Electron Configuration Worksheet: Master Chemistry Easily
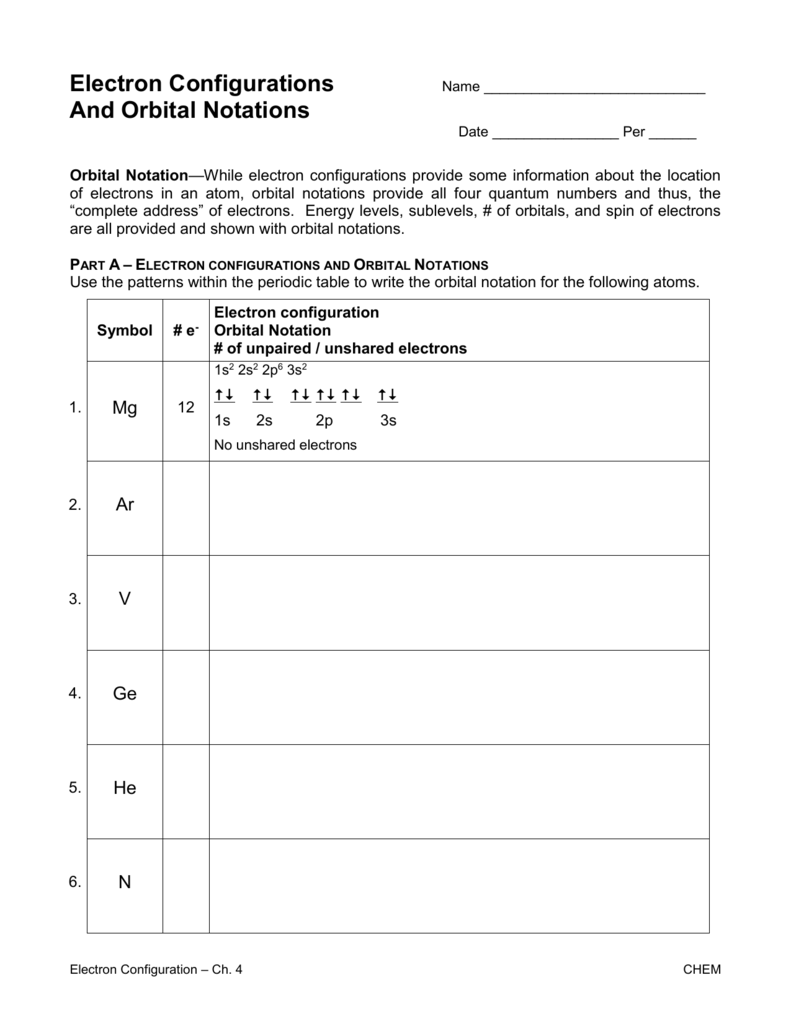
If you are looking to master electron configurations, this detailed guide is designed to help you understand and excel in this fundamental concept of chemistry. Electron configuration is more than just a notation on the periodic table; it is the key to understanding how atoms bond, form compounds, and interact in reactions. This article will take you through the essentials, from the basics to advanced applications, ensuring that by the end, you'll have a robust understanding of electron configurations.
What is Electron Configuration?

Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in atomic orbitals. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Atomic Orbital: An area around an atom where electrons are likely to be found.
- Electrons: These are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom.
- Energy Levels: Shells or levels where electrons can exist. These levels are designated by the quantum number (n).
⚠️ Note: Electron configurations are depicted with numbers and letters representing principal energy levels and subshells respectively.
Why is Electron Configuration Important?

- Understanding Atomic Structure: Electron configurations reveal how the electrons are distributed which affects how atoms will react and form bonds.
- Periodic Trends: They explain trends like electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic size.
- Chemical Reactivity: Knowing an atom’s electron configuration helps predict its chemical behavior.
Basic Rules of Electron Configuration

Before diving into the intricacies of writing electron configurations, here are some fundamental rules:
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill orbitals starting from the lowest energy level.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: Each orbital can contain a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
- Hund’s Rule: Electrons will singly occupy orbitals of equal energy before pairing up.
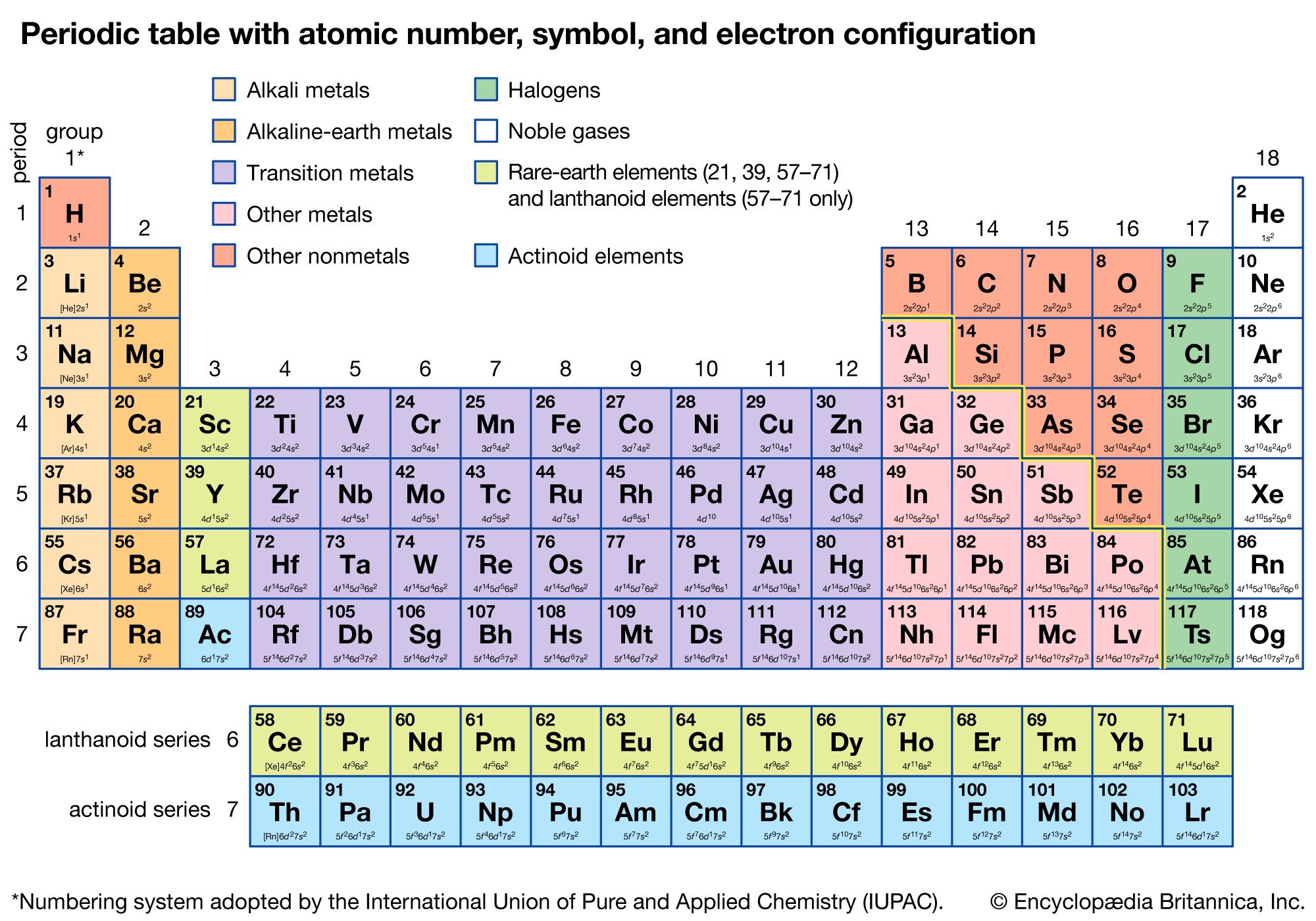
| Principle Energy Levels | Subshell | Number of Orbitals | Maximum Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| n=1 | 1s | 1 | 2 |
| n=2 | 2s, 2p | 1, 3 | 2, 6 |
| n=3 | 3s, 3p, 3d | 1, 3, 5 | 2, 6, 10 |
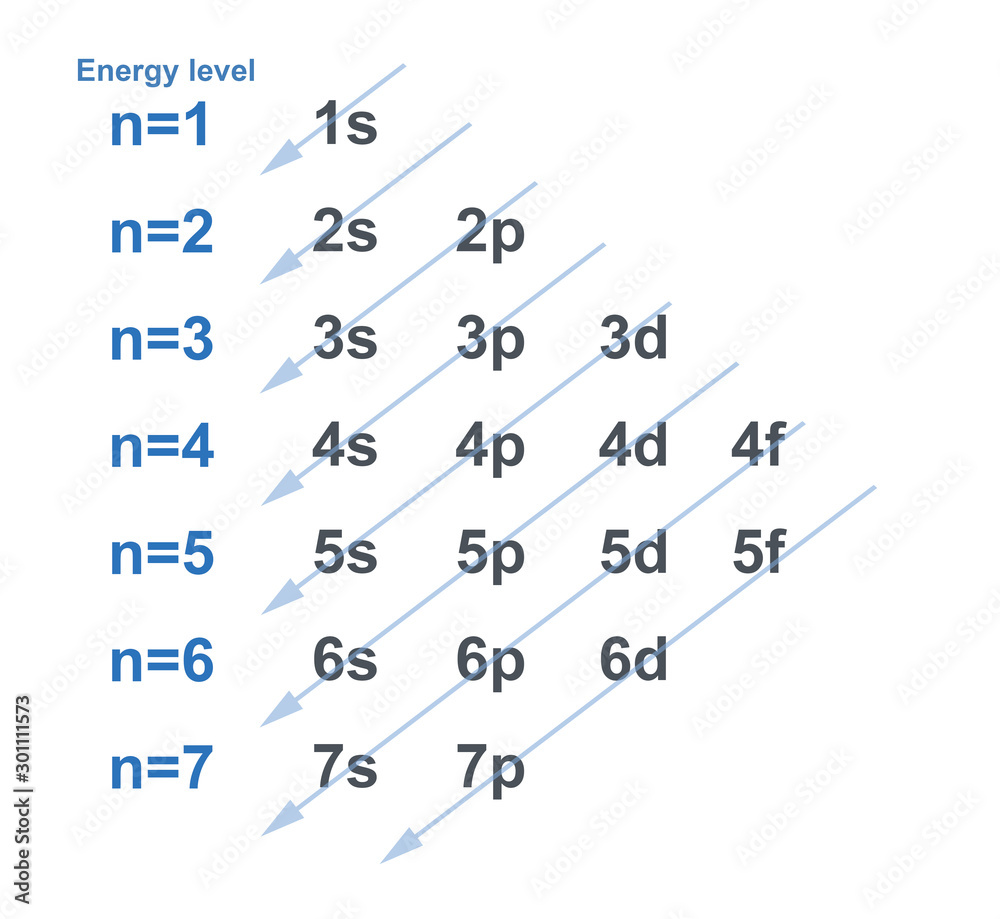
🌟 Note: Remember that the order of filling is not always sequential due to the overlap of energy levels as shown in the Aufbau diagram.
Steps to Write Electron Configurations

- Identify the Atomic Number: This number tells us the number of protons, which also equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
- Use the Aufbau Diagram: Fill the electron configurations according to the Aufbau sequence (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, etc.).
- Apply the Three Principles: Adhere to Aufbau, Pauli, and Hund’s rules when placing electrons.
- Notate Correctly: Use the notation like 1s22s22p6 to indicate the distribution.
📚 Note: For atoms with many electrons, mastering the shorthand notation (using noble gas cores) can save time and reduce errors.
Practical Applications of Electron Configurations
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding electron configurations helps predict which atoms will bond and how.
- Magnetism: The unpaired electrons in an atom determine its magnetic properties.
- Spectroscopy: Electron transitions between energy levels can be observed and analyzed through spectroscopic techniques.
Advanced Concepts

Here are some advanced applications of electron configurations:
- Orbital Hybridization: Explains bonding in complex molecules by mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals.
- Lewis Structures: Visualize bonding by drawing electron configurations for molecules.
- Molecular Orbital Theory: Describes how electron configurations change upon bonding between atoms.
Tips for Mastering Electron Configurations

- Practice Regularly: Repetition helps solidify the patterns.
- Use Mnemonics: Develop memory aids like “silly Sally swiftly shooed seven sheep,” which can help remember the Aufbau sequence.
- Visual Aids: Use diagrams and electron configuration charts to visualize the process.
- Group Study: Explaining electron configurations to others can reinforce your understanding.
- Integrate with Periodic Table: Use periodic trends to predict configurations and vice versa.
As we've explored, understanding and mastering electron configurations is crucial for anyone delving into chemistry. It's the foundation that explains atomic interactions, chemical bonding, and many other aspects of chemistry. By following the principles outlined here, practicing with examples, and using various learning aids, you can improve your grasp of this vital concept, turning complex chemistry into something you can easily navigate.
What does the term ‘electron configuration’ mean?

+
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in the energy levels, sublevels, and orbitals of an atom.
How do I know which energy level an electron will fill first?

+
The Aufbau principle dictates that electrons fill energy levels from the lowest to highest. However, there are exceptions due to overlap, which can be remembered using diagrams or mnemonics.
Why are electron configurations important for chemical reactions?

+
Electron configurations indicate the number of valence electrons, which determine an atom’s ability to form bonds, react, and participate in chemical reactions.



