5 Key Answers for Coulomb's Law Worksheet
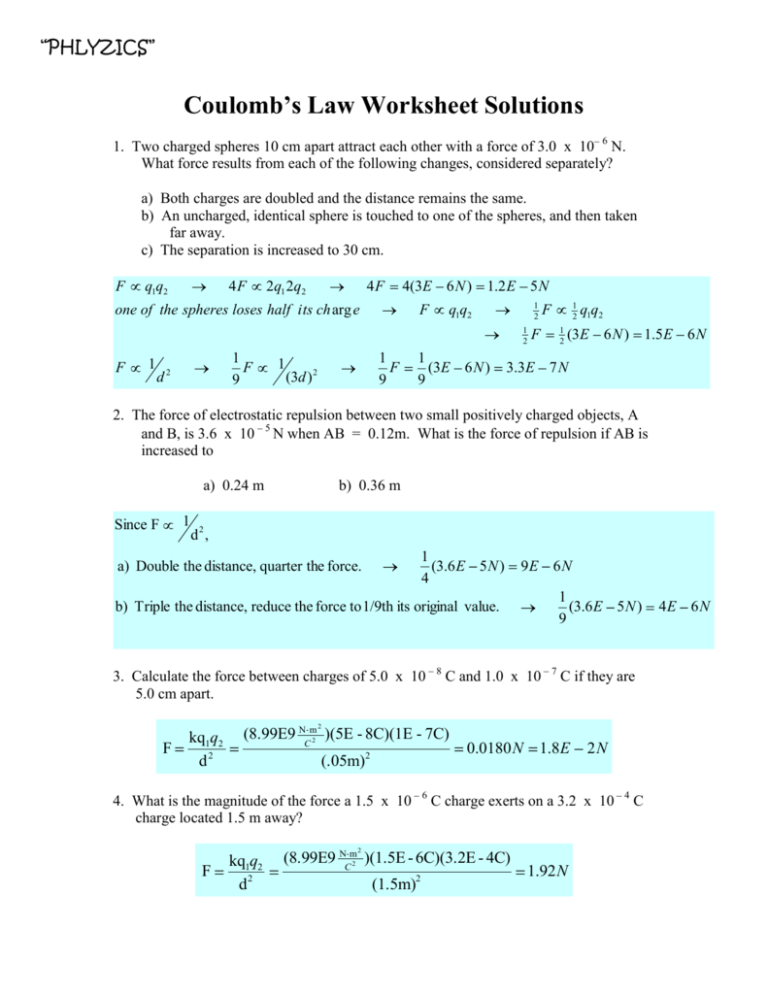
"Coulomb's Law Worksheet Answer Key"
Coulomb's law is fundamental for understanding the interaction between electrically charged particles. This simple formula captures the relationship between two point charges, which is expressed as: F = k_e * (q_1 * q_2) / r^2. Here, F stands for the electrostatic force, k_e is Coulomb's constant, q_1 and q_2 are the magnitudes of the charges, and r is the distance between them. As we delve into Coulomb's Law through the lens of a worksheet, let's explore five key answers to common problems that arise when dealing with this principle.
1. Understanding the Basics of Coulomb's Law

Before diving into calculations, it's essential to grasp the basic understanding of Coulomb's Law:
- Force (F): It's a vector quantity, pointing from one charge to the other. If the charges are like (both positive or both negative), the force is repulsive, and if unlike, it's attractive.
- Coulomb's Constant (k_e): In vacuum or air, its value is approximately 8.99 x 10^9 Nm²/C².
- Charge: Quantified in Coulombs (C) or microCoulombs (µC).
- Distance: Measured from the center of one charge to the center of another.

2. Calculating the Electrostatic Force Between Two Charges
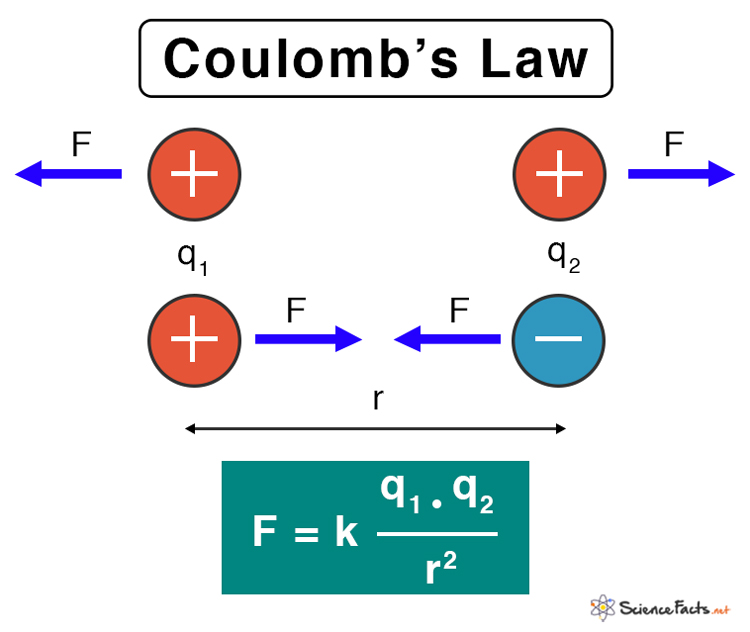
Let's take a worksheet problem to illustrate:
Two charges, q_1 = 3 µC and q_2 = -4 µC, are located 2 meters apart in a vacuum. Find the force they exert on each other:
- First, convert charges to Coulombs: q_1 = 3 * 10^-6 C, q_2 = -4 * 10^-6 C.
- Plug into Coulomb's equation: F = (8.99 * 10^9 Nm²/C²) * ((3 * 10^-6) * (-4 * 10^-6) / (2 m)²).
- Simplify to find F = -27 N.
⚡ Note: The negative sign indicates attraction, as unlike charges pull towards each other.
3. Charge Distribution on Conductors

Worksheet questions often involve understanding how charges distribute on conductors:
- Charges on a conductor reside on its surface, not inside, to minimize potential energy.
- Distribution is such that the field inside is zero, and outside, the charge density is highest where the curvature of the surface is greatest.
| Charge Quantity | Distance (r) | Force Magnitude | Attractive/Repulsive |
|---|---|---|---|
| +5 µC | 3m | 24.97 N | Repulsive |
| -7 µC | 4m | 22.38 N | Attractive |

🔹 Note: For spherical conductors, the electric field inside is zero. For other shapes, use vector superposition of charge distributions.
4. Electrostatic Fields Due to Multiple Charges

Calculating the electric field at a point due to multiple charges involves summing up the electric fields from each charge:
Take for example three charges placed at specific points in space:
- Charge A: +5 nC at (-1, 1) in Cartesian coordinates.
- Charge B: -6 nC at (1, -2).
- Charge C: +3 nC at (0, -2).
Find the electric field at (1, 0):
- Calculate the fields from each charge using E = k * q / r^2
- Add vectorially, accounting for direction to find the resultant electric field.

⚡ Note: Use geometric methods or vector components to sum up electric fields. Remember the directionality from the charges' signs.
5. Applications of Coulomb's Law

In real-world applications, Coulomb's Law has numerous uses:
- Electrostatic Precipitators: For dust and pollution removal.
- Inkjet Printers: Where ink droplets are precisely controlled using charge interactions.
- Electric Potential: Understanding charge behavior in terms of potential energy and work done.
As we conclude our exploration through Coulomb's Law, we've covered the basic principles, how to calculate force between charges, the behavior of charges on conductors, summing up electric fields, and practical applications. Understanding Coulomb's Law is pivotal for anyone delving into electromagnetism, electronics, or even everyday phenomena like static electricity. By grasping these concepts, you gain insights into how the invisible forces shape our physical world, from the minuscule to the grand scale.
What is the significance of the inverse square law in Coulomb’s Law?

+
The inverse square law is fundamental to how electrostatic forces decrease with distance. It shows that the force falls off rapidly with increasing distance, which has profound implications in the distribution of charge, electric field strength, and how fields spread out in space.
How does Coulomb’s Law relate to Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation?

+
Both laws follow the inverse square law, with Coulomb’s involving electric charges and Newton’s dealing with mass. However, gravitational force is always attractive, whereas electrostatic forces can be both attractive and repulsive, depending on the charges’ nature.
What are some common mistakes made when working with Coulomb’s Law?

+
Frequent errors include not accounting for signs of charges (forgetting that opposite charges attract and like charges repel), misusing units (e.g., not converting microCoulombs to Coulombs), and incorrectly summing up vector forces without considering direction.



