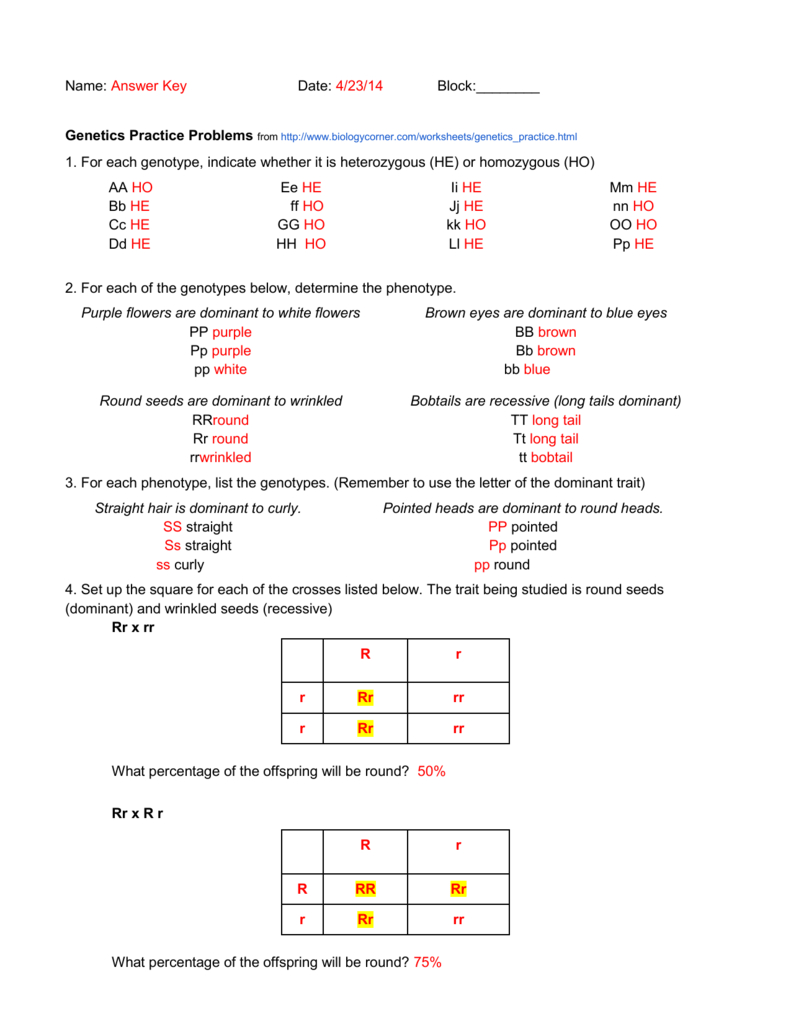
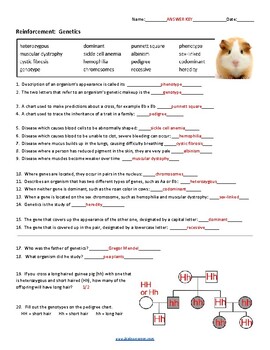
5 Key Answers for Basic Genetics Worksheet

In the field of genetics, understanding the basic principles and mechanisms is crucial for unraveling the complexities of inheritance, mutation, and the diversity of life. Here, we will delve into five key answers for a basic genetics worksheet, providing not only the answers but also the rationale behind them to enhance your understanding.
1. The Building Blocks of Life: DNA and Chromosomes


Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. It carries the instructions for development, function, growth, and reproduction. Here are the fundamental points about DNA:
- Each DNA molecule is composed of long strands, forming a double helix.
- Each strand consists of nucleotides, linked by sugar and phosphate backbones, with adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) as the bases.
- DNA is organized into structures known as chromosomes.
🌟 Note: Chromosomes are not just the result of DNA wrapping, but they are crucial for the accurate division and segregation of genetic material during cell division.
2. The Flow of Genetic Information: Central Dogma
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information:
- DNA Replication: The DNA molecule duplicates itself, ensuring each daughter cell receives a complete set of genes.
- Transcription: DNA's genetic information is copied into mRNA.
- Translation: mRNA serves as a template to synthesize proteins by ribosomes.
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Replication | DNA molecule replicates, creating identical copies for daughter cells. |
| Transcription | RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA from one DNA strand. |
| Translation | Ribosomes translate mRNA into proteins, guided by tRNA. |

3. Mendelian Genetics: Understanding Inheritance


Introduced by Gregor Mendel, Mendelian genetics explains how traits are passed from parents to offspring:
- Law of Segregation: Alleles separate into different gametes during meiosis.
- Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles for different traits segregate independently of each other.
- When studying inheritance patterns, consider both dominant and recessive alleles.
4. Genetic Mutations: Changes in DNA Sequence

A mutation is any alteration in the genetic material. Here are some key points:
- Mutations can occur due to errors in DNA replication, environmental factors, or chemicals.
- Types include:
- Point Mutations (substitution, deletion, insertion)
- Chromosomal Mutations (deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations)
- Some mutations are benign, while others can lead to genetic disorders or beneficial adaptations.
5. Genetic Variations: Source of Diversity

The diversity we see in living organisms is largely due to genetic variation. These variations come from:
- Recombination during sexual reproduction.
- Mutations.
- Gene flow between populations.
- Natural selection, genetic drift, and non-random mating.
🧬 Note: Genetic variations are the raw material for evolution, allowing species to adapt over time to environmental pressures.
By understanding these principles, we gain insights into the intricate mechanisms of life itself. From the basic structure of DNA to the inheritance patterns of traits, from the flow of genetic information to the impact of mutations, and the role of genetic variation in evolution, these concepts are the foundational pillars of genetics. As you move forward, this knowledge not only helps in comprehending how life works but also in tackling more advanced topics like gene regulation, epigenetics, and the application of genetics in medicine and biotechnology.
What is a gene?

+
A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein or RNA molecule, which in turn performs functions necessary for the cell’s operations.
Why are mutations significant?

+
Mutations introduce changes in the genetic code, which can lead to evolution, genetic disorders, or new traits. They are fundamental for genetic diversity.
How do chromosomes relate to DNA?

+
Chromosomes are structures within cells that contain a single, long DNA molecule, which carries many genes along with other DNA sequences that perform various regulatory functions.
Can genetic inheritance affect physical traits?
+
Absolutely. Physical traits, including eye color, hair texture, and even susceptibility to certain diseases, are influenced by genes inherited from parents.



