5 Ways Net Force Works
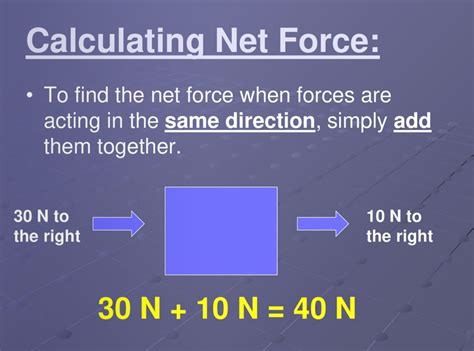
Introduction to Net Force
Net force is a fundamental concept in physics that refers to the overall force acting on an object. It is the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object, and it determines the acceleration of the object. In this post, we will explore 5 ways net force works and how it affects the motion of objects.
What is Net Force?

Net force is calculated by adding up all the forces acting on an object and resolving them into a single force. This can be done using vector addition, where the forces are added head to tail. The resulting force is the net force, which can be either positive or negative. A positive net force indicates that the object is accelerating in the direction of the force, while a negative net force indicates that the object is decelerating.
5 Ways Net Force Works
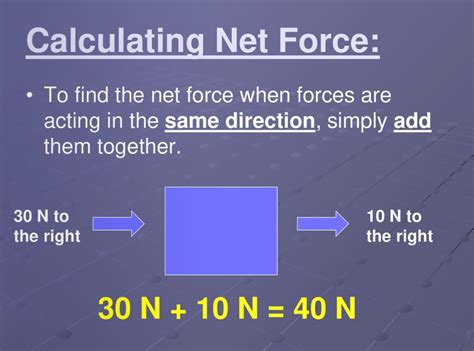
Here are 5 ways net force works: * Frictional Force: Net force can be used to calculate the frictional force acting on an object. For example, when an object is moving on a surface, the net force acting on it is the sum of the frictional force and the applied force. If the net force is positive, the object will accelerate, while a negative net force will cause it to decelerate. * Gravity: Net force is also used to calculate the force of gravity acting on an object. For example, when an object is dropped from a height, the net force acting on it is the sum of the gravitational force and the air resistance. If the net force is positive, the object will accelerate downwards, while a negative net force will cause it to slow down. * Normal Force: Net force can be used to calculate the normal force acting on an object. For example, when an object is placed on a surface, the net force acting on it is the sum of the normal force and the gravitational force. If the net force is positive, the object will exert a force on the surface, while a negative net force will cause it to sink into the surface. * Tension Force: Net force is also used to calculate the tension force acting on an object. For example, when an object is suspended from a string, the net force acting on it is the sum of the tension force and the gravitational force. If the net force is positive, the object will accelerate upwards, while a negative net force will cause it to fall. * Air Resistance: Net force can be used to calculate the air resistance acting on an object. For example, when an object is moving through the air, the net force acting on it is the sum of the air resistance and the applied force. If the net force is positive, the object will accelerate, while a negative net force will cause it to decelerate.
Examples of Net Force in Real-Life Situations
Net force is used in a variety of real-life situations, including: * Rockets: Net force is used to calculate the thrust of a rocket. The net force acting on a rocket is the sum of the thrust and the gravitational force, as well as the air resistance. * Cars: Net force is used to calculate the acceleration of a car. The net force acting on a car is the sum of the frictional force, the gravitational force, and the applied force. * Bicycles: Net force is used to calculate the acceleration of a bicycle. The net force acting on a bicycle is the sum of the frictional force, the gravitational force, and the applied force.
| Force | Description |
|---|---|
| Frictional Force | The force that opposes motion between two surfaces |
| Gravitational Force | The force that attracts objects towards each other |
| Normal Force | The force that acts perpendicular to a surface |
| Tension Force | The force that acts through a string or rope |
| Air Resistance | The force that opposes motion through the air |

💡 Note: Net force is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. When calculating net force, it is essential to consider the direction of each force acting on the object.
In summary, net force is a fundamental concept in physics that determines the acceleration of an object. It is calculated by adding up all the forces acting on an object and resolving them into a single force. Net force is used in a variety of real-life situations, including rockets, cars, and bicycles. By understanding how net force works, we can better appreciate the complex interactions between objects and their environment.
What is the difference between net force and frictional force?

+
Net force is the overall force acting on an object, while frictional force is a type of force that opposes motion between two surfaces. Frictional force is one of the forces that contributes to the net force acting on an object.
How is net force calculated?
+
Net force is calculated by adding up all the forces acting on an object and resolving them into a single force. This can be done using vector addition, where the forces are added head to tail.
What are some examples of net force in real-life situations?

+
Net force is used in a variety of real-life situations, including rockets, cars, and bicycles. It is also used to calculate the force of gravity, normal force, tension force, and air resistance acting on an object.



