5 Key Locations of the Eastern Front
Understanding the Eastern Front: 5 Key Locations

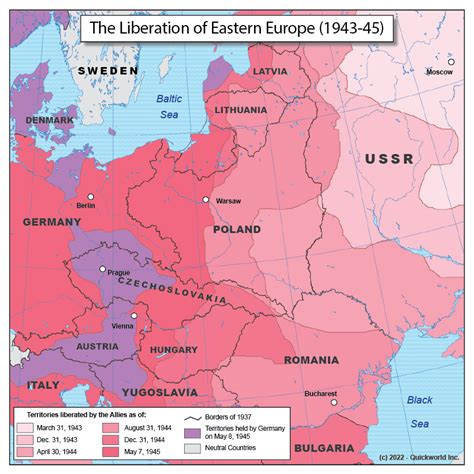
The Eastern Front, a theater of conflict during World War II, was a vast and complex battleground that spanned across multiple countries in Eastern Europe. The war on the Eastern Front was a clash between two major powers: Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. This blog post will explore five key locations that played a crucial role in the outcome of the war.
Leningrad (St. Petersburg, Russia)

The city of Leningrad, now known as St. Petersburg, was a significant location on the Eastern Front. In 1941, German forces, led by Adolf Hitler, launched a massive assault on the city, hoping to capture it and deal a devastating blow to the Soviet Union. The Siege of Leningrad, which lasted for 872 days, was one of the longest and most brutal in modern history. Despite being heavily bombed and shelled, the city held out, and the Soviet Union was able to maintain control.
🔥 Note: The Siege of Leningrad was a significant turning point in the war, as it showed the resilience and determination of the Soviet people.
Stalingrad (Volgograd, Russia)

Stalingrad, now known as Volgograd, was another crucial location on the Eastern Front. In 1942, German forces launched a massive assault on the city, hoping to capture it and gain control of the Volga River. However, the Soviet Union, led by Joseph Stalin, was able to defend the city, and the Battle of Stalingrad became a major turning point in the war. The Soviet Union’s victory marked a significant shift in momentum, and the German army began to retreat.
💪 Note: The Battle of Stalingrad was one of the bloodiest battles in human history, with estimates suggesting that over 1 million soldiers were killed or wounded.
Moscow, Russia

Moscow, the capital city of the Soviet Union, was a key location on the Eastern Front. In 1941, German forces launched a massive assault on the city, hoping to capture it and deal a devastating blow to the Soviet Union. However, the Soviet Union, led by Joseph Stalin, was able to defend the city, and the Battle of Moscow became a significant turning point in the war. The Soviet Union’s victory marked a major shift in momentum, and the German army began to retreat.
Kursk, Russia

Kursk, a city in western Russia, was a significant location on the Eastern Front. In 1943, German forces launched a massive assault on the city, hoping to capture it and gain control of the region. However, the Soviet Union, led by Georgy Zhukov, was able to defend the city, and the Battle of Kursk became a major turning point in the war. The Soviet Union’s victory marked a significant shift in momentum, and the German army began to retreat.
Berlin, Germany

Berlin, the capital city of Germany, was a key location on the Eastern Front. In 1945, Soviet forces, led by Georgy Zhukov, launched a massive assault on the city, hoping to capture it and deal a devastating blow to the German army. The Battle of Berlin was a brutal and intense fight, with both sides suffering heavy casualties. However, the Soviet Union was ultimately able to capture the city, and the German army surrendered.
🏆 Note: The capture of Berlin marked the end of World War II in Europe, and the Soviet Union was hailed as a hero for its role in defeating the Nazi regime.
In conclusion, the Eastern Front was a complex and brutal theater of conflict during World War II. The five key locations discussed in this post – Leningrad, Stalingrad, Moscow, Kursk, and Berlin – played a crucial role in the outcome of the war. Each location represented a significant turning point in the conflict, and the Soviet Union’s victories marked a major shift in momentum.
What was the Eastern Front?

+
The Eastern Front was a theater of conflict during World War II, fought between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union.
What was the significance of the Siege of Leningrad?

+
The Siege of Leningrad was a significant turning point in the war, as it showed the resilience and determination of the Soviet people.
What was the outcome of the Battle of Stalingrad?

+
The Soviet Union’s victory marked a significant shift in momentum, and the German army began to retreat.
Related Terms:
- front timur
- Eropa Bagian Timur
- Eropa Tengah
- Eastern Front ww1
- Eastern Front WW2
- Western Front ww2



