Mastering Worksheet 19.1: AD-AS Model Explained

The Aggregate Demand-Aggregate Supply (AD-AS) model is a pivotal concept in economics that helps us understand the fluctuations in the overall economy. Whether you're studying for an economics course or you're just curious about how national economies work, grasping this model is crucial. Let's delve into Worksheet 19.1, which focuses on the AD-AS model, and understand its intricacies.
Introduction to AD-AS Model


At its core, the AD-AS model illustrates the relationship between the total quantity of goods and services demanded in an economy and the total quantity supplied. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Aggregate Demand (AD): The sum of all expenditures in the economy at various price levels.
- Aggregate Supply (AS): The total production of goods and services that firms plan to sell at each price level.
Now let’s move forward to analyze how these curves interact to determine equilibrium price levels and output.
Equilibrium in the AD-AS Model

The equilibrium in the AD-AS model occurs where the AD curve intersects the AS curve. At this point:
- The economy is at full employment, meaning all who wish to work at current wage rates can find employment.
- The price level and real GDP are at a level where supply equals demand.
Short-Run and Long-Run Equilibrium

The AD-AS model can describe two forms of equilibrium:
- Short-Run Equilibrium: Here, the AS curve is relatively elastic, meaning changes in demand can significantly affect output levels without much impact on prices.
- Long-Run Equilibrium: This occurs when both AD and AS are fully adjusted. In the long run, the economy naturally adjusts to full employment output, and the AS curve becomes vertical at this level.
Shifts in AD and AS Curves

Changes in economic variables can shift these curves, impacting the equilibrium:
Shifts in Aggregate Demand

Aggregate Demand can shift due to changes in:
- Consumer Confidence
- Government Spending
- Investment by Businesses
- Net Exports
A rightward shift in AD leads to higher output and potentially higher price levels in the short run, while a leftward shift can result in economic contraction.
Shifts in Aggregate Supply

Aggregate Supply shifts can result from:
- Changes in Resource Prices
- Technological Innovations
- Changes in Expectations
- Taxation and Subsidy Policies
A rightward shift in AS implies an increase in the economy’s productive capacity, potentially lowering prices or increasing output without inflation.
Interpreting Worksheet 19.1
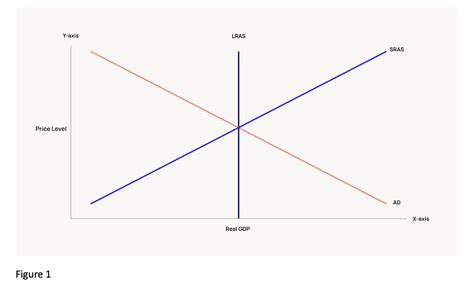
Worksheet 19.1 typically includes scenarios where you’re asked to analyze the effects of various economic shocks or policy changes on the AD-AS model:
| Scenario | Effect on AD | Effect on AS | Equilibrium Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in government spending | Increase (Right) | None | Output and Prices Increase |
| Technological Advance | None | Increase (Right) | Output Increases, Prices Decrease |
| Decrease in Consumer Confidence | Decrease (Left) | None | Output and Prices Decrease |
| Rise in Oil Prices | None | Decrease (Left) | Output Decreases, Prices Increase |

Analyzing Scenarios

When you encounter a scenario in Worksheet 19.1:
- Identify whether the change affects AD, AS, or both.
- Determine the direction of the shift.
- Assess the new equilibrium point, considering the short-run and potential long-run outcomes.
🛈 Note: Always consider the nature of the shock or policy change. Temporary shocks might affect only the short-run, while permanent changes will influence both short-run and long-run equilibriums.
In the end, mastering the AD-AS model through worksheets like 19.1 gives you the tools to not only understand economic policies but also to analyze the implications of various economic events on output, employment, and price levels. This understanding helps in crafting or assessing economic strategies to achieve desired economic outcomes.
What causes the AD curve to shift?
+
Aggregate Demand (AD) shifts due to changes in consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports. Factors like consumer confidence, tax policies, or global economic conditions can all influence these components.
How does an increase in the price of raw materials affect the AS curve?

+
An increase in raw material prices increases production costs, leading to a leftward shift in the AS curve, meaning reduced supply at each price level.
Can the AD curve shift in response to changes in the AS curve?

+
Yes, but indirectly. If AS shifts leftward, it can lead to higher prices, which might reduce consumer confidence, thus indirectly affecting AD through lower consumer spending.
What are the implications of operating below full employment on the AD-AS model?

+
Operating below full employment suggests that the economy is not at its potential output. This can lead to policy actions aimed at increasing aggregate demand to close the gap.
How can technology shift the AS curve?

+
Technological advances can increase productivity, effectively moving the AS curve to the right, allowing for more output at lower prices due to reduced production costs.