What is Mach Speed
Understanding Mach Speed: A Comprehensive Guide

Mach speed, also known as Mach number, is a fundamental concept in aerodynamics and physics. It represents the ratio of an object’s speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium, typically air. This dimensionless quantity is named after Austrian physicist Ernst Mach, who first proposed it in the late 19th century.
What is Mach Number?

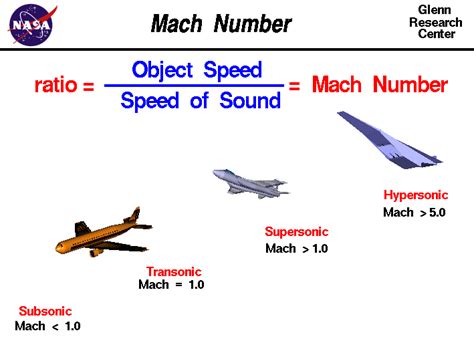
The Mach number (M) is defined as the ratio of an object’s velocity (v) to the speed of sound © in the surrounding medium:
M = v / c
where:
- M is the Mach number
- v is the velocity of the object
- c is the speed of sound
For example, if an object is traveling at a speed of 300 meters per second (m/s) and the speed of sound in the surrounding air is 340 m/s, the Mach number would be:
M = 300 m/s / 340 m/s = 0.88
Mach Regimes

The Mach number is used to classify the flow regime of an object into different categories, depending on its speed relative to the speed of sound. The main Mach regimes are:
- Subsonic: M < 0.8 (less than 80% of the speed of sound)
- Transonic: 0.8 ≤ M ≤ 1.2 (between 80% and 120% of the speed of sound)
- Supersonic: 1.2 < M < 5 (faster than 120% of the speed of sound)
- Hypersonic: M ≥ 5 (five times or more the speed of sound)
Each Mach regime has distinct characteristics and challenges. For instance, supersonic and hypersonic flows involve complex shock wave phenomena, while transonic flows exhibit unique sonic boom effects.
Importance of Mach Speed

Understanding Mach speed is crucial in various fields, including:
- Aerospace engineering: Mach number plays a critical role in designing and optimizing aircraft and spacecraft for efficient flight, stability, and safety.
- Wind tunnel testing: Mach number is used to simulate flight conditions and test aerodynamic models.
- Rocketry: Mach number is essential for optimizing rocket performance and navigation.
- Atmospheric science: Mach number helps scientists study atmospheric waves, jet stream dynamics, and weather patterns.
Real-World Applications
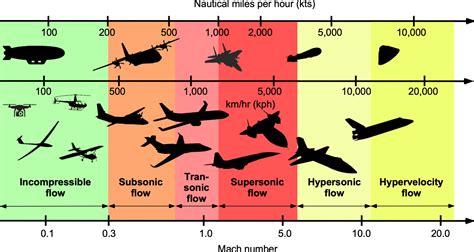
Mach speed has numerous practical applications:
- Supersonic aircraft: Military jets, such as the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, can reach Mach 3.5 (around 2,200 mph).
- Space exploration: The Space Shuttle could reach Mach 25 (around 17,500 mph) during re-entry.
- Rocket propulsion: Modern rockets can achieve Mach 10 (around 7,600 mph) or more.
- Wind turbines: Engineers optimize wind turbine blades to operate efficiently at various Mach numbers, maximizing energy production.
🚀 Note: The speed of sound varies with temperature, air pressure, and humidity. At sea level, the speed of sound is approximately 340 m/s (768 mph) at room temperature.
Conclusion

Mach speed is a fundamental concept in understanding the behavior of objects in different flow regimes. From aerospace engineering to atmospheric science, the Mach number plays a critical role in optimizing performance, safety, and efficiency. By grasping the principles of Mach speed, scientists and engineers can push the boundaries of innovation and exploration.
What is the speed of sound at sea level?

+
The speed of sound at sea level is approximately 340 m/s (768 mph) at room temperature.
What is the Mach number of a typical commercial airliner?

+
A typical commercial airliner cruises at around Mach 0.8 (around 530 mph).
What is the fastest recorded Mach number?

+
The fastest recorded Mach number is Mach 25.4 (around 18,000 mph), achieved by the NASA X-43A scramjet in 2004.