Unlocking the Secrets: Plasma Membrane Structure Answer Key
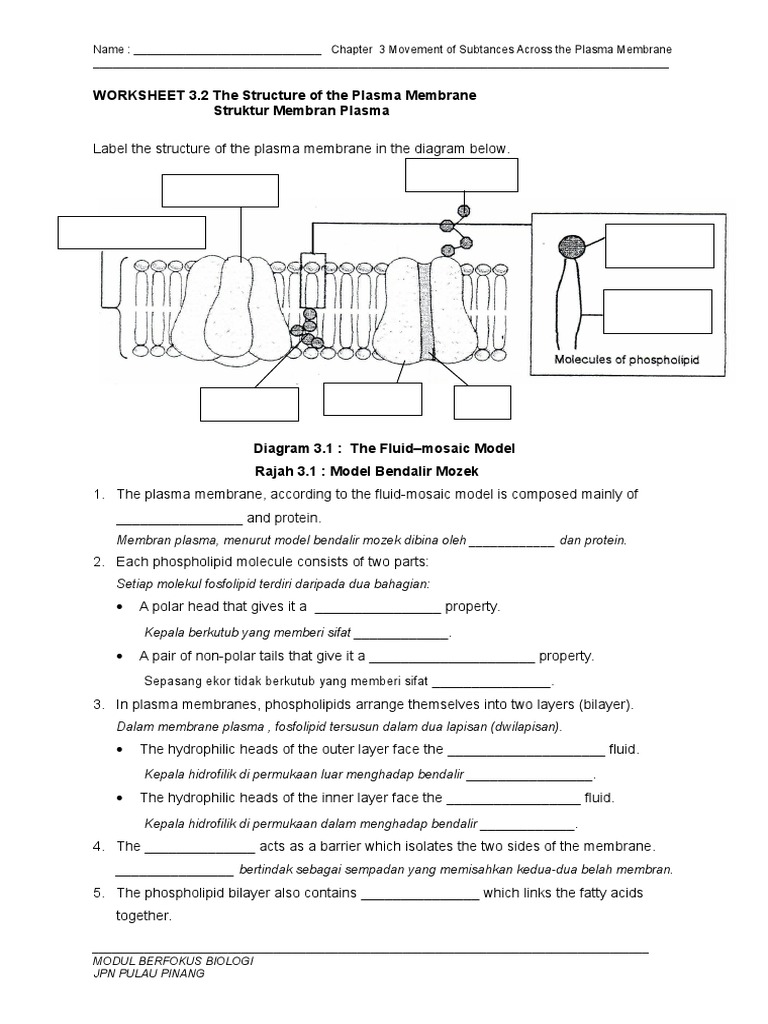
The plasma membrane, commonly known as the cell membrane, is a complex structure that not only envelops each cell but also serves as a dynamic barrier for regulating the flow of substances in and out. Understanding the structure of the plasma membrane is fundamental for students and professionals in biology, biochemistry, and related fields. This blog post delves into the intricacies of the plasma membrane's structure, providing a comprehensive answer key for better understanding and study.
The Composition of the Plasma Membrane

The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier, composed primarily of:
- Phospholipids: Forming the lipid bilayer, these are the primary structural components.
- Proteins: Including integral and peripheral proteins which perform various functions.
- Carbohydrates: Often attached to proteins or lipids, forming glycocalyx.
- Cholesterol: Stabilizes the fluidity of the membrane.

Phospholipid Bilayer

The phospholipid bilayer is the core structure of the plasma membrane. Each phospholipid molecule consists of:
- A hydrophilic head that faces the aqueous environment.
- Two hydrophobic tails that form the interior of the membrane, avoiding water.
💡 Note: This amphipathic nature of phospholipids allows them to spontaneously form a bilayer in an aqueous environment, optimizing both hydrophobic interactions.
Membrane Proteins

Membrane proteins are crucial for various cellular activities:
- Integral Proteins: Embedded within the membrane, they can function as ion channels, carriers, or receptors.
- Peripheral Proteins: Associated with the membrane's surface, they can act as enzymes or in signal transduction.
The proteins create a dynamic environment, moving within the lipid bilayer, which leads to the fluid mosaic model:
Fluid Mosaic Model
This model explains:
- The fluidity of the membrane due to the movement of lipids and proteins.
- The mosaic-like pattern where proteins are embedded in or attached to the lipid bilayer.
Carbohydrates and Glycoproteins

Carbohydrates in the form of glycolipids and glycoproteins are critical for:
- Cell-cell recognition.
- Formation of glycocalyx, which aids in cell adhesion and immune protection.
Cholesterol

Cholesterol:
- Reduces permeability to small, water-soluble molecules.
- Prevents phase transitions, maintaining fluidity in a broader temperature range.
Here's a simple table illustrating the components of the plasma membrane:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Phospholipids | Form the lipid bilayer structure |
| Proteins | Various functions like transport, enzyme activity, and signaling |
| Carbohydrates | Cell recognition and adhesion |
| Cholesterol | Regulates fluidity and permeability |

By understanding the structure of the plasma membrane, we gain insights into how cells maintain their internal environment, interact with external environments, and how various membrane-bound proteins function. This knowledge is vital for understanding cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
Why is the plasma membrane called a "fluid mosaic"?

+
The term "fluid mosaic" refers to the dynamic nature of the plasma membrane where lipids and proteins are free to move within the membrane, creating a mosaic pattern within a fluid environment.
What role do integral proteins play in the plasma membrane?

+
Integral proteins can serve as channels for ions or molecules, act as carriers for transport, or function as receptors for signaling molecules. They are essential for cellular communication and transport mechanisms.
How does cholesterol affect the fluidity of the plasma membrane?

+
Cholesterol helps in maintaining the fluidity of the membrane by reducing the packing of phospholipids, preventing phase transitions, and making the membrane less permeable to certain substances.
Can the structure of the plasma membrane change?

+
Yes, the structure of the plasma membrane can change dynamically in response to various stimuli like temperature, pH, or cell signaling events to adjust its function or to respond to external or internal changes.
By exploring the intricacies of the plasma membrane, we’ve uncovered the key elements that make it a dynamic and essential barrier for life. These insights not only deepen our appreciation for cellular biology but also pave the way for advancements in medical research, therapeutics, and cellular engineering. The fluid mosaic model continues to be a foundational concept in understanding how life functions at the smallest scale, making the study of plasma membrane structure both fascinating and essential.