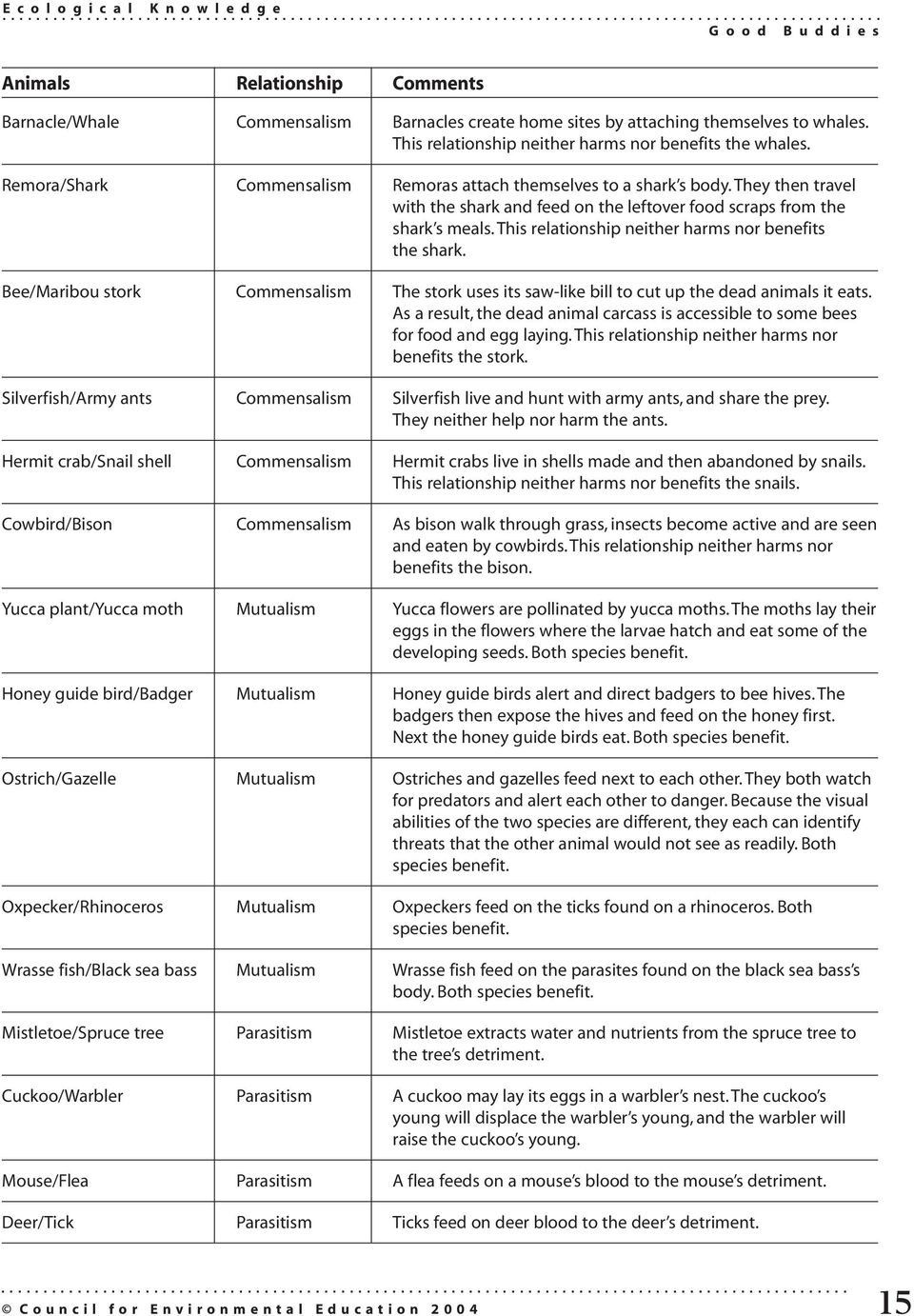
5 Ways to Identify Symbiosis Types: Worksheet Guide

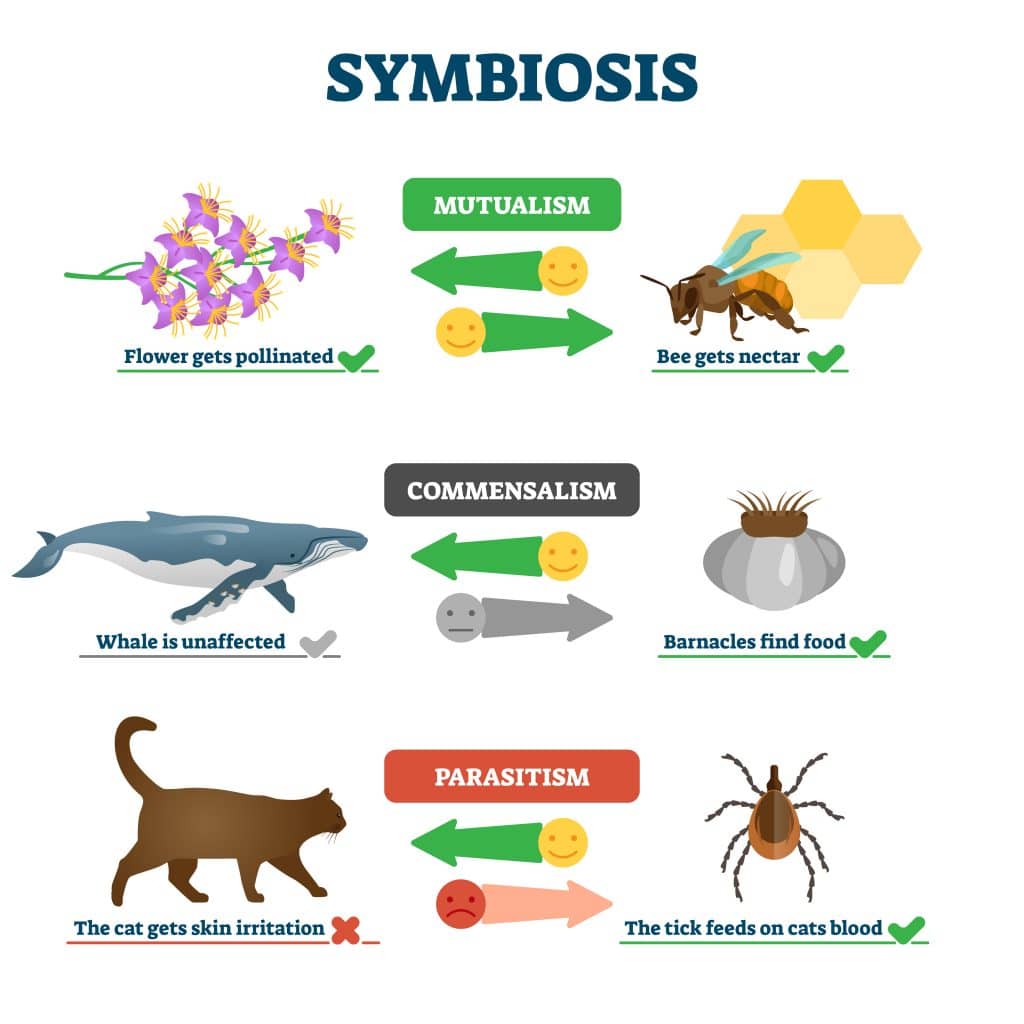
Symbiosis, the long-term interactions between different species, plays a crucial role in ecological systems. Understanding these relationships can provide insights into ecosystem dynamics, species survival strategies, and even evolution. This comprehensive guide will explore five distinct methods to identify and classify the types of symbiosis, making it an invaluable tool for both educators and students in biology or environmental sciences. Let's dive into the world of symbiosis, where mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and others weave the fabric of life's intricate tapestry.
Method 1: Observational Study

An observational study is one of the most direct ways to identify symbiosis types:
- Define your species: Identify the species you’re observing.
- Record interactions: Note behaviors, physical interactions, and any changes in the environment.
- Analyze the benefits: Determine if both species benefit (mutualism), one benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed (commensalism), or one benefits at the other’s expense (parasitism).
🔍 Note: Ensure observations are consistent over time to avoid misinterpretation due to one-off events.
Method 2: Habitat Analysis

Analyzing the habitat can reveal symbiosis types through environmental clues:
- Environmental factors: Consider if the habitat promotes or restricts the interaction between species.
- Niche interactions: Look for species sharing a similar niche or living in close proximity.
- Resource use: Evaluate how resources are shared or monopolized by one species.
Method 3: Laboratory Experiments

Controlled laboratory experiments offer insights into the nature of symbiosis:
- Isolate and manipulate: Separate the species involved to control for variables.
- Observe under stress: See how both species react when resources or environment changes.
- Document changes: Record physical changes, behavior, and survival rates.
⚗️ Note: Lab conditions might not replicate natural settings perfectly; use caution in interpreting results.
Method 4: Phylogenetic Analysis
Understanding evolutionary relationships can also help identify symbiosis types:
- Evolutionary history: Study the phylogenetic trees of the species involved.
- Ancestral relationships: Trace back the lineage to infer long-term interactions.
- Co-evolutionary changes: Look for signs of co-evolution, where species influence each other’s evolution.
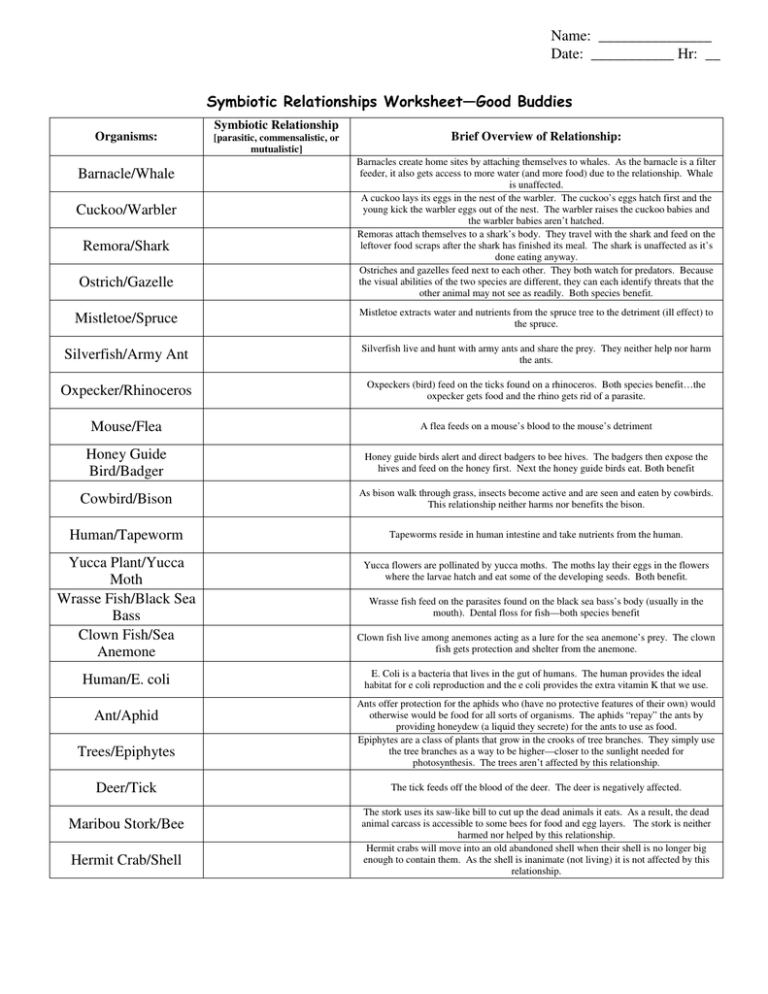
| Symbiosis Type | Examples of Co-evolution |
|---|---|
| Mutualism | Flowers and their pollinators (both evolve specific traits to benefit from each other). |
| Parasitism | Parasites evolving to evade host defenses, and hosts evolving counter-measures. |
Method 5: Field Surveys

Field surveys provide a snapshot of symbiosis in real-world ecosystems:
- Sampling: Collect samples from various ecosystems and study interactions.
- Track behaviors: Use technology like GPS collars to monitor behavior.
- Data analysis: Analyze data to identify patterns of interaction.
🌳 Note: Weather, time of year, and other environmental factors can affect field survey results.
By understanding and applying these five methods, you gain a robust toolkit for identifying and classifying symbiosis types. Each method has its unique strengths, from the directness of observation to the depth of genetic analysis. Combining these approaches offers a holistic view, enriching our understanding of how species interact in nature's ever-evolving theater. This guide not only serves as an educational resource but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity of life.
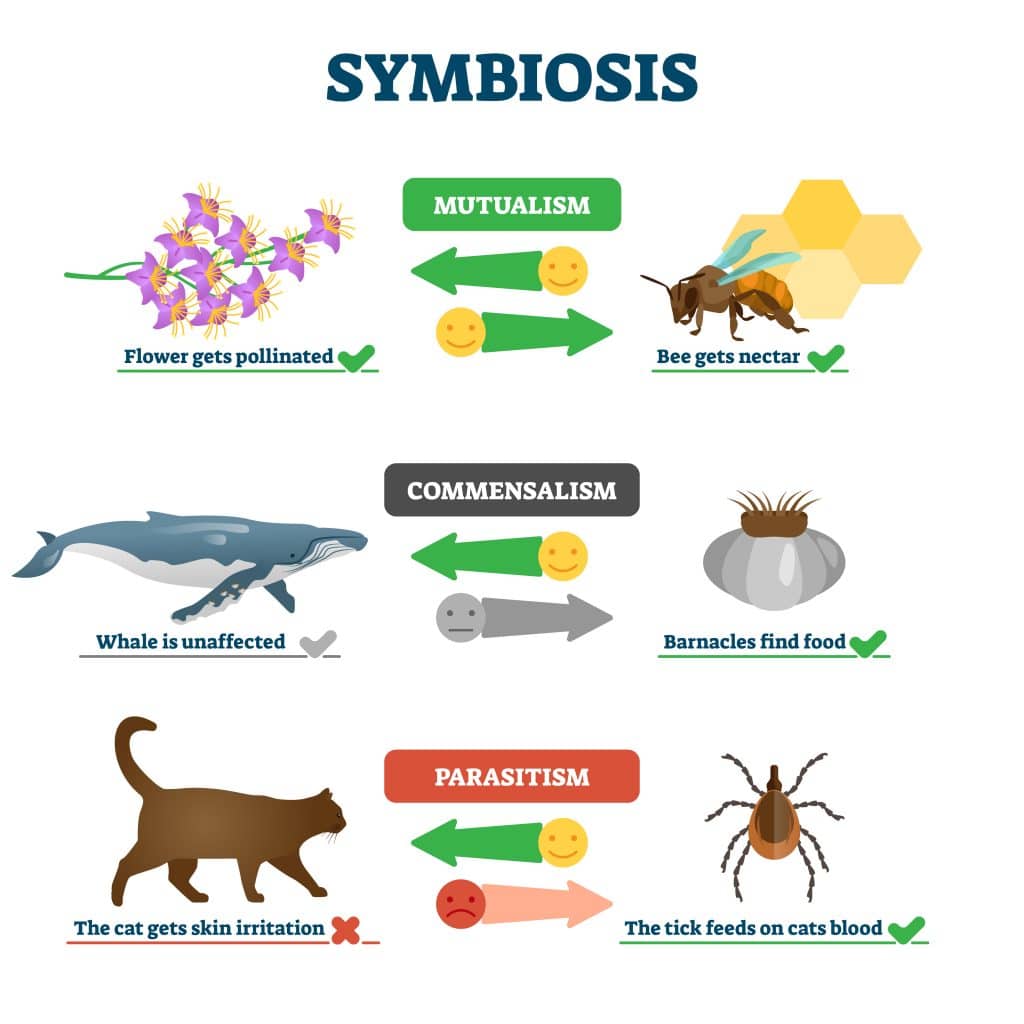
How can I tell if two species are in a mutualistic relationship?

+
Two species are in a mutualistic relationship when both receive benefits from the interaction. Look for traits like feeding habits or symbiotic structures that benefit both species over time.
Are there any symbiosis types other than mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism?
+
Yes, other types include amensalism, where one species is harmed and the other remains unaffected, and competition, where both species are negatively affected.
What is the significance of studying symbiosis in ecology?
+
Studying symbiosis provides insights into ecosystem stability, species interdependence, biodiversity, and evolutionary processes, helping us understand and predict ecological dynamics.
Can symbiosis change over time?
+
Yes, symbiosis can change over time due to environmental changes, co-evolution, or shifts in population dynamics, often transitioning from one type to another.