5 Essential Answers for White Man's Burden Worksheet

Understanding complex concepts from historical literature like Rudyard Kipling's poem "The White Man's Burden" can be quite a challenge. This analysis not only helps in understanding historical contexts but also explores themes of imperialism, racial superiority, and moral duty. Here are five essential answers that will assist you in completing a worksheet on "The White Man's Burden".
The Historical Context
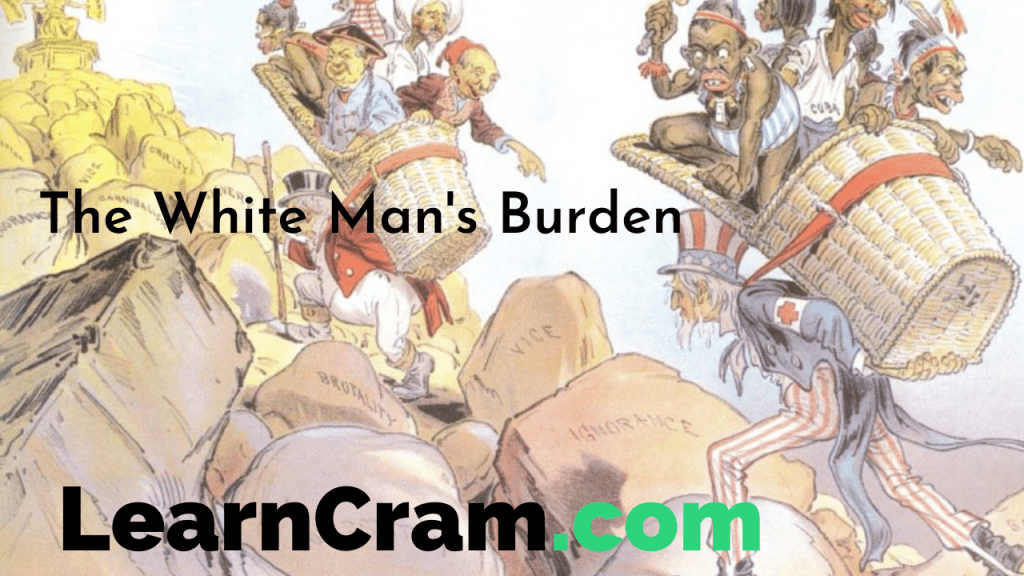
First and foremost, it’s crucial to understand the historical context in which Rudyard Kipling wrote his poem in 1899:
- The Spanish-American War: Kipling’s poem was written in the context of this war, where the United States emerged as a colonial power by acquiring territories like Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines.
- Imperialism and Colonialism: The late 19th century was the peak of European imperialism, where colonial powers sought to extend their influence over territories around the globe.
- Justification of Colonization: Kipling’s work provides a rationale for why Western powers felt it was their duty to “civilize” non-Western nations.
🔍 Note: Kipling’s poem reflects the attitudes of the time towards colonization, which we now view through a lens of cultural imperialism and ethnocentrism.
Interpreting the Poem

To interpret “The White Man’s Burden,” consider these key points:
- Racial Hierarchy: The poem assumes a superior role for the white race, offering a burden in the form of moral and cultural enlightenment to the colonized.
- Duty vs. Exploitation: There is a dual narrative where the colonizers are both burdened with a duty and criticized for exploiting those they seek to help.
- Sacrifice and Nobility: The idea of sacrifice is celebrated, highlighting the supposed noble intentions behind colonialism.
Reactions and Critique

The poem wasn’t without controversy. Here are some reactions and critiques:
- Support from Imperialists: It was seen as a justification for imperialism by proponents.
- Criticism by Anti-Imperialists: Many, including Mark Twain, used it to expose and criticize the underlying racist and paternalistic attitudes.
- Modern Perspectives: Today, it’s often studied as an example of colonial literature that propagated racial stereotypes and justified imperialism.
The Burden’s Impact

The impact of “The White Man’s Burden” extends beyond its immediate historical context:
- Political Influence: It influenced political discourse, providing a rhetorical device for pro-imperialist factions.
- Cultural Influence: The poem has been referenced in various cultural works, highlighting its lasting effect on perceptions of race and colonialism.
- Educational Purposes: It’s used in educational settings to discuss themes of imperialism, ethics, and historical justification.
The Burden in Modern Literature

The phrase “White Man’s Burden” has transcended Kipling’s original poem:
- Parodies and Satires: Works like Mark Twain’s “To the Person Sitting in Darkness” parody the idea of moral superiority.
- Critical Analysis: Modern scholars and authors critique or reinterpret the poem to understand and discuss imperialism’s legacy.
- Revisiting History: Contemporary authors often look back on the poem to reflect on how these attitudes have shaped colonial history and its aftermath.
In concluding our analysis of "The White Man's Burden," we've touched upon the historical backdrop, the poem's interpretation, the reactions it incited, its lasting impact, and how it resonates in modern literature. The poem encapsulates not only Kipling's vision of imperialism but also the broader imperialist sentiment of his era, making it a profound study of historical ethics and cultural attitudes. This examination provides a deeper understanding of how literature can both reflect and influence societal views, especially on contentious topics like colonialism and racial superiority.
What was Rudyard Kipling’s personal view on imperialism?

+
Rudyard Kipling was a proponent of British imperialism. He believed in the moral duty of Britain to bring civilization, technology, and Christian values to less developed parts of the world, a view reflected in his work.
How did “The White Man’s Burden” influence policy?

+
While not directly influencing policy, the poem shaped public discourse, making it easier for imperialistic policies to be supported by the populace, especially in countries like the United States and Britain during their imperial expansions.
Why is “The White Man’s Burden” relevant today?

+
The poem remains relevant because it captures historical attitudes toward race, colonialism, and imperialism. It serves as a lens through which modern society can critique past and present forms of cultural superiority and paternalistic interventions in international relations.
How should we approach studying “The White Man’s Burden” today?

+
Approach the poem with a critical eye, understanding its historical context, while also considering modern perspectives on race, ethics, and the lasting effects of colonialism. It’s crucial to acknowledge both the poem’s cultural impact and its problematic nature.