5 Fascinating Facts About Yellowstone Wolves

Imagine the serene, almost untouched wilderness of Yellowstone National Park, where nature thrives in its most raw and splendid form. Among the many incredible residents of this unique ecosystem, wolves capture the heart and imagination like none other. They have become iconic figures, not just for their majestic nature, but for the pivotal role they play in balancing this biodiverse haven. Here, we delve into five fascinating facts about Yellowstone wolves, revealing their intriguing lives, complex behaviors, and the immense ecological impact they have.
1. The Reintroduction of Wolves to Yellowstone


In 1995, wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone National Park after an absence of over seventy years. This decision marked a pivotal moment in conservation history. Here are some key points:
- Decision Context: The reintroduction aimed to address imbalances created by the eradication of wolves in the early 1900s. Without wolves, the park's ecosystem, particularly its predator-prey dynamics, had been significantly altered.
- Reintroduction Process: Wolves were carefully selected from Canada, primarily from Alberta, and were brought to Yellowstone in crates.
- Impact: The wolves' reintroduction has been pivotal, catalyzing what is known as a "trophic cascade," where their presence influenced not just prey species but the entire food web and landscape.
2. The Yellowstone Wolf Project
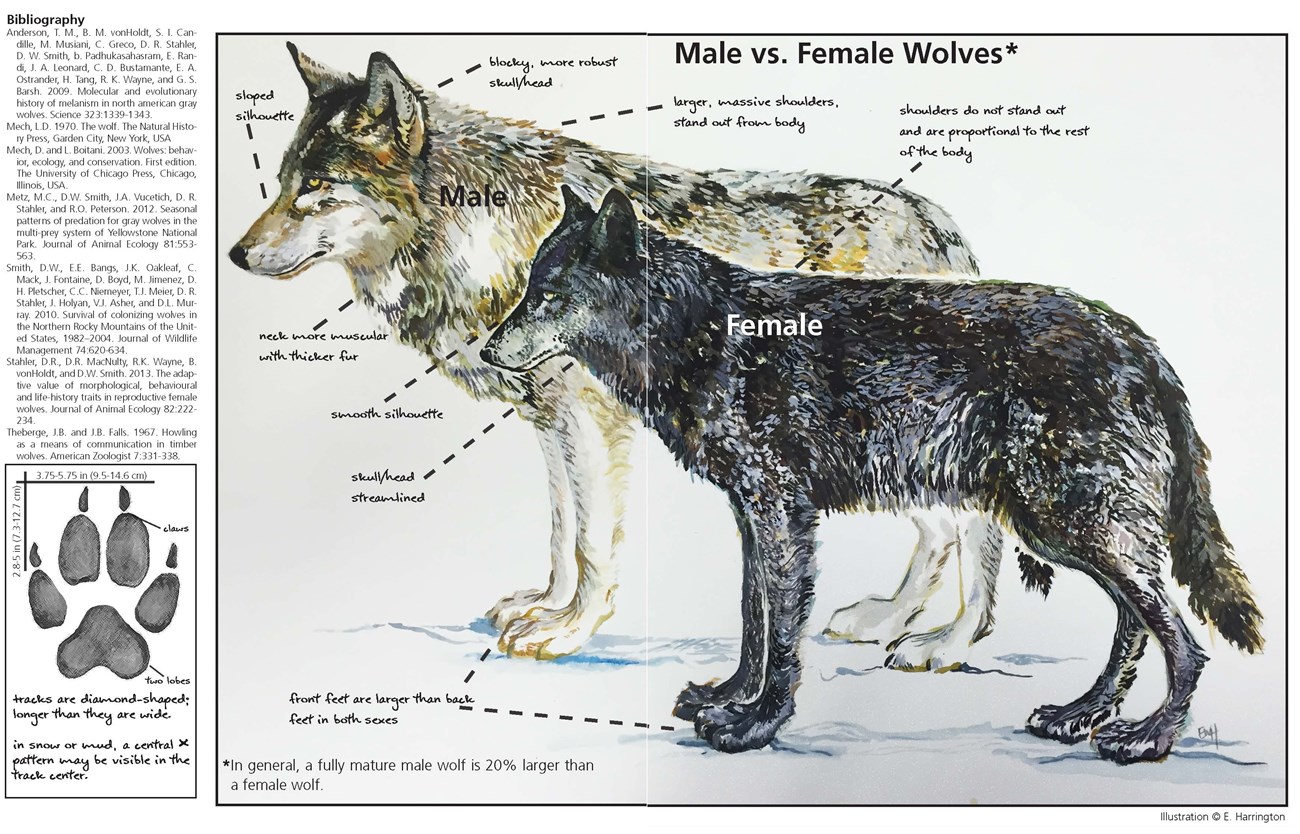
The Yellowstone Wolf Project, initiated in the mid-1990s, has been instrumental in studying the ecological and behavioral aspects of these fascinating animals:
- Research Objectives: The project aims to understand wolf population dynamics, predation patterns, and their interaction with other species.
- Findings: Wolves have been found to not only control the elk population but indirectly affect a range of other animals and vegetation by altering prey behavior and distribution.
- Technological Advancements: The use of GPS collars, cameras, and other advanced technologies has allowed for detailed monitoring of wolves' movements and behaviors.
3. The Role of Wolves in Ecological Balance

Wolves have proven to be more than just top predators; they are vital ecosystem engineers:
- Trophic Cascade: By reducing the number of elk, wolves help young trees and willows grow, providing habitat for species like beavers and migratory birds.
- Vegetation: The change in elk feeding behavior due to wolves has allowed for the regeneration of vegetation, benefiting the park's overall health.
- Waterways: Increased vegetation stabilizes stream banks, improving water quality and habitat for aquatic species.
🌱 Note: Wolves indirectly foster biodiversity by creating conditions that allow various species to thrive.
4. Wolf Social Structure and Behavior

The social structure of Yellowstone wolves is intricate and fascinating:
- Pack Dynamics: Wolves live in packs, typically consisting of an alpha pair, their offspring, and sometimes related adults. This social structure is essential for hunting, protection, and raising young.
- Communication: Wolves use a combination of vocalizations, body language, and scent marking to communicate within the pack.
- Hierarchy: The alpha wolves lead, and social status is established through behaviors like standing tall, tail positions, and aggressive displays.
5. Challenges and Controversies

Despite their ecological benefits, wolves in Yellowstone face several challenges:
- Public Perception: The wolf's status as both an emblem of conservation success and a potential threat to livestock in neighboring areas has led to heated debates.
- Management: Balancing the recovery of the wolf population with the needs of local residents and other wildlife species is a constant challenge.
- Political Influence: Decisions regarding wolf management often reflect political rather than purely ecological considerations.
As we wrap up this journey into the world of Yellowstone wolves, it's clear that these animals are not just important for their own existence but for the health and diversity of the entire ecosystem. Their story is one of survival, adaptation, and the intricate dance of nature. From their pivotal role in the food chain to the complexities of human-wolf coexistence, Yellowstone wolves embody the balance that nature strives for. Their presence has reshaped the park, offering a living example of how vital biodiversity is for ecological health and how complex conservation can be when human interests come into play.
Why were wolves reintroduced to Yellowstone?
+
Wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone in 1995 to restore ecological balance by controlling the elk population, which had grown exponentially in their absence, affecting the park’s vegetation and other wildlife.
How do wolves affect other species in Yellowstone?

+
Through predation and fear, wolves change the behavior of prey species like elk, allowing vegetation to recover, which benefits species from beavers to migratory birds.
What is a trophic cascade?

+
A trophic cascade refers to the indirect impacts of an apex predator on lower trophic levels via its effects on its prey. In Yellowstone, wolves indirectly support a variety of species by controlling the elk population, thus allowing plant life to thrive.