Mastering DNA Replication: Your Essential Worksheet Guide
In the intricate world of biology, understanding the process of DNA replication is crucial for anyone interested in genetics, molecular biology, or biomedical sciences. This complex yet fundamental process ensures that every cell in an organism receives an exact copy of the genetic material necessary for its function and survival. Whether you're a student navigating through high school biology or an undergrad in a life sciences program, mastering DNA replication through interactive worksheets can significantly enhance your comprehension and retention of this vital concept.
What is DNA Replication?
DNA replication is the biological process by which cells copy their DNA before cell division. This process is pivotal for genetic continuity. Here's a brief overview:
- Origin of replication: DNA replication begins at specific points in the genome known as origins of replication.
- Unwinding: Enzymes called helicases unwind the double helix, creating a replication fork.
- Single-stranded binding proteins: These proteins stabilize the unwound DNA strands.
- Primase: Synthesizes an RNA primer, a short sequence necessary to start DNA synthesis.
- DNA polymerases: These enzymes extend the primer, synthesizing new DNA strands in a 5' to 3' direction, adding nucleotides to the growing chain.
- Leading and Lagging strands: The continuous synthesis occurs on the leading strand, whereas the lagging strand forms Okazaki fragments which are later connected.
- Proofreading and repair: DNA polymerases have a proofreading function, correcting mistakes during replication.
Why Use Worksheets?

Worksheets are an effective tool for learning DNA replication because:
- They provide a structured method for practicing and retaining knowledge.
- They break down complex information into manageable parts, aiding in memory consolidation.
- They engage visual and kinesthetic learners by offering diagrams and interactive activities.
- They can include varied question types like multiple choice, fill-in-the-blanks, labeling diagrams, etc., which cater to different learning styles.
- They encourage self-assessment, helping students identify areas they need to review.
Components of an Effective DNA Replication Worksheet

A well-designed worksheet should include the following elements:
- Overview of DNA replication: A brief recap of what DNA replication entails.
- Step-by-step replication process: Breaking down the replication process into stages for clarity.
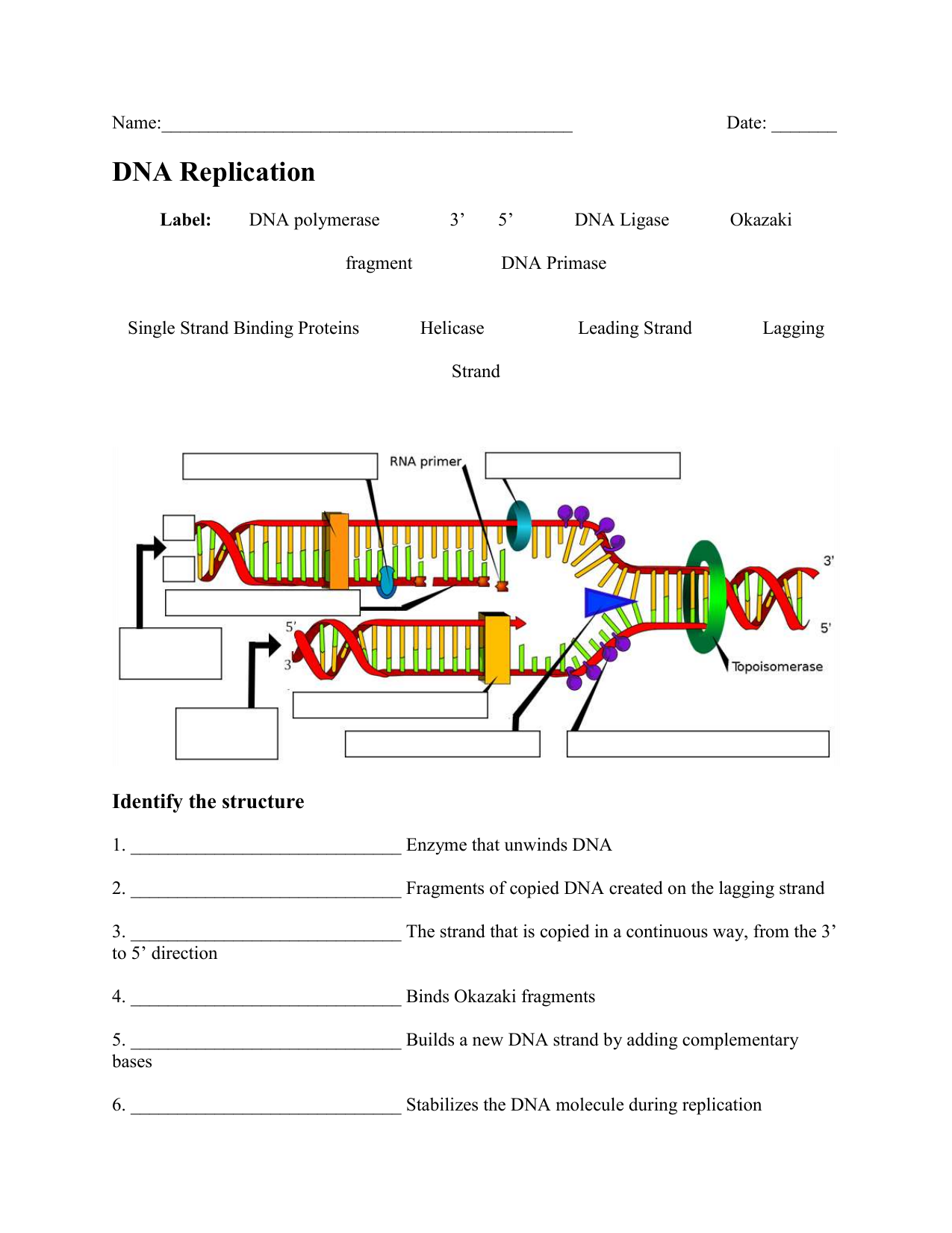
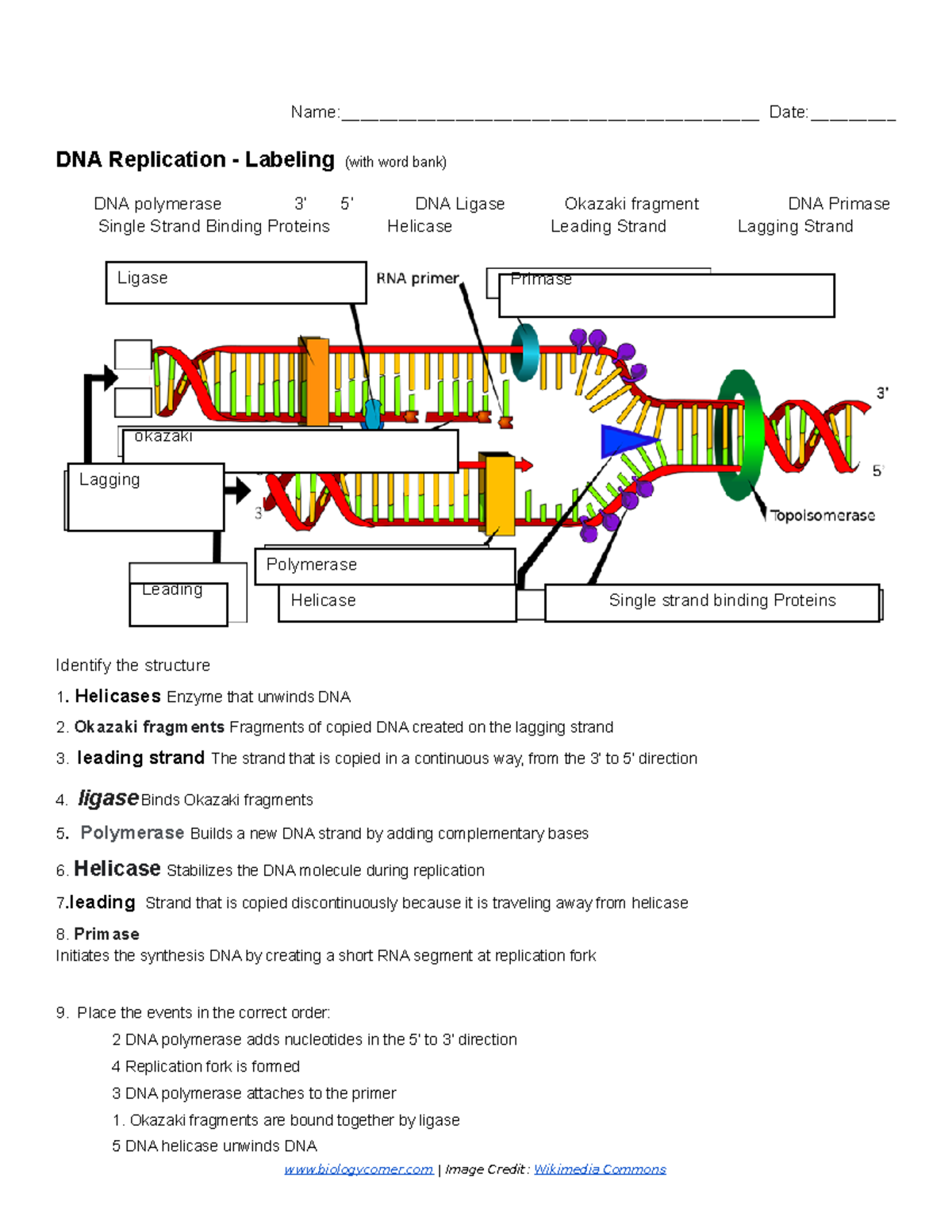
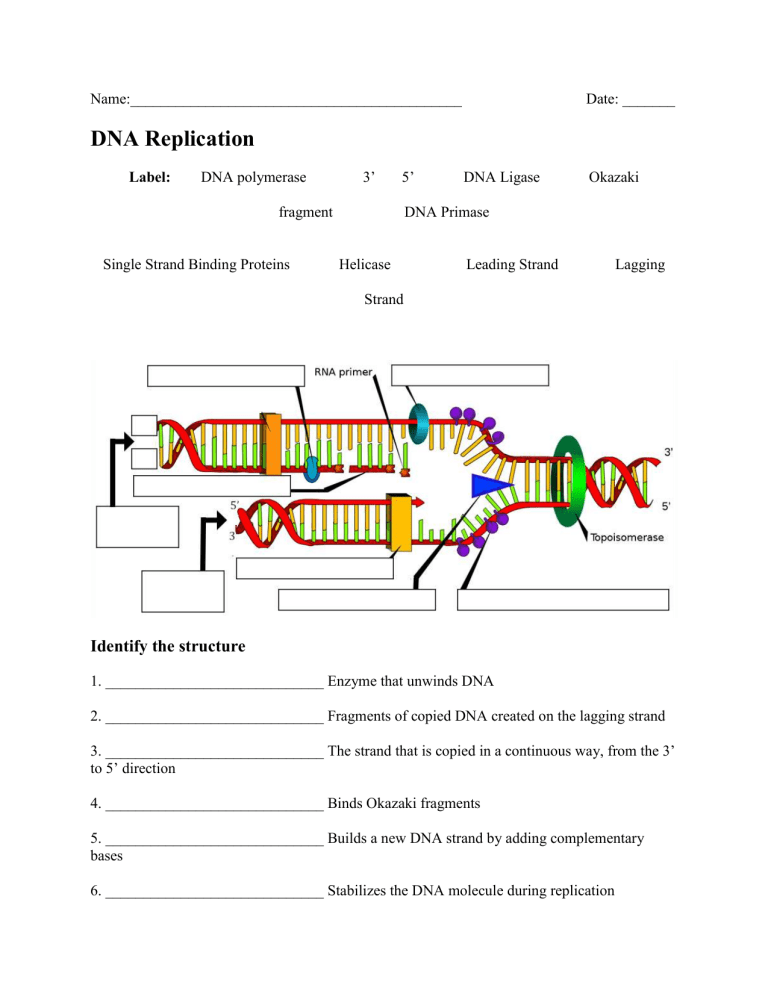
- Labeling diagrams: Worksheets should include diagrams of the replication fork with labels to identify enzymes and other key components.
- Short answer questions: Encouraging students to explain processes or predict outcomes.
- Multiple-choice questions: To reinforce learning of facts and terminology.
- Open-ended questions: To stimulate higher-order thinking and application of knowledge.
- Crossword or word search puzzles: Fun ways to familiarize with terminology.
Example Worksheet Layout

Here's a sample layout for a DNA replication worksheet:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Overview and importance of DNA replication. |
| Fill-in-the-Blanks | Students fill in the blanks to complete sentences about replication steps. |
| Label the Diagram | A diagram of a replication fork with labels missing; students label parts like helicase, primase, etc. |
| Multiple Choice | Questions to solidify knowledge on enzymes, DNA strands, and replication process details. |
| Short Answers | Students explain the role of enzymes, or describe the semi-conservative nature of replication. |
| Application | Scenario-based questions where students predict outcomes or errors in replication. |
| Crossword or Puzzle | Vocabulary and terminology puzzles to reinforce learning. |
| Review | Space for notes or a brief summary for self-assessment. |

Let's dive into how you might design a question for each section:
- Fill-in-the-Blanks: "The enzyme that unwinds the DNA helix at the replication fork is called _______ (helicase)."
- Label the Diagram: Provide a replication fork diagram with labels missing, asking students to label the leading strand, lagging strand, primase, Okazaki fragments, etc.
- Multiple Choice: "Which enzyme is responsible for synthesizing RNA primers during DNA replication? A) DNA Polymerase III, B) Primase, C) Topoisomerase, D) Single-stranded Binding Protein"
- Short Answers: "Explain the difference between leading and lagging strand synthesis."
- Application: "A mistake in replication has led to a mismatched base pair in a gene important for a protein. Describe what happens next."
- Puzzle: A crossword or word search with terms like polymerase, helicase, replication fork, etc.
📝 Note: Worksheets can be tailored to the learner's knowledge level, so adjusting the complexity and focus of questions is important for effective learning.
The essence of mastering DNA replication through worksheets is not just about memorization but understanding the intricate dance of enzymes and nucleotides that ensure the continuation of life at its most fundamental level. The structured format of worksheets, when used effectively, can help demystify this process, making it accessible and intriguing for learners of all ages.
Regular practice with these worksheets can lead to a deeper understanding, aiding in exam preparation or even in personal enrichment in the field of biology. They provide a valuable framework for revisiting key concepts, reinforcing knowledge through varied question types, and encouraging critical thinking about one of nature's most essential mechanisms.
What is the significance of Okazaki fragments?

+
Okazaki fragments are essential in DNA replication for synthesizing the lagging strand. Since DNA synthesis occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction and the strands are antiparallel, the lagging strand needs to be synthesized in short segments that are later joined together. These fragments facilitate this discontinuous synthesis process.
How does proofreading occur during DNA replication?
+
DNA polymerases have a 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity, which allows them to remove nucleotides that have been incorrectly paired during replication. This proofreading mechanism ensures high accuracy in copying the genetic code.
Why do cells replicate DNA?

+
Cells replicate DNA to ensure that each new cell formed during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) has an exact copy of the genetic material. This replication is crucial for growth, repair, reproduction, and maintaining genetic continuity across generations.



