What is an Afterburner Explained

What is an Afterburner?
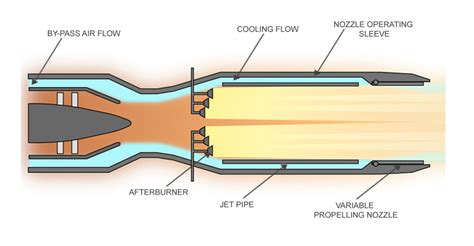
An afterburner is a component used in some jet engines to increase the engine’s thrust during certain phases of flight, typically when the aircraft needs an extra boost of power. The afterburner is essentially a secondary combustion chamber located at the rear of the engine, where fuel is injected and burned to produce additional thrust.
To understand how an afterburner works, let’s take a step back and look at the basic components of a jet engine. A typical jet engine consists of a compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, and nozzle. Air is drawn into the engine, compressed by the compressor, mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber, and then ignited to produce a hot gas. This hot gas expands through the turbine, which drives the compressor, and then exits the engine through the nozzle, producing thrust.
How Does an Afterburner Work?

An afterburner is a modification to the basic jet engine design that allows for additional fuel to be injected into the hot gas stream after it has exited the turbine. This additional fuel is then burned, producing a significant increase in thrust.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the afterburner process:
- Fuel Injection: When the afterburner is engaged, fuel is injected into the hot gas stream through a series of nozzles or fuel injectors.
- Ignition: The fuel is then ignited by a spark or flame, which causes the fuel to burn rapidly, producing a significant increase in temperature and pressure.
- Expansion: The hot gas produced by the afterburner then expands through the nozzle, producing a high-velocity exhaust gas that exits the engine.
- Thrust Increase: The increased velocity of the exhaust gas produces a significant increase in thrust, which can be as much as 50% or more over the non-afterburning thrust.
When is an Afterburner Used?

Afterburners are typically used during specific phases of flight, such as:
- Takeoff: Afterburners can be used to increase thrust during takeoff, allowing the aircraft to lift off the ground more quickly and easily.
- Climb: Afterburners can be used to increase thrust during the climb phase of flight, allowing the aircraft to reach cruising altitude more quickly.
- Combat: Afterburners are often used in military aircraft to increase thrust during combat, allowing the aircraft to accelerate rapidly and gain an advantage over enemy aircraft.
- Emergency Situations: Afterburners can be used in emergency situations, such as when an aircraft needs to rapidly accelerate to avoid a collision or other hazard.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Afterburners

Afterburners have both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Increased Thrust: Afterburners can produce a significant increase in thrust, which can be useful during certain phases of flight.
- Improved Performance: Afterburners can improve an aircraft’s performance, allowing it to accelerate more rapidly and climb more steeply.
Disadvantages:
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Afterburners consume a significant amount of fuel, which can reduce an aircraft’s range and endurance.
- Increased Maintenance: Afterburners require more maintenance than non-afterburning engines, as they have more complex systems and components.
- Reduced Engine Life: Afterburners can reduce the life of the engine, as the high temperatures and pressures produced by the afterburner can cause wear and tear on the engine components.
💡 Note: Afterburners are typically used in high-performance military aircraft, such as fighter jets, and are not commonly used in commercial aircraft due to their high fuel consumption and maintenance requirements.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Compresses air before it enters the combustion chamber |
| Combustion Chamber | Where fuel is mixed with air and ignited to produce a hot gas |
| Turbine | Driven by the hot gas, which drives the compressor |
| Nozzle | Where the hot gas exits the engine, producing thrust |
| Afterburner | A secondary combustion chamber where fuel is injected and burned to produce additional thrust |

In conclusion, afterburners are a critical component of high-performance jet engines, allowing for significant increases in thrust during certain phases of flight. While they offer advantages in terms of performance, they also have disadvantages, including increased fuel consumption and maintenance requirements.
What is the main purpose of an afterburner?
+
The main purpose of an afterburner is to increase the thrust of a jet engine during certain phases of flight, such as takeoff and combat.
How does an afterburner work?

+
An afterburner injects fuel into the hot gas stream after it has exited the turbine, which is then ignited to produce a significant increase in thrust.
What are the disadvantages of afterburners?

+
The disadvantages of afterburners include increased fuel consumption, increased maintenance requirements, and reduced engine life.
Related Terms:
- MSI Afterburner
- Afterburner jet
- Afterburner download
- Engine afterburner
- How does an afterburner work
- Afterburner design