Welder's Work Environment: Hazards and Safety Precautions

Welder's Work Environment: Hazards and Safety Precautions
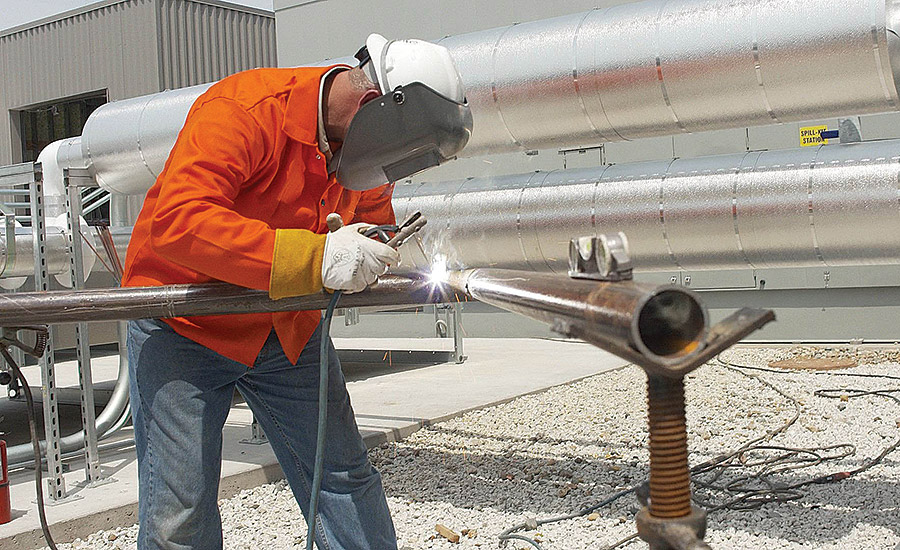

Welding is a crucial process in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and repair. However, it poses significant risks to the health and safety of welders if proper precautions are not taken. The work environment of a welder is filled with hazards that can cause injuries, illnesses, and even fatalities. In this article, we will discuss the common hazards in a welder’s work environment and the essential safety precautions to mitigate these risks.
Hazards in a Welder's Work Environment

A welder’s work environment is filled with hazards that can be broadly classified into physical, chemical, and biological hazards.
Physical Hazards
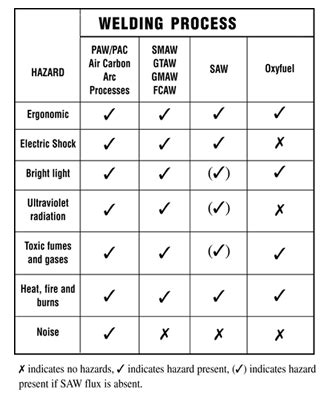
- Electric Shock: Welding equipment can be a source of electric shock, especially if it is not properly maintained or used.
- Arc Flash: The intense heat and light emitted by the welding arc can cause burns and eye damage.
- Fire and Explosion: The sparks and hot metal particles generated during welding can ignite flammable materials, causing fires and explosions.
- Noise: Welding processes can generate high levels of noise, leading to hearing loss and other auditory problems.
Chemical Hazards
- Fumes and Gases: Welding processes release fumes and gases, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and ozone, which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Chemical Burns: The use of chemical cleaning agents and other substances in welding can cause chemical burns and skin irritation.
Biological Hazards
- Infectious Diseases: Welders may be exposed to infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis, from contaminated equipment or work environments.
- Cancer: Prolonged exposure to welding fumes and other carcinogenic substances can increase the risk of cancer.
Safety Precautions for Welders

To mitigate the hazards in a welder’s work environment, it is essential to implement safety precautions, including:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Welding Helmet: A welding helmet with a shaded lens can protect the eyes and face from the intense heat and light of the welding arc.
- Gloves: Insulated gloves can prevent electrical shock and protect the hands from heat and flames.
- Welding Jacket and Pants: Fire-resistant clothing can protect the skin from burns and flames.
- Respiratory Protection: A respirator can filter out fumes and gases, reducing the risk of respiratory problems.
Work Environment Safety
- Proper Ventilation: Good ventilation can reduce the concentration of fumes and gases in the work environment.
- Fire Prevention: Keeping the work environment clean and free of flammable materials can prevent fires and explosions.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance of welding equipment can prevent electrical shock and other hazards.
Safe Welding Practices
- Proper Training: Welders should receive proper training on safe welding practices and equipment operation.
- Work at a Safe Distance: Welders should work at a safe distance from the welding arc to prevent eye damage and burns.
- Use Proper Welding Techniques: Welders should use proper welding techniques to prevent accidents and injuries.
Importance of Safety Training and Equipment Maintenance

Safety training and equipment maintenance are crucial in preventing accidents and injuries in the welding industry.
- Regular Safety Training: Regular safety training can ensure that welders are aware of the hazards in their work environment and know how to mitigate them.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regular equipment maintenance can prevent electrical shock, arc flash, and other hazards associated with welding equipment.
Conclusion

Welding is a hazardous occupation that requires careful attention to safety precautions. By understanding the hazards in a welder’s work environment and implementing safety precautions, welders can reduce the risk of injuries and illnesses. It is essential for employers to provide regular safety training and equipment maintenance to ensure a safe working environment for welders.
What are the most common hazards in a welder’s work environment?
+
The most common hazards in a welder’s work environment include electric shock, arc flash, fire and explosion, noise, fumes and gases, chemical burns, infectious diseases, and cancer.
What personal protective equipment (PPE) should welders wear?

+
Welders should wear a welding helmet with a shaded lens, insulated gloves, welding jacket and pants, and a respirator to protect themselves from the hazards of welding.
Why is regular safety training and equipment maintenance important?

+
Regular safety training and equipment maintenance are crucial in preventing accidents and injuries in the welding industry. They can help welders understand the hazards in their work environment and know how to mitigate them.



