5 Proven Ways to Solve Multiple Allele Crosses Quickly

When delving into the complex world of genetics, particularly in the study of inheritance patterns, multiple alleles can introduce both complexity and fascination into our understanding. Whether you're a student grappling with basic genetic principles, or an enthusiast exploring the depths of genetic diversity, mastering multiple allele crosses can accelerate your learning curve and improve your analytical skills. Here, we'll explore five proven strategies to solve multiple allele crosses quickly and accurately, helping you to not just understand but excel in genetics.
Understanding Multiple Alleles
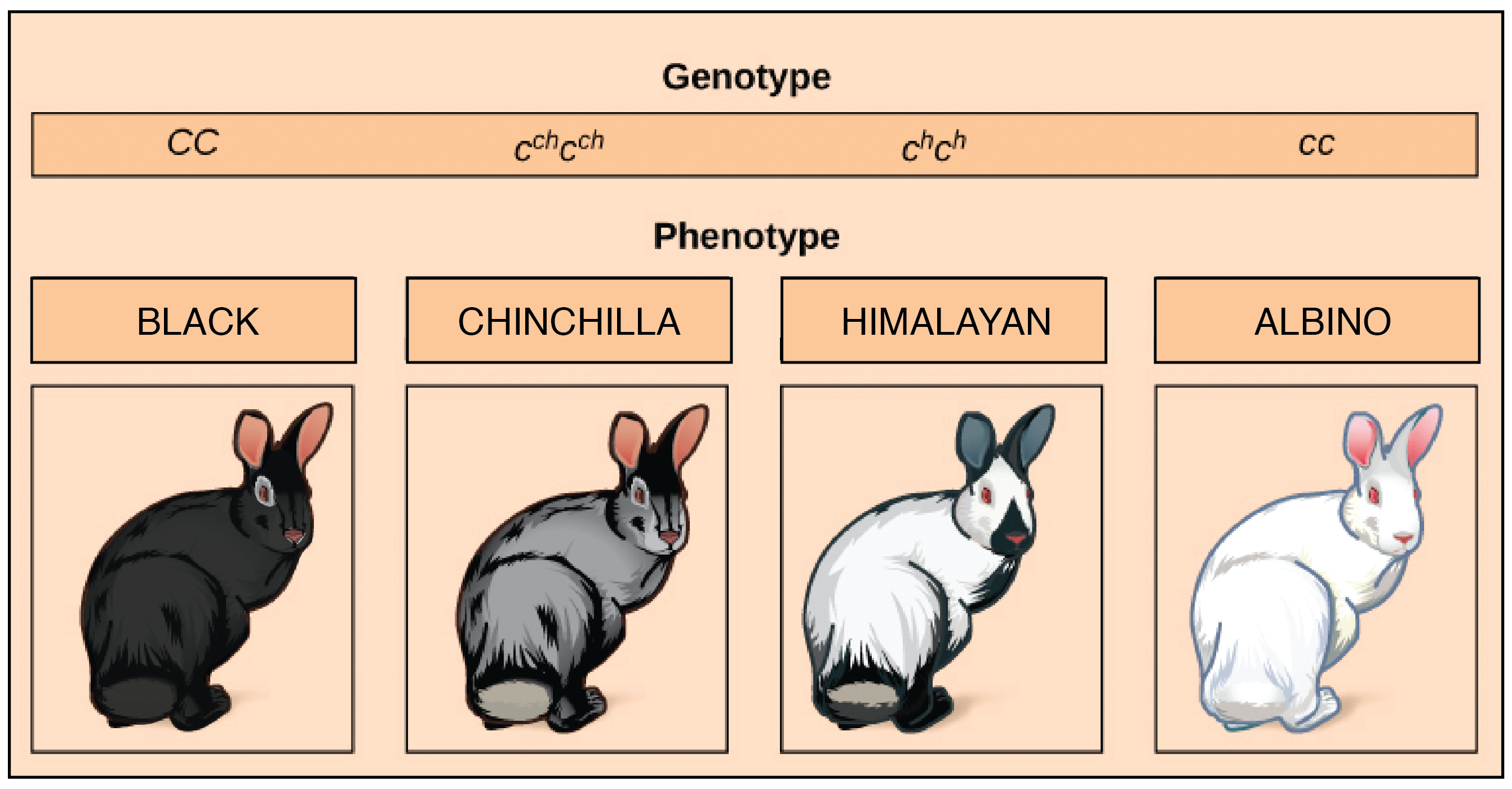
Multiple alleles refer to a series of alleles at a single locus in a population. Unlike simple Mendelian genetics where you often deal with only two alleles (like for eye color with brown and blue), multiple alleles offer a more varied gene pool. Classic examples include the ABO blood type system in humans, with alleles for type A, B, O, and the coat color in rabbits or cats.
Strategy 1: Use the Punnett Square for Clarity

One of the foundational tools in genetics is the Punnett Square. Here’s how you can use it for multiple allele crosses:
- Set up the Square: If dealing with a single gene system like blood types, draw a 3x3 square because each parent can contribute one of three alleles.
- Determine Parental Genotypes: Note that parents carry two alleles, but they can pass only one allele to their offspring. Write all possible allele combinations from each parent along the top and side of the square.
- Fill in the Square: Use the Punnett Square to predict the probability of offspring genotypes by filling in all possible combinations.
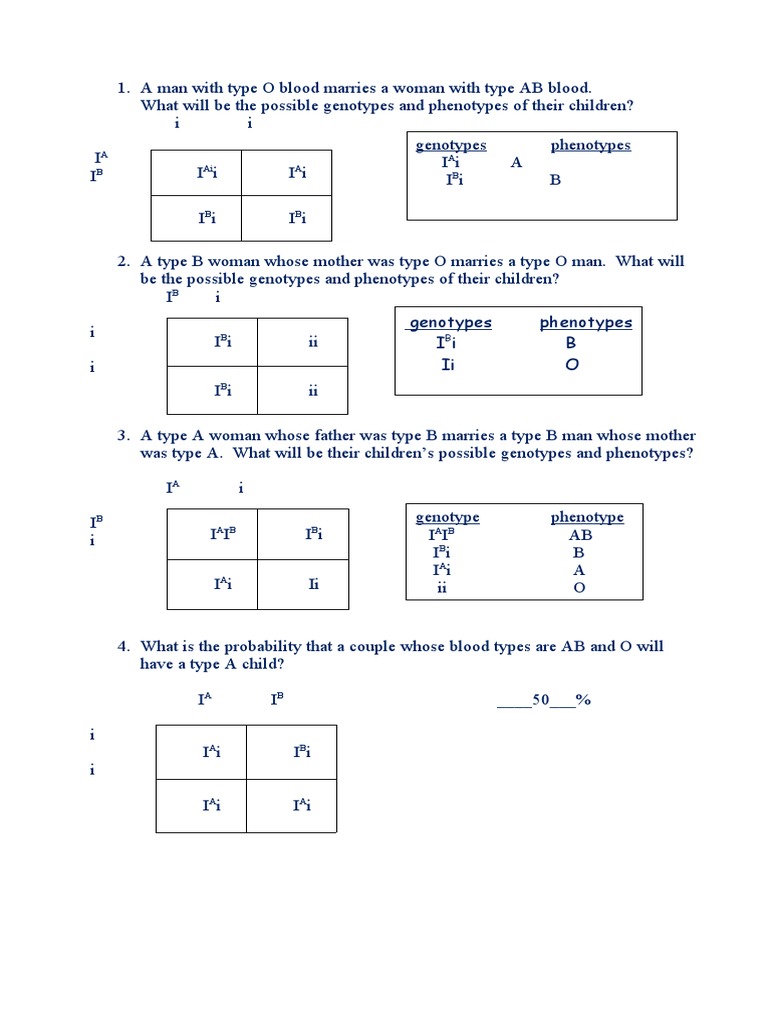
Image: [Placeholder for a visual of a Punnett Square for blood type inheritance]
Strategy 2: Leverage Genetic Ratios

Understanding the ratios of offspring genotypes or phenotypes can greatly simplify multiple allele problems:
- Ratios in ABO Blood Types: In humans, the possible genotypes lead to predictable ratios when considering ABO blood types. A person with type AB has a 100% chance of passing on either A or B, but someone with type O has 100% O.
- Punnett Square Shortcuts: For example, in a cross between an AB parent and an O parent, every offspring will be either A or B (but not AB), creating a simple ratio prediction.
Strategy 3: Color-Code Your Alleles

Visual aids can greatly simplify understanding complex genetic crosses:
- Use Colors: Assign colors to each allele (e.g., red for A, blue for B, and yellow for O in ABO blood types). This visual cue can help track genotypes and phenotypes more easily.
- Implement Colored Diagrams: Create visual representations or draw charts that use colors to distinguish between different alleles, enhancing your ability to follow the inheritance pattern.
Table:
| Blood Type | Alleles | Color Code |
|---|---|---|
| A | A and O | Red and Yellow |
| B | B and O | Blue and Yellow |
| O | O and O | Yellow and Yellow |
| AB | A and B | Red and Blue |
Strategy 4: Practice with Real-World Examples

Reinforcing theoretical knowledge with practical examples is one of the best ways to learn:
- Blood Type Inheritance: Use familial blood types to predict the likelihood of inheritance for offspring, helping to solidify your understanding of dominant, co-dominant, and recessive alleles.
- Case Studies: Study real-life case studies or scenarios from genetic counseling where multiple allele systems play a key role.
Strategy 5: Simplify through Memorization

While genetics involves much more than memorization, there are certain facts that, once learned, can save time:
- Memorize Genetic Terminology: Terms like heterozygous, homozygous, dominant, co-dominant, and recessive can be memorized to understand and quickly solve allele crosses.
- Know Common Alleles: Familiarize yourself with commonly studied alleles in species like humans, fruit flies, or lab animals for quick recognition.
💡 Note: Memorization should complement understanding, not replace it. Use these shortcuts to enhance your problem-solving speed, not to bypass the process of learning genetics.
In our exploration of these strategies, we've delved into various methods to manage the complexity of multiple allele crosses. By applying the Punnett Square method, understanding genetic ratios, employing visual aids like color-coding, practicing with real-world scenarios, and memorizing key genetic concepts, you can enhance your ability to solve these problems quickly. Each strategy builds upon the next, creating a comprehensive toolkit for tackling genetics challenges. The next time you encounter a multiple allele problem, remember these tips to demystify the process and see your problem-solving capabilities soar.
What are multiple alleles?

+
Multiple alleles refer to a set of three or more alleles that can exist at a single gene locus within a population. This contrasts with simple dominant-recessive traits where only two alleles are typically considered.
Can you give an example of a multiple allele system?

+
A classic example is the ABO blood type system in humans, where there are three alleles (A, B, and O) that determine blood group.
Why are Punnett Squares useful for multiple allele crosses?

+
Punnett Squares visually represent the probability of inheriting each possible combination of alleles from parents, making complex genetics problems more manageable.
How does color-coding alleles help in genetic analysis?

+
Color-coding alleles provides a visual reference that simplifies tracking inheritance patterns and understanding the genetic outcomes, especially in cases with co-dominant alleles like AB blood type.