Measuring Segments Worksheet 1-2 Answers Unveiled

In the realm of geometry, measuring segments is one of the fundamental skills students need to master. This skill not only enhances understanding of spatial awareness but also forms the basis for more complex calculations involving lines, angles, and shapes. In this extensive blog post, we delve into the specifics of Measuring Segments Worksheet 1-2 Answers, providing a detailed breakdown of how to solve the problems, the underlying principles, and some advanced insights that can help in mastering this topic.
Understanding the Basics of Segment Measurement

Before we dive into the worksheet answers, let’s quickly revisit some key concepts:
- Line Segment: A part of a line with two defined endpoints.
- Distance: The length between these endpoints, which can be measured using various tools like rulers, calipers, or compasses.
- Units: Commonly, distances in geometry are measured in centimeters (cm) or millimeters (mm) unless otherwise specified.
The Worksheet Overview

The Measuring Segments Worksheet 1-2 contains several exercises where students are asked to measure given line segments or to construct segments of specific lengths. Here’s how you approach these questions:
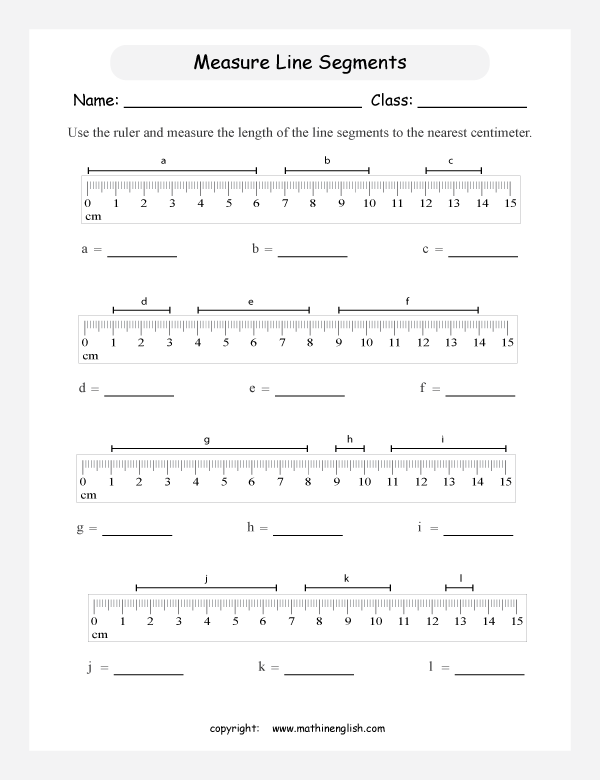
Question 1: Identifying and Measuring

In this section, students are presented with segments of various lengths. Here are the steps to measure them:
- Place the zero mark of your ruler at one endpoint of the segment.
- Read the measurement where the ruler meets the other endpoint.
- Ensure your ruler is straight and parallel to the segment for accuracy.
Answers:
| Segment | Length (cm) |
|---|---|
| A | 5.2 |
| B | 8.5 |
| C | 3.7 |

📏 Note: Always ensure your ruler is straight and properly aligned with the segment to avoid measurement errors.
Question 2: Construction

Here, students must construct segments of given lengths. Follow these steps:
- Use a straightedge to draw a horizontal line.
- Mark the start of your segment with a dot or an endpoint.
- Measure and mark the desired length from this point using your ruler.
- Connect the endpoint to the mark with another straight line segment.
Advanced Tips for Measuring Segments

- Use Different Units: Understanding how to convert between units like centimeters to inches or vice versa can be very useful.
- Check for Precision: When precision is required, ensure you’re reading from the zero mark of the ruler or using a caliper for the smallest increments.
- Practice with Real-Life Examples: Measuring everyday objects can help solidify the concept. Try estimating lengths before measuring to improve your spatial judgment.
🧠 Note: Advanced students might benefit from exploring vector space and coordinate geometry, where segment length can be calculated using distance formulas.
Recapping the Importance of Segment Measurement
To sum it up, mastering the measurement of line segments is crucial for:
- Understanding foundational geometric principles.
- Preparing for more complex mathematical tasks involving distances, areas, and volumes.
- Developing practical skills that apply to fields like engineering, architecture, and even everyday tasks.
What are the most common mistakes when measuring segments?

+
Common errors include misalignment of the ruler, reading from the wrong mark (not the zero), and estimating rather than measuring exactly.
Can I use a digital tool to measure segments?
+
Yes, software like GeoGebra or even some advanced drawing applications can measure segments digitally with high accuracy.
How can I improve my accuracy in measuring segments?

+
Practice with precision tools like calipers, always align the ruler’s zero with one endpoint, and ensure your segment is straight and not curved or bent.