supporting its allies.
Fact 6: The D-Day Invasion Was the Largest Seaborne Invasion in History
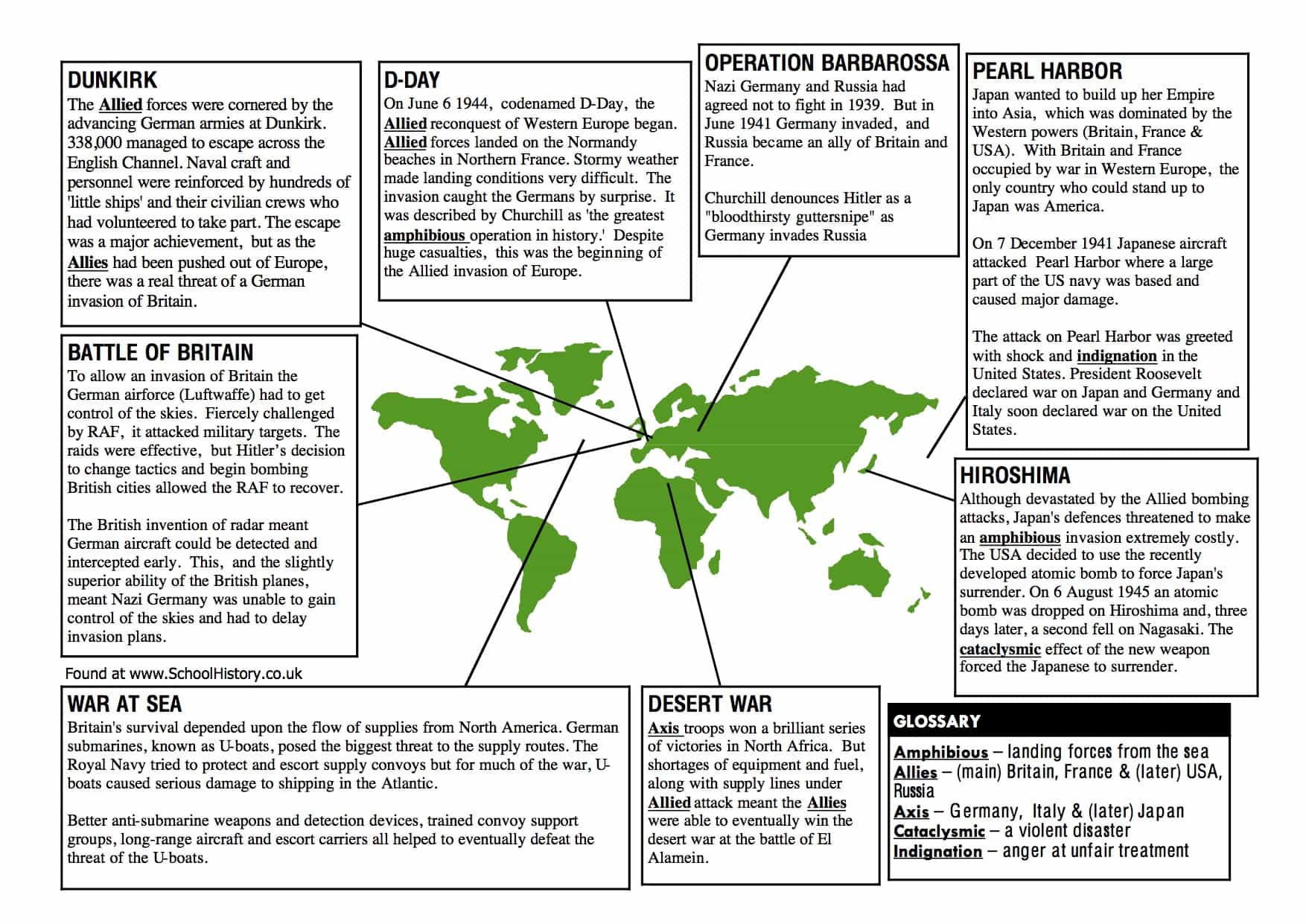
The D-Day invasion, which took place on June 6, 1944, was the largest seaborne invasion in history, with over 156,000 troops landing on five beaches in Normandy, France. The invasion, code-named Operation Overlord, was a turning point in the war, as it marked the beginning of the end of Germany’s occupation of Western Europe. The bravery and sacrifice of the Allied troops who took part in the D-Day invasion will always be remembered as a testament to their courage and determination.
Fact 7: The War Resulted in the Formation of the United Nations

The aftermath of WW2 saw the formation of the United Nations, an international organization dedicated to promoting peace, security, and cooperation among nations. The United Nations was established in 1945, with the aim of preventing future wars and promoting diplomacy and dialogue. The organization has played a crucial role in maintaining international peace and security, and its formation was a direct response to the devastation and chaos caused by WW2.
📝 Note: The seven facts highlighted in this blog post demonstrate the complexity and scale of WW2, and serve as a reminder of the importance of promoting peace, understanding, and cooperation among nations.
In summary, WW2 was a global conflict that involved most of the world’s nations and resulted in the loss of millions of lives. The war was fought between two main alliances, the Allies and the Axis powers, and was marked by significant events, including the invasion of Poland, the Holocaust, and the D-Day invasion. The war had far-reaching consequences, including the formation of the United Nations, and serves as a reminder of the importance of promoting peace and cooperation among nations.
What were the main causes of WW2?

+
The main causes of WW2 were the aggressive expansion of Nazi Germany, the policy of appeasement, and the rise of fascist and nationalist ideologies in Europe and Asia.
Who were the main leaders of the Axis powers?

+
The main leaders of the Axis powers were Adolf Hitler of Germany, Benito Mussolini of Italy, and Hirohito of Japan.
What was the significance of the D-Day invasion?

+
The D-Day invasion was a turning point in the war, as it marked the beginning of the end of Germany’s occupation of Western Europe and paved the way for the Allied victory.