5 Tips to Master Coulomb's Law in Physics

Understanding Coulomb's Law is essential for anyone delving into the fascinating world of physics, particularly in electromagnetism. Named after the French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, this law provides a fundamental framework for understanding the electric force between two charged particles. Whether you're a student struggling with physics homework or a curious enthusiast exploring the mysteries of electricity, here are five essential tips to help you master Coulomb's Law.
Understand the Basic Formula


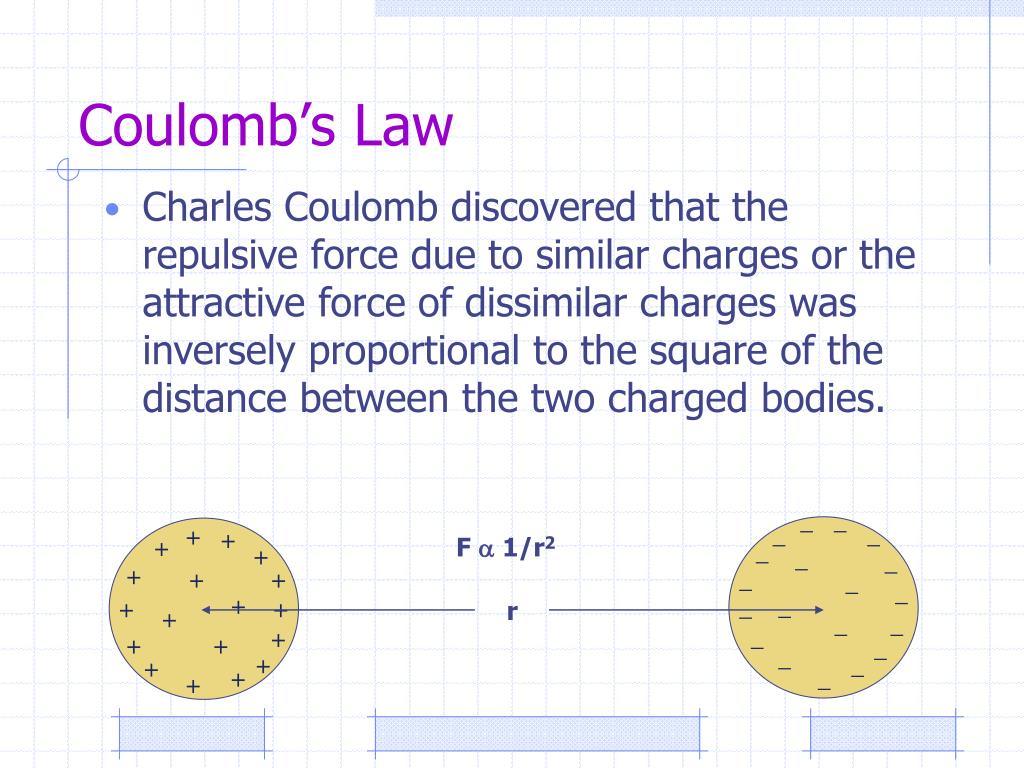
The cornerstone of Coulomb’s Law is the equation:
F = k * (q₁ * q₂) / r²
- F: The magnitude of the electric force between two point charges.
- k: Coulomb’s constant, approximately 8.99 x 10⁹ Nm²/C² in vacuum or air.
- q₁ and q₂: The charges on the two particles in coulombs ©.
- r: The distance between the centers of the two charges in meters (m).
📝 Note: Remember that this force can be attractive (if the charges have opposite signs) or repulsive (if the charges have the same sign).
Master the Concept of Electric Field


An electric field surrounds a charge, and understanding this concept is vital for applying Coulomb’s Law in more complex scenarios. Here’s how to approach it:
- Every charge creates an electric field around itself which affects the force experienced by other charges.
- The strength of the electric field (E) at a point due to a single point charge can be found using: E = k * q / r²
- Learn to visualize and sketch electric fields for different charge configurations to better understand the interactions.
🧭 Note: The direction of the field lines is away from positive charges and towards negative charges.
Get Comfortable with Vector Analysis


Coulomb’s Law often involves forces that aren’t directly in line with the axes you might be working with. Here’s how to handle vector components:
| Vector Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Force Direction | Along the line connecting the charges. |
| Decomposition | Force can be broken into x, y, or z components for easier calculation. |
| Sign Convention | Force is repulsive if both charges are positive or negative; attractive if charges are opposite. |

By resolving forces into their x, y, and z components, you can simplify calculations and better understand the resultant force on each charge.
⚠️ Note: Use vector addition to find the net force when there are multiple charges affecting a single particle.
Apply It Practically

Physics isn’t just about theory; it’s about application. Here are some practical approaches:
- Use simulations or interactive tools to visualize the forces acting between charges.
- Construct simple experiments using basic tools like charged balloons, hanging threads, and a straw to observe Coulomb’s Law in action.
- Relate Coulomb’s Law to everyday scenarios like the force exerted by a charged object on a neutral one or static electricity.
Practice with Worked Examples

To truly master Coulomb’s Law, one must work through numerous examples. Here are some tips:
- Start with simple scenarios: two charges in a vacuum, and gradually increase complexity.
- Include situations where the medium isn’t air or vacuum, considering the effect of dielectric constants.
- Review past exam problems or online resources for practice questions.
🔍 Note: Always check units and pay attention to the signs of charges in your calculations.
In mastering Coulomb’s Law, consistency in your study approach and understanding the interconnectedness of charge, electric field, and force are key. By grasping the fundamental concepts, practicing with examples, and applying the theory to real-life situations, you'll build a solid foundation in electromagnetism, opening doors to deeper physics exploration. Through these tips, the law's complexity and beauty become more accessible, making it easier for you to navigate through the intricate patterns of electric forces in our universe.
What is the significance of Coulomb’s Law in everyday life?
+
Coulomb’s Law explains phenomena like static electricity, lightning, and the behavior of charged particles in technology like inkjet printers, static eliminators, and touch screens.
Can Coulomb’s Law be applied in non-vacuum environments?

+
Yes, in non-vacuum environments, the force is still governed by Coulomb’s Law but modified by the dielectric constant of the medium, which reduces the force compared to a vacuum.
How does Coulomb’s Law relate to the electric field?

+
The electric field created by a charge can be thought of as the force per unit charge that would act on a positive test charge placed at a point in space. The relationship is given by E = F/q, where E is the electric field, F is the force, and q is the test charge.
What happens when two charged objects are brought closer together?

+
According to Coulomb’s Law, as the distance between two charged objects decreases, the force between them increases inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r²), making the force stronger as they get closer.
Why is Coulomb’s constant a key part of the law?

+
Coulomb’s constant (k) provides the proportionality factor between the product of charges and the distance squared, ensuring the units work out to give the correct force in Newtons (N) and also accounting for the electromagnetic nature of the interaction.



