Ionic Charges Worksheet: Easy Predictions Explained
Understanding the concept of ionic charges is pivotal for students navigating through the realm of chemistry, particularly when it comes to predicting chemical reactions, bonding behaviors, and the solubility of ionic compounds. This post aims to provide a comprehensive guide to easily predicting ionic charges, helping students simplify what might initially seem like a complex topic. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how elements behave in ionic bonds, allowing you to make confident predictions about ionic charges.
What Are Ions?
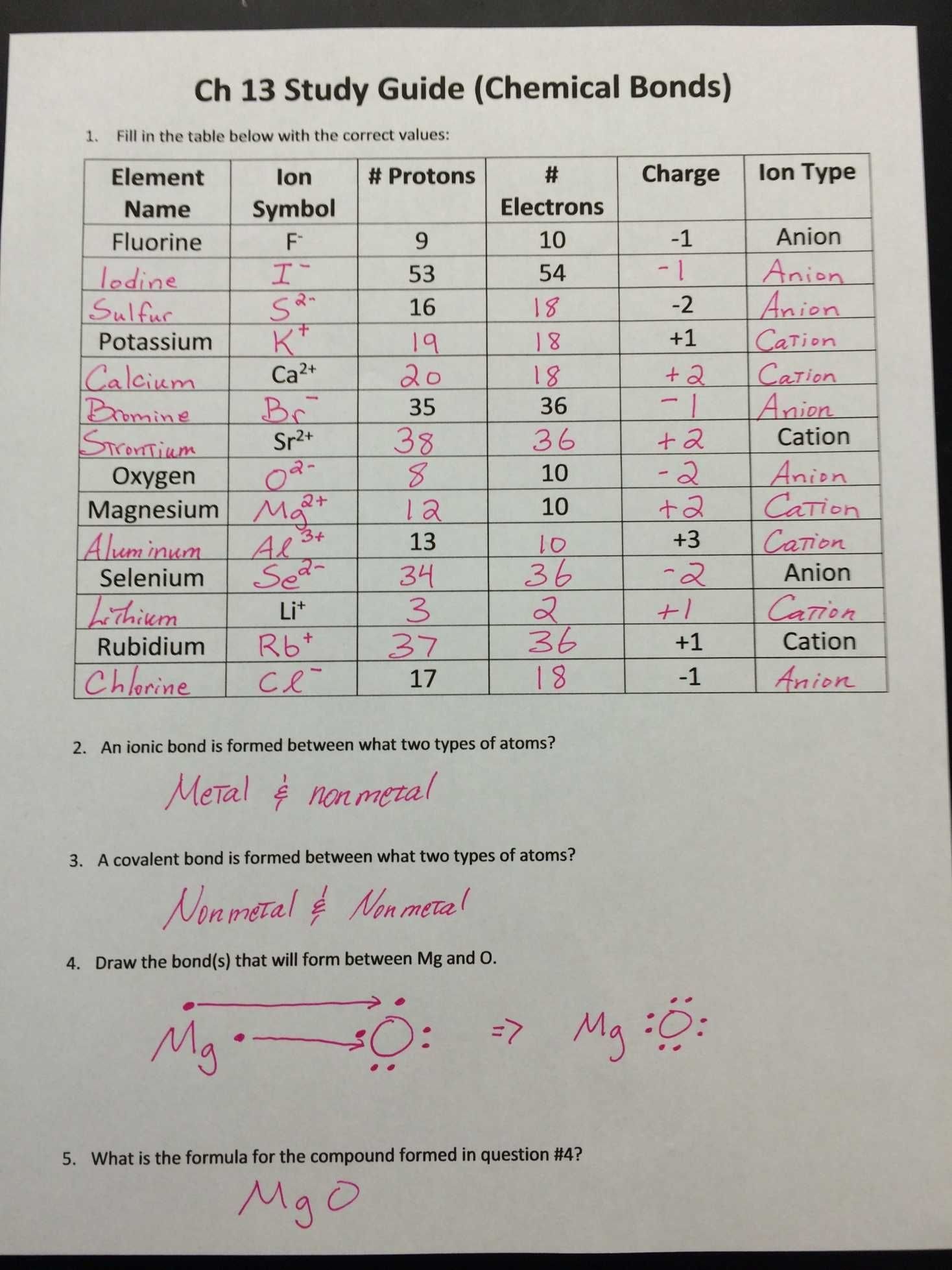
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained electrons, leading to an electrical charge. This charge is either positive (cation) or negative (anion). Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Cations: Formed when atoms lose electrons, gaining a positive charge. For instance, sodium (Na) becomes Na+ when it loses one electron.
- Anions: Formed when atoms gain electrons, resulting in a negative charge. Chlorine (Cl) becomes Cl- when it gains one electron.
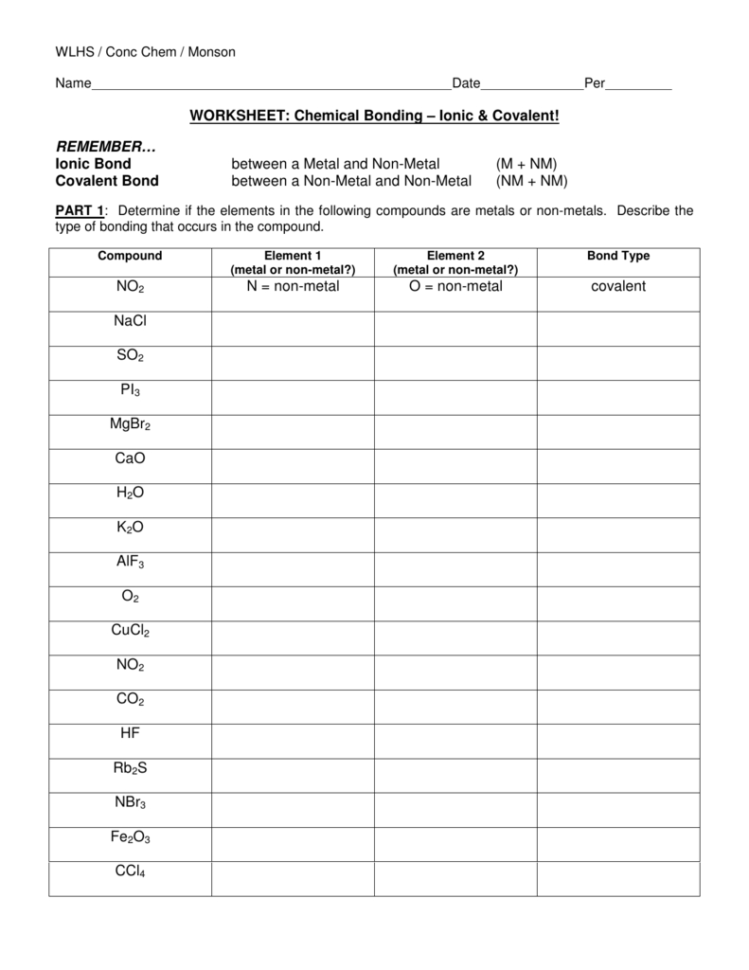
Understanding the Periodic Table

The periodic table is not just a list of elements; it’s a blueprint for understanding how elements interact. Here’s how to use it to predict ionic charges:
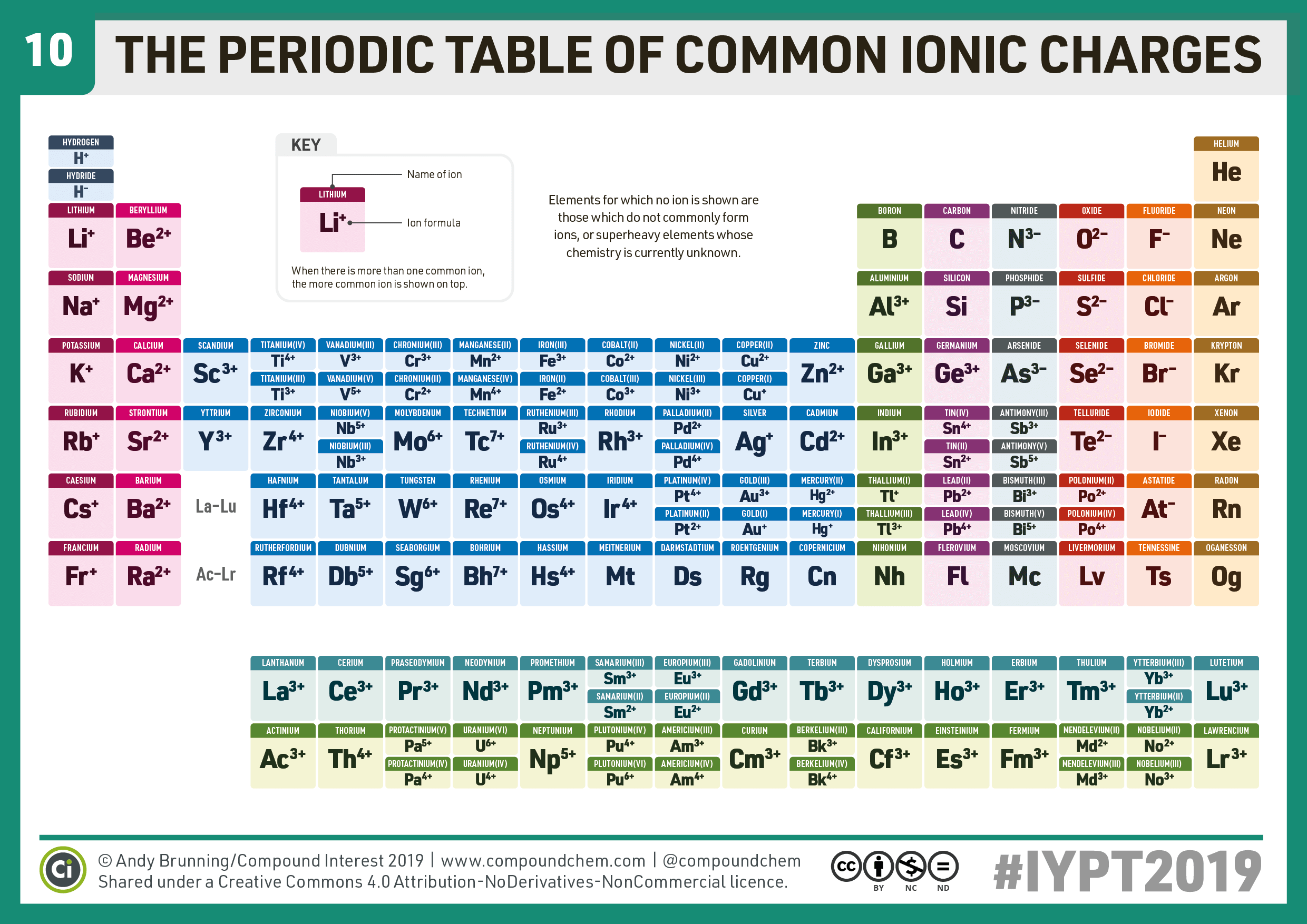
- Group 1 (Alkali Metals): Elements like Lithium (Li) and Sodium (Na) form ions with a charge of +1.
- Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals): Elements like Magnesium (Mg) and Calcium (Ca) form ions with a charge of +2.
- Group 13 (Boron Group): Boron (B) can form various ions, but Aluminum (Al) typically forms Al3+.
- Group 15 (Nitrogen Group): Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) often form anions with a -3 charge, but they can also have +3 or +5 states.
- Group 16 (Chalcogens): Oxygen (O) and Sulfur (S) generally form -2 anions.
- Group 17 (Halogens): Elements like Fluorine (F) and Chlorine (Cl) form -1 anions.
- Group 18 (Noble Gases): These elements do not typically form ions due to their full valence shell.
Predicting Ionic Charges

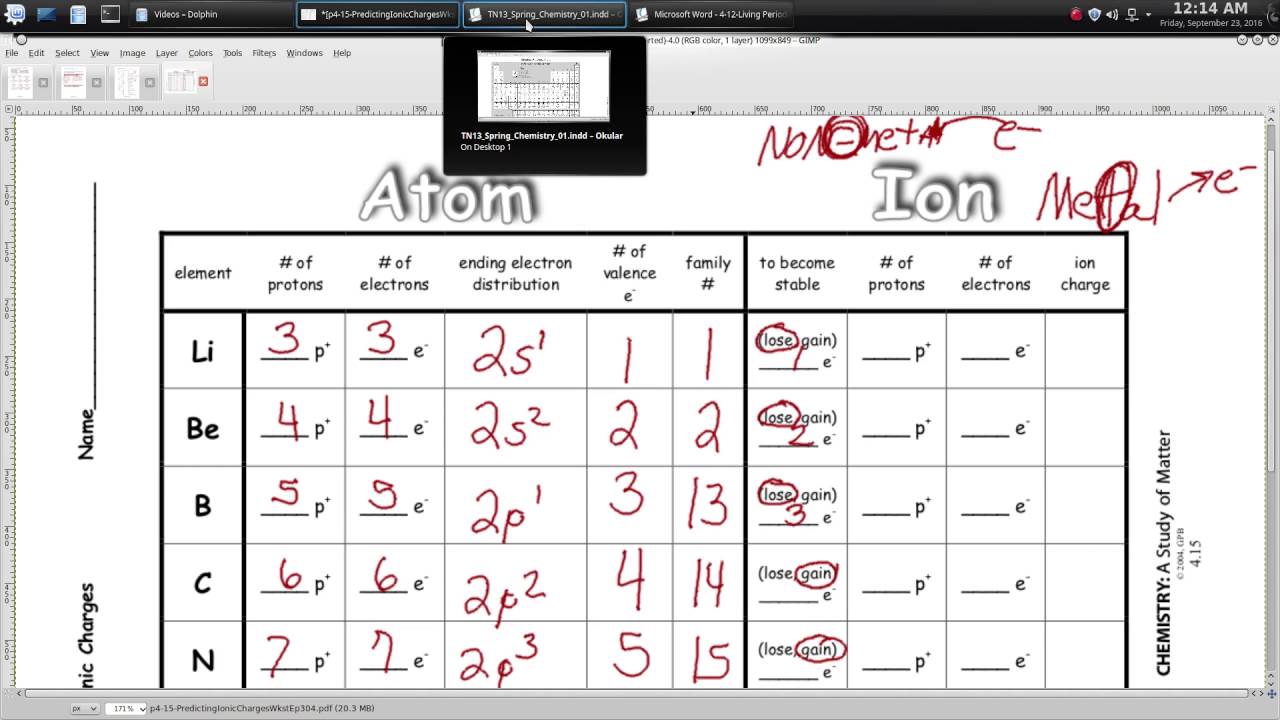
Predicting ionic charges involves understanding the electron configuration and the tendency of elements to achieve a stable electron octet or achieve a noble gas configuration. Here’s how to approach this:
For Main Group Elements:
- Identify the Group Number: The group number of an element often indicates the common ionic charge. Elements in groups 1 to 2 and 13 to 18 typically follow this pattern.
- Electron Configuration: Look at the electron configuration. Elements will often lose or gain electrons to achieve a full valence shell, similar to the nearest noble gas.
For Transition Metals:
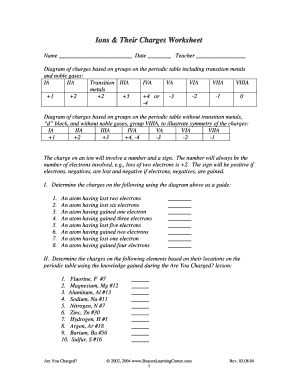
Transition metals are less straightforward as they can exhibit multiple ionic charges. Here are some tips:
- Common Charges: Iron (Fe) often forms +2 or +3 ions, Copper (Cu) typically forms +1 or +2 ions.
- Roman Numerals: Use Roman numerals in compound names to indicate the charge of the transition metal, e.g., Iron (III) Oxide.
- Historical Names: Traditional names like “Ferrous” or “Ferric” for iron also denote different ionic states.
Practical Tips for Predicting Charges
Here are some hands-on tips to improve your accuracy in predicting ionic charges:
Charge Tables:

| Element | Typical Charge |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | +1, -1 (Hydride) |
| Lithium (Li) | +1 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | +2 |
| Aluminum (Al) | +3 |
| Oxygen (O) | -2 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | -1 |

Patterns and Exceptions:

While there are patterns, chemistry is full of exceptions. Here are some common ones:
- Zinc (Zn): Always forms a +2 cation.
- Silver (Ag): Typically forms a +1 cation.
- Transition Metals: Can form multiple charges; using historical names or Roman numerals helps in identification.
Applying Your Knowledge

Once you’ve grasped the basics of predicting ionic charges, you can apply this knowledge to understand chemical reactions better, predict the solubility of compounds, and even delve into complex topics like oxidation states:
- Chemical Formulas: Write out chemical formulas with correct ionic charges to ensure proper balance of charges.
- Redox Reactions: Recognize the changes in oxidation states by understanding the charges involved in reactants and products.
- Complex Ions: Identify complex ions by their net charge, which might not always reflect the typical charge of the central metal ion.
💡 Note: Remember, transition metals can show multiple ionic charges, so context or historical names can be crucial in identifying their specific charge in compounds.
In summary, predicting ionic charges becomes intuitive with practice. The key is to understand the periodic table's group trends, the electron configurations, and be aware of the exceptions, especially with transition metals. This knowledge not only simplifies the understanding of chemical reactions but also enhances one's ability to predict the behavior of substances in various chemical contexts.
Why do some elements have multiple ionic charges?

+
Elements, particularly transition metals, can exhibit multiple ionic charges due to the availability of various energy levels for their electrons. This flexibility allows them to lose or gain electrons in different ways, depending on the reaction conditions or the atoms they are bonding with.
How can I remember the typical charges for each group?

+
Use mnemonic devices or patterns related to the group numbers in the periodic table. For example, elements in group 1 form +1 ions, and this pattern continues with group 2 forming +2, group 13 often forming +3, etc. Regular practice and visual aids like charge tables can also help.
What’s the difference between an ion and an isotope?

+
An ion is an atom or molecule with an electrical charge due to the loss or gain of electrons, whereas an isotope refers to atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, thus different masses, but the same number of protons.
How do ionic charges affect solubility?

+
The solubility of ionic compounds in water or other solvents depends on the nature of the ions involved. Generally, compounds with highly charged or larger ions tend to be less soluble due to stronger ionic bonding.
Can atoms become ions without losing or gaining electrons?
+
Yes, in some cases, atoms can become ions through the process of ionization, where they can lose or gain electrons due to the influence of electromagnetic radiation or high-energy collisions, not just chemical reactions.